Over the past few months, Polymarket has grown in popularity as one of the largest prediction markets. This article will discuss what Polymarket is, how it works, the factors that make it popular, its various risks, as well as the ecosystem of the prediction market.
Article Summary
- 🔎 Polymarket: A platform that facilitates users’ trading to predict the outcome of various events in the future.
- ⚙️ Participation Prediction: Shares are units that represent user participation in a market, and their value can fluctuate depending on buying and selling activity.
- 🎯 Peer-to-Peer based: Prizes earned by winners come from the losses of other users within the marketplace, not from the platform.
What Is Polymarket?
Polymarket is a decentralized prediction market platform that allows users to predict the outcome of various future events ranging from politics, sports, finance, elections, economics, and others.
The platform utilizes the high transaction speed and low fees of the Polygon network as its primary infrastructure. However, Polymarket also supports several other networks for deposits, including Solana, Ethereum, and Base.
How Polymarket Works
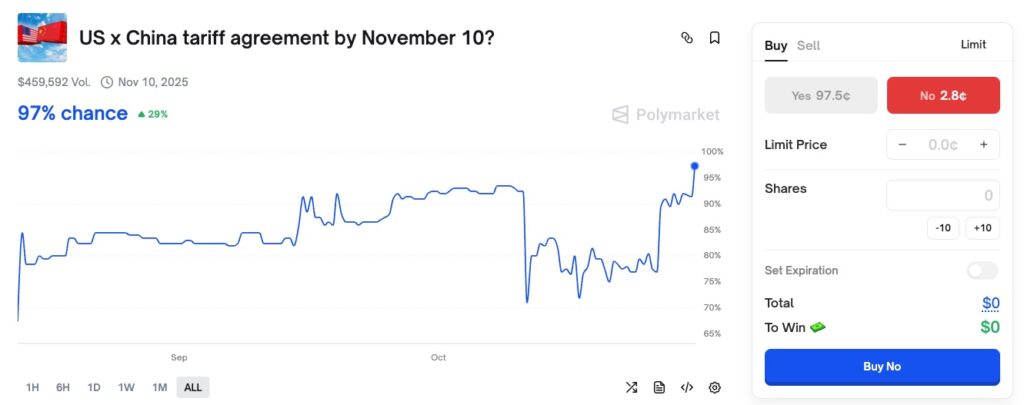
In Polymarket, users can trade units called shares, a representation of ownership in a prediction. Each share reflects the user’s position on an event, such as voting “Yes” or “No” on a market.
Furthermore, the price of shares can change based on market activity, the more people buy “Yes” shares, the higher the probability. If the price of “Yes” shares is at $0.97 or 97 cents, the probability of the event occurring is considered to be about 97% and the price of “No” shares is 3 cents or the probability is about 3%.
To clarify, Polymarket simply brings together “Yes” and “No” traders in search of a final outcome of $1. Why is that? Because shares will be rewarded $1 for correct predictions until the period is over.

Example:
<div style="white-space: pre-wrap; line-height: 1; font-family: Arial, sans-serif;">Prediction "America raises tariffs on China on November 10th?" - User A buys 100 "Yes" shares at $0.97/shares, total cost: $97 - User B buys 100 "No" shares at $0.3/shares, total cost: $3 If the final result is "No", then the value of user B's 100 shares is $100, with a profit of $97 and user A' s shares become worthless. </div>
Users can buy or sell unit shares using 2 methods, namely limit orders and market orders, the probability percentage is taken based on the midpoint between the bid and ask, which may cause the probability percentage to be slightly different from the price of the shares due to the spread in the market.
While the prediction period is still ongoing, the price of shares or probabilities may change according to the buying and selling activity of users in the market, depending on how much interest traders have in the “Yes” or “No” side.
Polymarket Rules

The settlement period of prediction markets in Polymarket depends on the rules of each market and the type of event being predicted. In general, the settlement process involves UMA smart contracts as Polymarket’s main Oracle system.
After the market period ends, users can propose resolution, which is the process of determining the final outcome of the prediction through the UMA Oracle. At this stage, the proposer must deposit a bond of 750 USDC until the verification process is complete.
Once the bond is submitted and the transaction is processed, the system will enter the challenge phase for 2 hours. During this period, other users can challenge the proposed result if they find it not credible. If no one challenges within that time, the market is declared resolved and the proposer gets their bond back as well as the 5 USDC prize.
Once the market ends, users with shares on the winning side can claim a prize of $1 per share held.
However, the market settlement process may take longer in case of a challenge or dispute. In this case, the challenger must post a bond of 750 USDC to submit an answer that differs from the proposer. This process usually takes an additional 1-2 days.
Next, a voting process will be conducted by UMA token holders to determine the final answer that is considered correct. This voting process lasts for 2 days.
- If the challenger wins, it will receive half the USDC of the proposer’s bond.
- If the challenger loses, he will lose half USDC of his bond.
Popular Polymarket Factors
1. Market Flexibility
Each prediction market on Polymarket has an expiry date. As long as the market is active, users are free to buy or sell shares. This flexibility to in and exit the market at any time is what makes Polymarket so popular among users and the community.
2. User vs User Model
Unlike traditional prediction markets, Polymarket does not act as the party that determines the prediction results. The platform only serves as a facilitator that brings users together to transact with each other in determining prediction results.
Specifically, the profits earned by winning users come from the price movements of shares formed in the market. This means that the profits received reflect the results of the buying and selling dynamics between users, not from the platform.
Polymarket Risk
1. Potential User Losses
Despite the flexibility, users still have the potential to lose 100%. Users may lose the entire value of their shares if the final result of the prediction does not match the selected position until the period ends. In addition, losses can come due to the high volatility of the shares price if it moves against the prediction.
2. Risk of Speculative Behavior
In fact, markets on Polymarket operate 24 hours in real-time, with predictions for new events constantly emerging. Of course, the combination of never-ending market activity and the potential for multi-fold gains can potentially encourage users to speculate excessively.
Based on news from CoinMarketCap, Singapore has blocked Polymarket access as a measure to combat online gambling.
Prediction Market Ecosystem: Kalshi vs. Polymarket

Kalshi is one of the prediction marketplaces that has risen in popularity with the sector. Kalshi is Polymarket’s biggest competitor as it is fully regulated in the United States (US), unlike Polymarket which was blocked by US authorities in 2022. But, Polymarket is now licensed by the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) and is optimizing its system to comply with regulations.
However, the main difference between Polymarket and Kalshi is user access. As Kalshi operates legally in the US, users are required to complete a Know Your Customer (KYC) process before being able to participate in the marketplace. Meanwhile, Polymarket can be accessed directly through Web3 wallets such as Phantom or MetaMask without the need for an identification process.

Based on transaction volume data from the past two months, Kalshi recorded nearly twice the trading volume of Polymarket in September and October 2025. Finally, in September, Kalshi’s transaction volume reached US$2.86 billion, and increased to US$4.14 billion in October.
Prediction Market Projects on Base and Solana Networks
1. Limitless
Limitless is a prediction market built on the Base network, with mechanisms similar to Polymarket at first glance. The platform offers flexibility of access, where users can participate using Web3 wallets, email addresses, or social media accounts. However, compared to Polymarket and Kalshi, its market category and transaction volume are still relatively lower.

On October 22, 2025, Limitless released their token with the ticker $LMTS. Community sentiment on the X platform was negative after allegations surfaced that the project founders conducted a token sale on the first day of the Token Generation Event (TGE), as stated by the @CryptoKaleo account.
Consequently, it hurt community trust and early token performance, as many believed such actions undermined the project’s credibility and growth.

After the TGE, transaction volumes on the Limitless platform saw a significant drop. This is likely due to users’ expectations of potential airdrops through the points program that was previously in place. As of writing this article, there is no specific advantage that sets Limitless apart from its competitors.
2. Worm.wtf

Worm.wtf is a new prediction market platform built on Solana. Featuring a community-driven fee model that allows market creators to earn a 2.5% fee from each trade made by other participants.

The worm.wtf prediction market offers two ways to make markets:
- Through the platform, users can create markets with AI by simply entering a prompt containing the prediction they want to make.
- Through X (Twitter), users can simply tweet a prediction and tag worm.wtf’s official account @WormPredict to automatically create a market from the post.
Conclusion
Polymarkets offer easy access and a familiar way of working for crypto traders, but carry much greater risk. Hence, users can suffer significant losses, even losing their entire capital. On the other hand, the high volume of transactions in recent months suggests that interest in the prediction market sector is still very much alive. It will be interesting to see how competition and innovation in this sector will develop in the future.
Disclaimer: All articles from Pintu Academy are intended for educational purposes and do not constitute financial advice.
References
- Polymarket documentation, “What is Polymarket?“, Polymarket, accessed on October 29, 2025.
- Jonathan G, “Polymarket: Turn predictions into profits”, Phantom, accessed on October 29, 2025.
- Brandon Kae and Ivan Wu, “Kalshi and Polymarket record $1.4 billion trading month as institutional backing surges”, The Block, accessed on October 30, 2025.
- Jonathan G, “Kalshi: Trade what you believe in”, Phantom, accessed on October 30, 2025.
