When you trade crypto on an exchange, you will find a table of changing numbers in red and green in real-time. It is called the order book. This tool can help traders determine the most suitable price to sell or buy an asset. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at what an order book is and how to read it.
Article Summary
- 📚 Order book is a real-time feature that tracks the demand and supply of each crypto asset on exchanges. It displays pending buy and sell limit orders for crypto pairs.
- 🌟 There are several important elements in the order book: the price, the bid and ask columns, the quantity of the asset, and the volume or total assets that are bid or asked for.
- 📈 For traders, the order book monitors asset buying and selling pressure, sees the market depth, compares bids and asks, and observes spreads.
What is an Order Book?
The order book is a real-time feature that tracks the demand and supply of crypto assets on trading exchanges. It displays a table containing information about all purchases (bid or buy) and sales (ask or sell) of a crypto trading pair. Examples of trading pairs include BTC/USDT, ETH/USDC, SAND/USDT, and others.
In the order book, there are several important elements, which are as follows:
- Price: The price offered by a trader to buy or sell a crypto asset.
- Bid column: This is the part of the order book listing the price buyers want to buy the crypto asset at. This column shows how much the buyer intends to buy at each price.
- Ask column: This is the section of the order book listing the price sellers want to sell the crypto asset at. This column shows how much the seller intends to sell at each price.
- Quantity: The amount of crypto assets offered at a particular price. Each price has the quantity of assets willing to be bought or sold at that price level.
Volume or total: The total amount of crypto assets bid or asked for at each price.
Order books used by centralized exchanges (CEX) such as Binance and Coinbase are centralized and controlled by their respective platforms. The platform controls the entire operation, including the custody of traders’ funds, order handling, liquidity management, and order book management.
Besides the standard order book used on CEXs, there is also a decentralized order book used on DEX. Read more in the article What is Decentralized Order Book?
How to Read an Exchange Order Book

In every crypto transaction, two parties must be involved: the seller and the buyer. When you buy a crypto asset, it means that someone is willing to sell the asset to you, and vice versa. The transaction will be executed on the order book when the prices submitted by the buyer and seller match.
The order book actually displays the limit order queues of other people. People who trade with market orders (sell or buy an asset at the market price), will not appear in this feature as they execute the transaction immediately without waiting in the order book queue.
Limit orders allow traders to set orders and wait for the best price, while market orders are executed immediately at the market price.
So, basically, the order book shows how many limit orders (buy and sell) are active in real-time. The buy limit order queue is shown in green (bid), and the sell limit order queue is in green (ask).
You can read it from the centre which shows the traded price; for example, the price of BTC/USDT in the image below is at 28,453.03 US dollars.
In the ask column (sell), the price will increase from bottom to top, indicating that sellers want to get the highest possible selling price. While in the bid column (buy), the price will decrease from top to bottom, indicating that buyers want to get the cheapest possible buying price.
This is the basic principle of reading an order book, where traders try to get the most profitable price according to their position, either as a buyer or seller.
Read also: What is A Limit Order? and A Guide to Use Limit Orders on Pintu.
For more details, check out the example of an order book on the BTC/USDT crypto asset below.

- The price in the middle is the last traded price of BTC/USDT, which is 28,453.03.
- The red price is the price of the sell limit order queue, and the green price is the price of the buy limit order queue.
- Amount (BTC): The order amount in USD at each price.
- Total: The total number of orders accumulated from the best bid (sell or buy) price at this price level. For example, at the sell offer price, with the second best ask price of 28,453.05 US dollars, the total quantity that matches is 145,228.35063. It means that at 28,453.05 US dollars, there are 5,10414 queued up for sale for a total of 145,228.35063.
- 0.01 on the top right: You can group orders with a price difference of 0.01 USD, 0.1 USD, 1 USD, 10 USD, 50 USD, or 100 USD.
If you want to sell 20 BTC/USDT via market order, the order will be executed gradually from the best bid price of 28,453.03 to the next best bid price. The last traded and best bid prices will be updated once your order is filled.
Understanding the Market Depth

Market Depth is a real-time measure of limit order volume. It indicates the ability of a trading platform or centralized exchange (CEX) to execute large orders without affecting the price. Market depth is also a key indicator of the liquidity of a CEX.
The deeper the market depth (the more liquid), the smaller the market impact of large orders and the lower the risk of price manipulation.
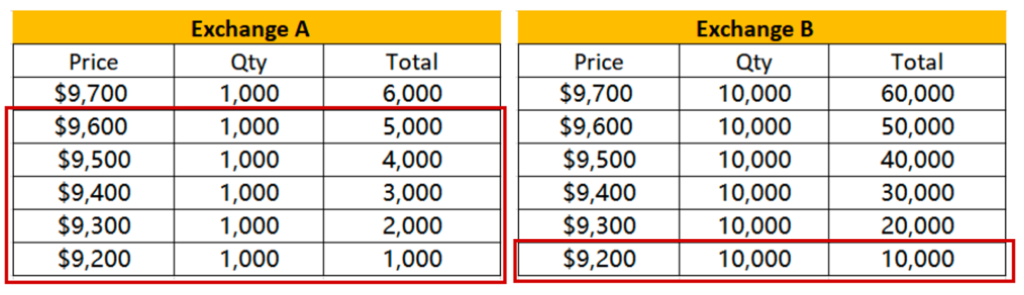
From the image above, for example, you want to buy 5,000 BTC/USDT through a market order on an exchange.
With a lower market depth on Exchange A, you would have to buy at a different price and spend more money, pushing the price up.
To buy $5,000 BTC on Exchange A, you must buy 1,000 contracts five times at $9,200, $9,300, $9,400, $9,500, and $9,600. You would spend $5,000 to buy 0.532 BTC in total. When your order is executed, the best ask price will be pushed to $9,700.
With deeper market depth on Exchange B, you can efficiently execute orders at the same price, resulting in lower trading costs and minimal price impact.
You can easily execute the order on Exchange B because there are 10,000 BTC/USDT sell orders at the best ask price of $9,200. Thus, you spend $5,000 to buy 0.543 BTC; the best ask price remains at $9,200 after the order is executed.
As such, better market depth on Exchange B results in lower trading fees and less impact on the price. It benefits you and other traders.
How to Use the Order Book
The order book in crypto trading is a good tool for determining the entry price to sell or buy. Here’s how to use the order book that can help you make decisions for trading:
- Monitor selling and buying pressure: The order book can help you see the number of queues for selling and buying orders.
- Compare Bid and Ask: If there are more orders on the bid side, it could indicate a bullish sentiment. On the other hand, if there are more orders on the ask side, it could indicate a bearish sentiment.
- Analyze Market Depth: The deeper the market depth, the more liquid the market is. It means that there are more orders available at various price levels.
- Take Note of Changes: The order book constantly changes in real-time as new orders come in. Pay attention to changes in the order book, as this can provide clues about changes in market sentiment.
- Price Difference (Spread): Analyze the difference between the best bid and ask prices, called the spread. A smaller spread indicates a more liquid market.
- Constant Monitoring: The crypto market is very volatile. You must constantly monitor your order book when buying and selling assets to stay on top of rapid price changes.
Conclusion
Using the order book is a skill that requires practice and a deep understanding of the market. Combine information from the order book with technical and fundamental analysis knowledge to make better trading decisions.
But keep in mind that the order book changes in real-time, so constant monitoring is required to understand the ongoing price trends. These are essential skills in crypto trading that can help you make better decisions.
Buying Crypto Assets on Pintu App
You can invest in crypto assets such as BTC, ETH, SOL, and others without worrying about fraud on Pintu. In addition, all crypto assets on Pintu have passed a rigorous assessment process and prioritize the principle of prudence.
The Pintu application is compatible with various popular digital wallets, such as Metamask, to facilitate transactions. Download the Pintu app on the Play Store and App Store! Your safety is guaranteed because Pintu is regulated and supervised by Bappebti and Kominfo.
In addition to making transactions on the Pintu app, you can learn more about crypto through various Pintu Academy articles that are updated weekly! All Pintu Academy articles are created for educational and knowledge purposes, not as financial advice.
FAQ
1. What is an order book in crypto trading?
An order book is a real-time list of all buy bids and sell asks for a crypto asset on an exchange.
2. What is the difference between bid and ask in an order book?
The bid is the price buyers are willing to pay, while the ask is the price sellers are willing to accept.
3. How do you read an order book on an exchange?
You read it by viewing bid orders on the left and ask orders on the right to assess buying and selling pressure.
4. What does spread mean in an order book?
The spread is the gap between the highest bid and lowest ask, indicating the market’s liquidity level.
References
- Will Kenton, What Is an Order Book? Definition, How It Works, and Key Parts, Investopedia, accessed 17 Oktober 2023.
- Alex Lielacher, Order Book: What Is It and How To Use It in Crypto Trading? Be(in)Crypto, accessed 17 Oktober 2023.
- Blockchain.com Team, How do I read the order book? Blockchain.com, accessed 17 Oktober 2023.
- Young Platform Academy Team, What’s the Order Book and how to read it? Young Platform, accessed 18 Oktober 2023.
