The demand for speedy and efficient money transfers anywhere is one of the key factors that drive the adoption of cryptocurrencies. As a result, the use of Bitcoin is expanding quickly in nations like El Salvador that have significant remittance rates.
With the increasing adoption of cryptocurrencies, many countries, including Indonesia, have begun exploring the development of a regulated digital currency or Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC). This is due to several weaknesses possessed by cryptocurrencies, such as extreme volatility, which makes them difficult to be used for daily transactions.
So, what is Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) and what is the difference between CBDC vs cryptocurrency? Learn more in this article.
Article Summary
- 💵 Central Bank Digital Currency or CBDC is a digital version of the official currency issued by the government. CBDCs are issued and regulated by the monetary authority or central bank of a country.
- 🏛 Like fiat money, the value of CBDC will be based on or equal to physical money issued by the central bank. Likewise with the supply or the amount of money in circulation.
- 🔗 CBDC will allow the general public to make digital payments, but more quickly and securely, which is the advantage of crypto technology.
- 📈 Bank Indonesia is looking into the creation of CBDCs to speed up digital transactions and broaden financial inclusion in light of Indonesia’s expanding use of electronic money transactions and cryptocurrencies.
What is Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC)?
Central Bank Digital Currency or CBDC is a digital version of the official currency issued by the government. CBDC is issued and regulated by the monetary authority or central bank of a country. CBDC is similar to cryptocurrency and operates using a digital ledger (can be blockchain, may not), to speed up and increase the security of digital transaction processes.
💡 One of the differences between CBDC and cryptocurrency lies in the absence of pseudonymity (pseudonymity) in the use of CBDCs. The value of CBDCs is also completely dependent on government policies, and so is the amount of supply.
Currently, physical money is the only type of central bank money available to the general public. CBDC will allow the general public to make digital payments, but more quickly and securely, which is the advantage of crypto technology.
What are the differences between CBDC and Crypto?
The first thing to remember about a CBDC is that it is not a cryptocurrency. CBDC is fully regulated by a central authority or bank, as opposed to a decentralized cryptocurrency. As we know, the ownership and authority of crypto can be completely in the hands of its users, unlike CBDC.
In simple terms, CBDC assets will be issued and stored using a centralized method. CBDC acts as a digital version of fiat money such as the rupiah or the United States dollar. So, your personal details along with the transaction will be attached to your CBDC assets. However, transaction details will only be available to the sender, recipient, and bank.
This is what makes CBDC different from crypto. As we know, crypto transaction details are publicly available, but without revealing personal data such as the real name of the user. Here are some other differences between CBDC and crypto.
| Crypto | CBDC |
| Pseudonymous (real name and personal details unknown) | Not pseudonymous (real name and personal details are known by the bank) |
| The value fluctuates depending on the market | The value is the same as or based on the official currency |
| Using public blockchain | Using a private digital ledger or private blockchain |
| Decentralized, and decisions are made by consensus | Centralized or regulations and decisions are regulated by the government |
| Crypto can be used for speculative purposes as well as for payments | CBDC can only be used for payments and other monetary transactions |
💡 How are CBDCs different from stablecoins? Stablecoins are digital assets whose value is pegged to fiat currencies to facilitate investment and trading. Stablecoins are issued by private companies and use certain systems or mechanisms to ensure their value remains stable. While the CBDC is officially issued by the government or central bank and is a digital version of the fiat money in circulation.
Which Countries are Using CBDCs?
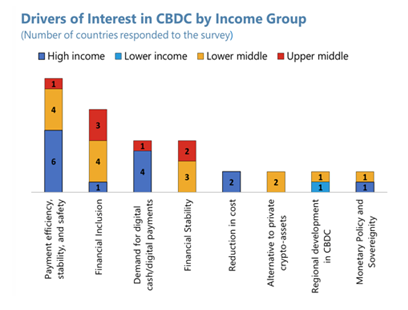
There are currently around 100 countries exploring CBDCs. According to the data from the IMF above, crypto adoption is greater in countries with higher digital penetration and remittances and weaker macroeconomic fundamentals — such as high inflation.
This is what makes financial institutions highlight the importance of tracking crypto activity and regulating it appropriately. So then, the option to create a centralized digital currency was explored by several countries. The following are countries that have or are currently developing CBDCs.
Bahamas
In October 2020, the Central Bank of the Bahamas issued the Sand Dollar, which is a CBDC and digital version of the Bahamas dollar. The Bahamas is one of the pioneers in pushing for CBDCs, seeing it as a good way to reach its people that spread across the hundreds of islands that make up the archipelago.
Citing CoinDesk, the Bahamas recently confirmed that its citizens can use Sand Dollars to pay their taxes. In a survey of the Caribbean region’s economic and financial policies released in May 2022, the IMF recorded that the Sand Dollar currently represents only 0.1% of all currencies in circulation.
Nigerian
The Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) officially launched “eNaira”—the central bank’s digital currency (CBDC)—on October 25, 2021.
As of now, eNaira is only given to people who have bank accounts, but its coverage is expected to eventually extend to anyone with a cell phone even if they don’t have a bank account. Around 38 million people (36% of the adult population) are unbanked in Nigeria and eNaira is expected to increase financial inclusion in the country.
China
At the end of 2021, China also issued E-CNY or Digital Yuan which aims to become a retail “digital money” and is fully supported by the People’s Bank of China (PBoC). Due to the growing usage of digital wallets such as WeChatPay and Alipay, a lot of people in China are no longer using cash and many locations no longer take coins and paper money.
CBDC in Indonesia
Bank Indonesia itself is also exploring the development of a CBDC. Quoted from Kompas.com, Deputy Governor of Bank Indonesia (BI) Doni Primanto Joewono said, at the end of this year BI will issue a study containing plans and concepts for central bank digital currency.
Citing a release published by Bank Indonesia, CBDC exploration has six main objectives, namely:
- Providing digital payment tools without risks, using central bank money
- Reduce the risk of non-state digital currency
- Expanding the scope and efficiency of payment systems, including cross-border transactions
- Expansion and acceleration of financial inclusion
- Provision of new monetary policy instruments,
- Ease of distribution of fiscal subsidies.
Previously, the IMF had also advised Indonesia to use retail CBDCs, which was motivated by the high number of cash transactions in Indonesia. Meanwhile, data from Katadata shows that until 2021, money transactions Indonesia’s electronics industry is known to grow by around 49% to reach Rp 305.4 trillion.
What are the Benefits and Advantages of CBDC?
From the monetary side, the existence of digital money can support financial system stability, including reducing money traffic for crimes, such as money laundry and terrorism financing. From the fiscal side, some of the benefits include expanding the tax payer base and facilitating the distribution of government aid funds.
In the case of Indonesia, digital finance is good to support financial inclusion. With around 60% of Indonesia’s population connected to the internet, the existence of CBDCs is advantageous in the use of digital money for financial inclusion.
In general, here are the benefits and advantages of CBDC:
- 💵 Improve financial access. Digital currency can be distributed on mobile devices, increasing access and usability for citizens who are far from bank branches and cannot access physical cash.
- 💡 Encouraging digital innovation. The CBDC platform-based software model lowers entry barriers for startups in the payments sector, encourages competition and innovation, and pushes financial institutions towards service globalization.
- 🏛 Improve monetary policy. CBDC gives the central bank direct influence over the money supply, simplifies the distribution of government benefits to individuals, and increases control over transactions for tax control
What are the disadvantages and Risks of CBDC?
Although it has various advantages including encouraging increased financial inclusion, CBDC also carries various risks. Among others:
- 🤔 The security of user data is not guaranteed. Depending on the technological capabilities of each country that publishes it, the security of user data may not be guaranteed by the CBDC.
- 🗺 CBDC has geographical restrictions. CBDC usage is very limited as it is only accepted in the country that issued it. Unlike crypto which can be transacted by anyone in any part of the world.
- 🏦 The central bank can turn into a direct competitor to payment service providers. This can result in the bank losing revenue. In addition, new investment opportunities with CBDCs can reduce consumer savings demand.
References
- Board of Governors of The Federal Reserve System, Money and Payments: The U.S.Dollar in the Age of Digital Transformation, The Fed, accessed on July 25, 2022
- Communication Department, CBDC Role in Strengthening Implementation of Central Bank Mandate, Bank Indonesia, accessed on July 25, 2022
- Amelia Yesidora, Mengenal CBDC, Mata Uang Digital dengan Teknologi Uang Kripto, Katadata, accessed on July 25, 2022
- What Is Central Bank Digital Currency?, Consensys, accessed on July 25, 2022
- Jack Schickler, The Bahamas’ ‘Sand Dollar’ Needs Improved Cybersecurity, IMF Says, CoinDesk, accessed on July 25, 2022
- Jack Ree, Five Observations on Nigeria’s Central Bank Digital Currency, IMF, accessed on July 25, 2022
- Krishna Srinivasan, Opening Remarks at Peer-Learning Series on Digital Money/Technology: Central Bank Digital Currency and the Case of China, IMF, accessed on July 25, 2022
- Ahmad Naufal Dzulfaroh, Bank Indonesia Rencana Terbitkan Rupiah Digital, Bagaimana Prospeknya?, Kompas.com, accessed on July 25, 2022
