Have you ever wondered what it would be if a Dapp had Ethereum’s capabilities with Solana’s speed and scalability? This is what Neon EVM brings to the table: a protocol that combines both. So, what is Neon EVM all about? How does it work? Find out the answers in the following article.
Article Summary
- ⛓️ Neon EVM is a protocol that combines Ethereum’s capabilities with Solana’s speed and scalability. With Neon EVM, developers can easily migrate Ethereum apps to Solana.
- 🌉 Neon EVM works like a bridge between Ethereum and Solana. It processes Ethereum-like transactions through Neon Proxy. After that, the transaction will be forwarded to the Neon EVM program in Solana for execution.
- 🥇 Neon EVM has several key features, such as NeonScan, NeonPass, Neon Faucet, and Neon DAO for governance.
- 🪙 The NEON token is the native token in the Neon EVM ecosystem, used for transaction fees and governance of Neon EVM.
About Ethereum Virtual Machine
Before we get into the details of Neon EVM, we first need to understand EVM or Ethereum Virtual Machine. It is the center of Ethereum’s functionality thanks to its role as a place to execute smart contracts. In other words, EVM is the main engine for developing various DApps as well as executing transactions.
Another role of EVM is to improve composability between networks. Through EVM, all applications built on it become compatible with each other. EVM adoption also supports using standardized tokens such as ERC-20 and ERC-271. As a result, EVM has a significant role in the Web3 ecosystem, especially in the DeFi and NFT protocols.
You can learn more about EVM technology and how it works in the following article.
What is Neon EVM?
Neon EVM is a protocol that integrates the Ethereum ecosystem with the Solana network. Neon EVM’s technology allows developers to utilize the capabilities of EVM and the Ethereum ecosystem, along with Solana’s superior scalability and transaction speed.
Thanks to Neon EVM’s interoperability, developers can easily expand or migrate Ethereum applications to Solana. You could say that Neon creates a miniature Ethereum ecosystem on top of the Solana blockchain.
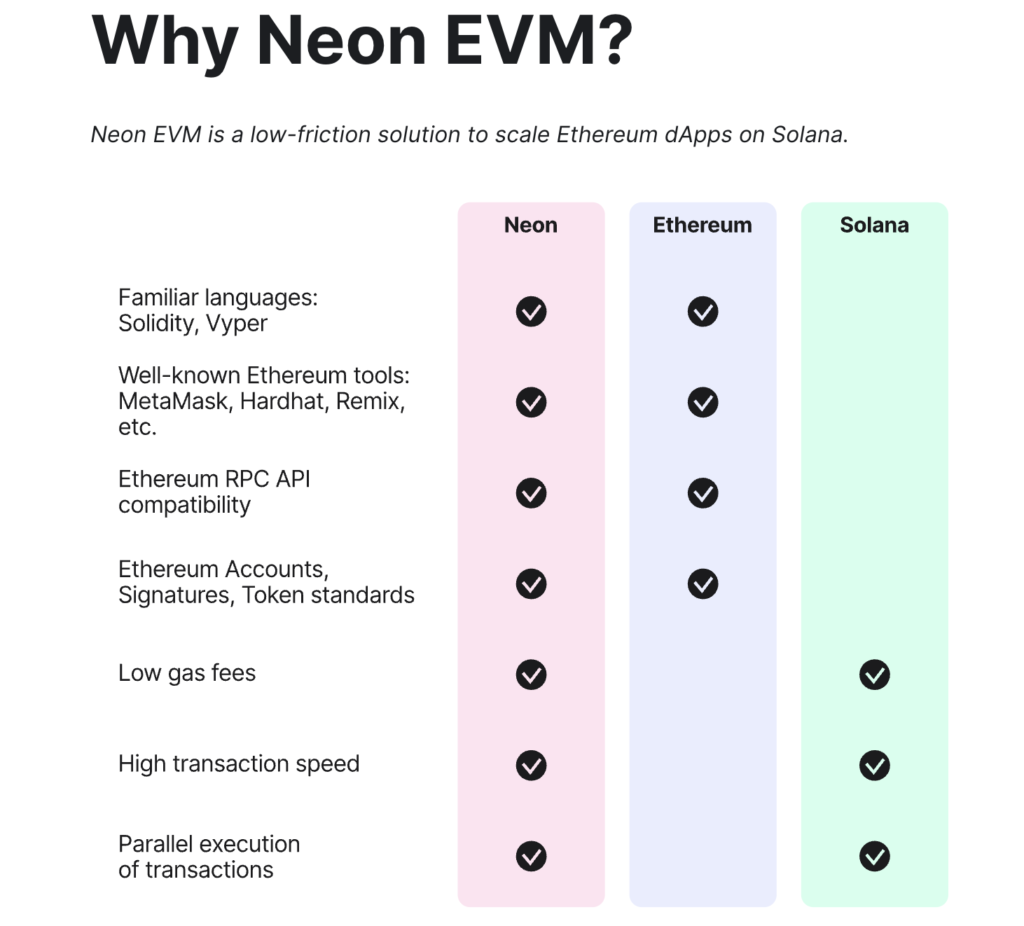
One of the highlights of the Neon EVM is its use of the Solana architecture, which allows it to execute transactions in parallel. As a result, transaction throughput is improved, along with lower costs.
How Does Neon EVM Work?
As mentioned earlier, the Neon EVM acts as a bridge that allows Ethereum apps to access Solana’s high transaction speed and low fees. Here is an overview of how Neon EVM works:
The process first starts with the user creating and signing a transaction Ethereum-like. After that, the transaction will be sent to Neon Proxy through the Neon API service. Once received, Neon Proxy will forward the wrapped transaction to the Neon EVM program in Solana.
Neon Proxy acts as a bridge between the Ethereum blockchain and Solana. The responsible party for running the Neon Proxy server is the Neon operator. In exchange for supporting the migration process, Neon operators are rewarded with NEON tokens.
After moving to the Solana network, the smart contract in Neon will unwrapped and check the user’s signature on the transaction. The transaction will then be executed in the Solana BPF. Finally, Solana and Neon EVM will perform a state change after the transaction is successfully executed.
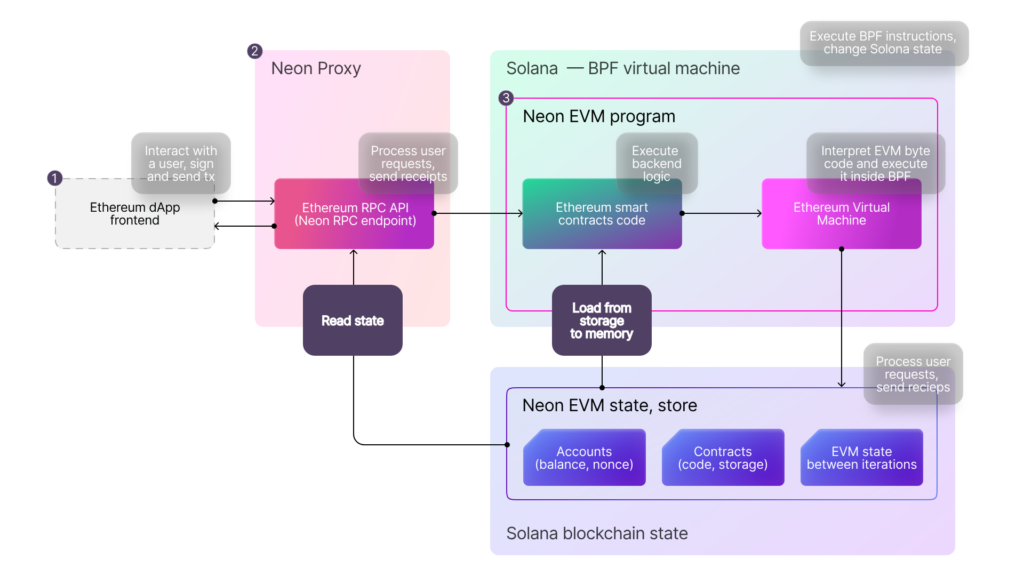
Simply put, it wrapped Ethereum-like transactions into Solana transactions. The transaction is then sent to the Solana network to be processed. Currently, Neon EVM achieves a throughput of around 4,500 TPS with an average gas fee of 0.002 NEON per transaction.
Neon EVM enables any Ethereum native application to run on Solana. This can be accomplished without requiring any changes to its codebase and includes all of the standard Ethereum tooling. Developers can continue to write smart contracts in Solidity, utilize MetaMask to fund dApps, or use the Truffle environment to deploy dApps on Solana.
Love Ethereum technology? Here are 4 L2 Ethereum altcoins that have potential in the next bull market.
Neon EVM Features
The following are Neon EVM’s key features:
1. NeonScan
NeonScan is a block explorer and analytics platform for the Neon EVM ecosystem. It allows users to examine and analyze Neon transactions on the Solana blockchain.
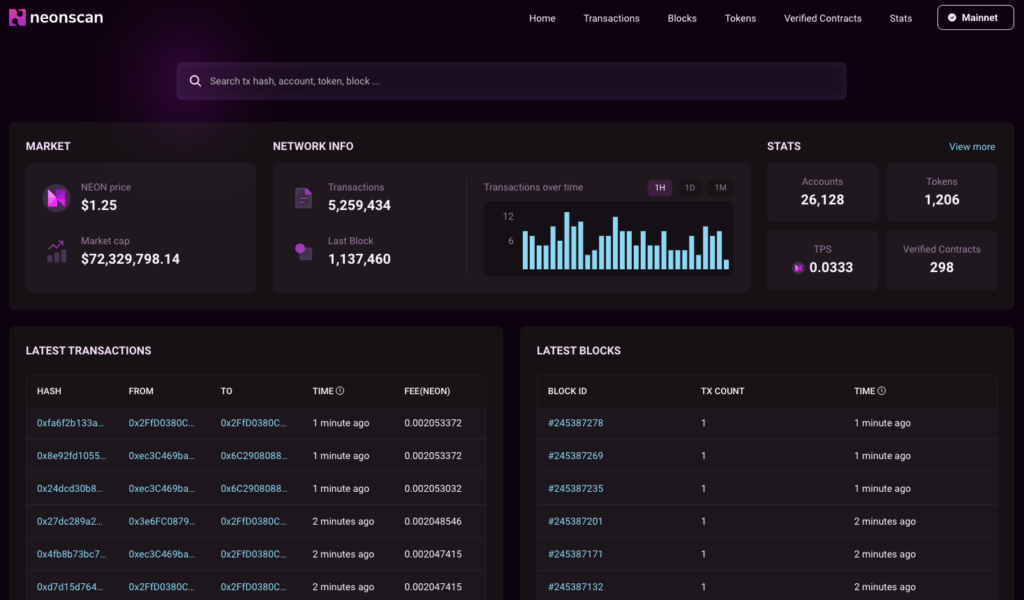
Using NeonScan, users can track transactions, blocks, and associated tokens on Neon EVM’s mainnet. It provides a transparent view of the network’s activity to verify transactions, monitor token movements, and understand block information.
2. NeonPass
NeonPass is a tool to facilitate the transfer of ERC-20 tokens between Solana and Neon EVM. It’s important to note that each transaction results in a gas fee, payable in either NEON or SOL tokens (depending upon the originating network).
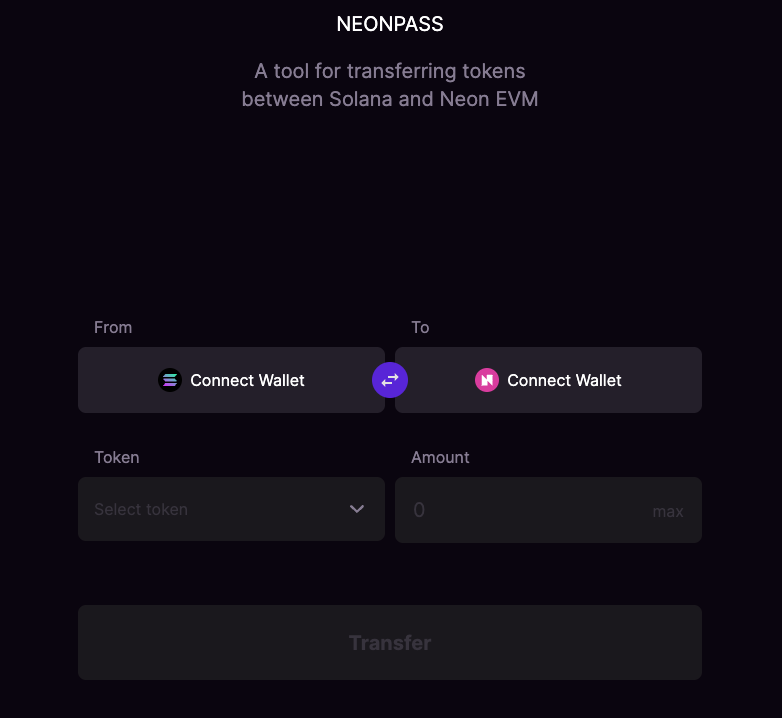
To use NeonPass, users must first connect their EVM-compatible wallet to the Neon EVM network. After connecting, users can directly send assets. Once successful, remember to verify that the transaction happened using NeonScan.
3. Neon Faucet
Neon Faucet Neon Faucet is a service created to help users get NEON or other ERC-20 testnet tokens. The main use of these tokens is to test applications on DevNet, Neon’s development network.
By providing testnet tokens, Neon Faucet allows developers to test their applications in a risk-free environment before releasing them to the mainnet. To use Neon Faucet, users need to connect their wallets.
As part of its commitment to ensuring cross-chain interoperability, the Neon EVM testnet can use a variety of supported tokens instead of native tokens.
4. Neon DAO
The Neon DAO supports the Neon Foundation by providing custodial services as well as research and development. It operates as several smart contracts launched in Solana.
This gives the Neon DAO a governance layer to control the functionality of the Neon EVM. DAO participants can submit and vote on proposals related to Neon EVM operations.
Neon EVM Advantages
- ✨ Practical. Development teams can deploy Ethereum dApps to Solana without reconfiguration. They can also use programming languages (Solidity or Viper) and standard tooling that is already in use.
- 🌐 Expanding User Base. By moving dApps from the Ethereum ecosystem to Solana, developers can gain a new user base in Solana. They also had access to Solana’s ample liquidity.
- ⚡ High Scalability. Using the Solana blockchain, various dApps can enjoy high transaction speeds with low gas fees.
NEON Token as Investment
NEON is the native token used in the Neon EVM ecosystem. It has two main functions, which are as a utility token and a governance token.
As a utility token, NEON facilitates transactions on the Neon platform, such as gas fees, dApp deployment, and interaction with dApps. Meanwhile, as a governance token, NEON owners can participate in voting and submitting proposals related to the development of Neon EVM.
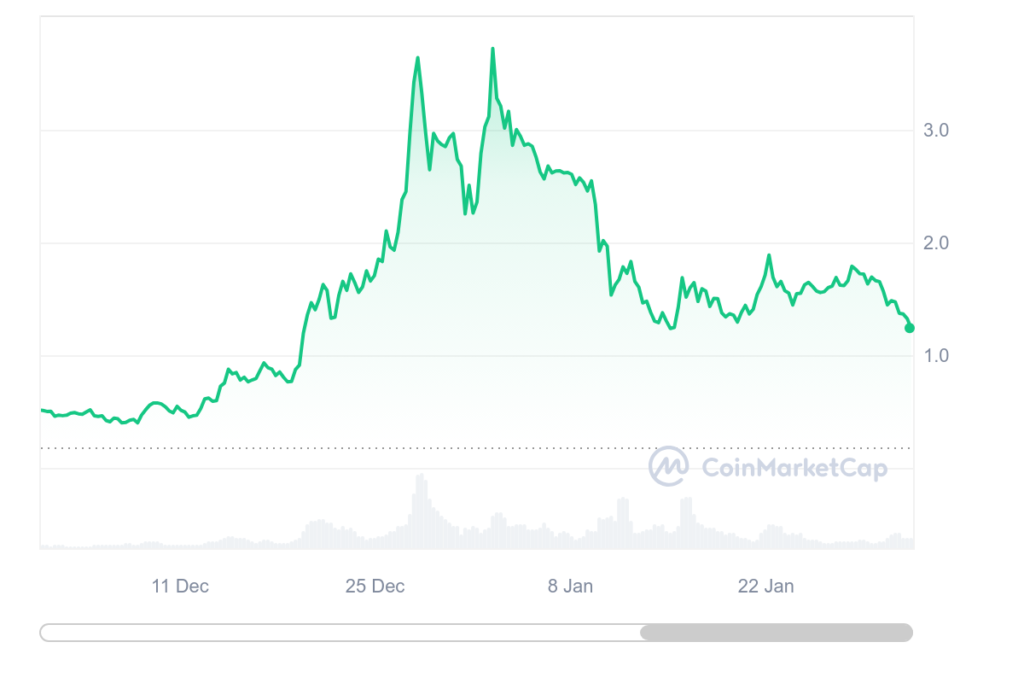
NEON has a total supply of 1 billion NEONs, of which 57.65 million are already circulating in the market. After experiencing a long rally, on February 1, the price of NEON was at US$ 1.26. Meanwhile, NEON’s highest level ever reached US$ 3.8.
NEON EVM continues to show the development of its ecosystem. Several Ethereum projects, such as Curve and Sobal, have joined the Neon EVM ecosystem. There are also other protocols, such as The Graph and Pyth Network. Meanwhile, Aave is also currently voting on the possibility of deploying to Neon EVM.
As the main bridge between the Ethereum and Solana ecosystems, Neon EVM could be the developer’s choice for building their apps. Unfortunately, so far, the barrier for Neon is that their EVM technology has yet to be at full capacity. However, if you refer to Neon EVM’s roadmap, by 2024, they will focus on realizing the full compatibility of Neon EVM.
If Neon EVM succeeds in making their EVM full capacity by 2024, coupled with Solana becoming one of the main narratives in the next bull market, it may become one of the sought-after projects. After all, no protocol currently offers technology and concepts like Neon EVM.
Solana being one of the narratives of the next bull market is inseparable from the airdrops in its ecosystem. Want to get an airdrop? Find out how in the following article.
Conclusion
Neon EVM is an innovative project that seeks to bring Solana’s scalability and low transaction fees into the Ethereum ecosystem. With this integration, Neon EVM offers convenience for developers because they can still use more familiar tools while taking advantage of Solana’s scalability.
With the technology and solutions that Neon EVM presents, it is certainly interesting to watch the future of this protocol. While Neon EVM has a promising future, it is important to keep researching the possible risks.
How to Buy NEON Token on Pintu
After knowing what Neon EVM is, you can start investing in NEON by buying it on Pintu app. Here is how to buy crypto on Pintu application:
- Create a Pintu account and follow the process of verifying your identity to start trading.
- On the homepage, click the deposit button and top up the Pintu balance using your preferred payment method.
- Go to the market page and look for NEON.
- Click buy and fill in the amount you want.
- Now you have NEON!
In addition to NEON, you can safely and conveniently purchase a wide range of cryptocurrencies such as BTC, ETH, SOL, and others safely and easily on Pintu. Pintu diligently evaluates all its crypto assets, highlighting the significance of being cautious.
Pintu is also compatible with popular wallets such as Metamask to facilitate your transactions. Download Pintu app on Play Store and App Store! Your security is guaranteed because Pintu is regulated and supervised by Bappebti and Kominfo.
Aside from buying and trading crypto assets, you can expand your knowledge about cryptocurrencies through various Pintu Academy articles. Updated weekly, all Pintu Academy articles are made for knowledge and educational purposes, not as financial advice.
References
- Neon EVM Docs, Why Neon EVM? accessed on 30 January 2024.
- Ethereum Team, Ethereum Virtual Machine, accessed on 30 January 2024.
- Emiliy Shin, What is Neon EVM? Data Wallet, accessed on 30 January 2024.
- Consensys, Neon: An Ethereum Virtual Machine on Solana, accessed on 30 January 2024.
