Over the past few months, the blockchain landscape has been brought to the forefront by the inscriptions phenomenon. The surge in transactional activities linked to inscriptions has posed challenges to every blockchain network, resulting in escalated transaction fees and, in certain instances, network outages. This article aims to delve into the inscriptions phenomenon within blockchain infrastructure, shedding light on the associated scalability challenges.
Article Summary
- 📟 The inscriptions method was introduced by the Ordinals protocol on the Bitcoin blockchain in early 2023. It allows users to embed or inscribe data such as NFTs and images through the smallest unit (Satoshi) on the Bitcoin blockchain.
- 🖼️ The inscriptions method generates ‘true NFTs’ by directly embedding images or text onto the blockchain.
- 🧩 Tom Lehman introduced Ethscriptions on Ethereum in June 2023. Other EVM blockchains, such as Polygon, Arbitrum, Avalanche, and others, widely adopted this method.
- ⛓️ Solana adheres to the Libreplex protocol for inscriptions, whereas Cosmos Hub employs the Asteroid protocol.
Development of Inscriptions on EVM Blockchains
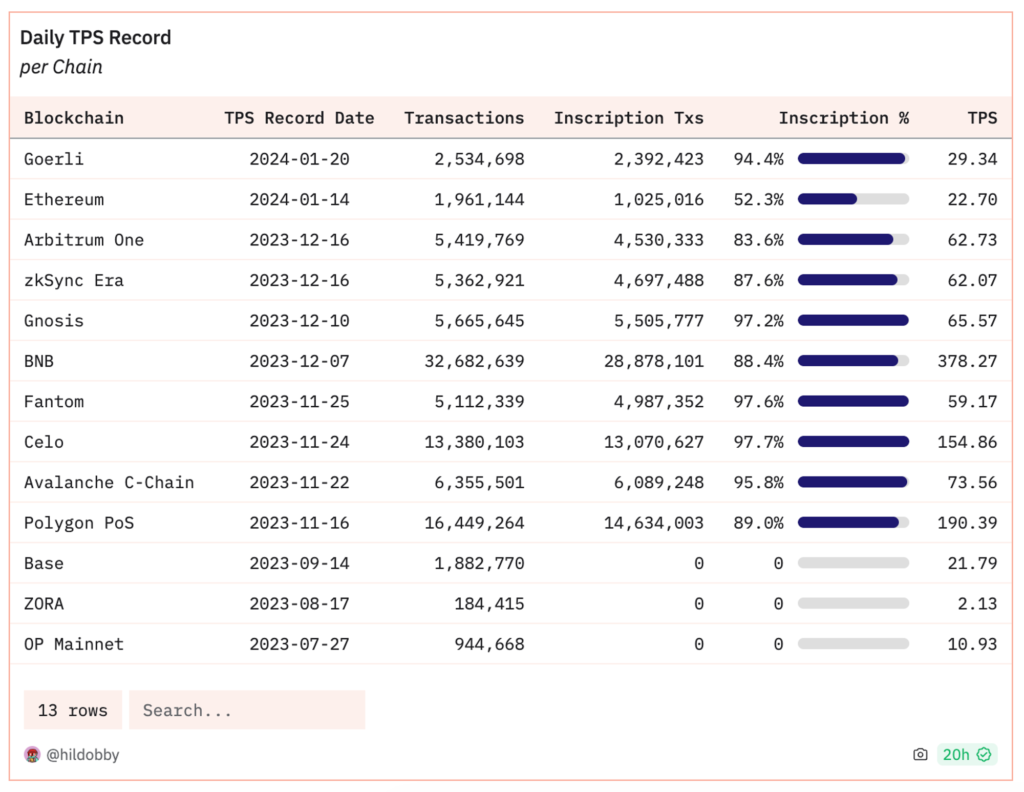
The Ordinals protocol introduced the concept of inscriptions in early 2023, enabling users to inscribe data, including NFTs and images, using the smallest unit (Satoshi) on the Bitcoin blockchain.
Following the surge in inscriptions’ popularity, the technique extended to Ethereum, establishing itself as the pioneering method among EVM blockchains known as Ethscriptions. Tom Lehman introduced Ethscriptions in June 2023. Despite its trendiness, inscription transactions on Ethereum have been insignificant, mainly due to the high gas fees on the Ethereum blockchain.
The Ethscriptions approach saw widespread adoption across various blockchains compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), including BNB Smart Chain, Polygon, Arbitrum, Avalanche, Fantom, and others. This widespread adoption has resulted in the flourishing of inscription methods across nearly all blockchain platforms.
Read more about Ethscriptions in this article.
Etherscan reported that nearly 95% of transactions on the EVM blockchain in November-December 2023 were predominantly inscriptions transactions. This surge in activity has significant implications, leading to increased daily transactions, higher gas fees, and longer transaction processing times. On December 16 alone, the total gas fee spent on inscriptions amounted to approximately 8.3 million US dollars.
What Makes Inscriptions Popular?

Inscriptions quickly gained popularity for various reasons. Initially, the adoption of the Ordinals method by numerous projects across different blockchains, coupled with ongoing innovations, has simplified and made the creation of inscriptions both accessible and affordable. The method, which involves directly embedding images or text onto the blockchain, is promoted to generate ‘true NFTs’.
Furthermore, market dynamics also play an important role in the popularity of inscriptions. The BTC price hike and the euphoria surrounding the BTC ETF at the end of 2023 encouraged many people to enter the Bitcoin ecosystem, where inscriptions emerged as the most trending and influential asset.
Subsequently, the emergence of BRC-20 tokens, such as ORDI, which dominated the market through inscription techniques, catalyzed individuals to recognize new opportunities to maximize the burgeoning cryptocurrency.
Learn more about ORDI in the article What is the ORDI Token and What Does it Do?
Finally, the emergence of Ethscriptions in the Ethereum ecosystem boosted the popularity of inscription tokens. EVM blockchains started creating their inscription tokens, thus accelerating the recognition and adoption of inscription tokens among market participants.
Inscriptions on Solana
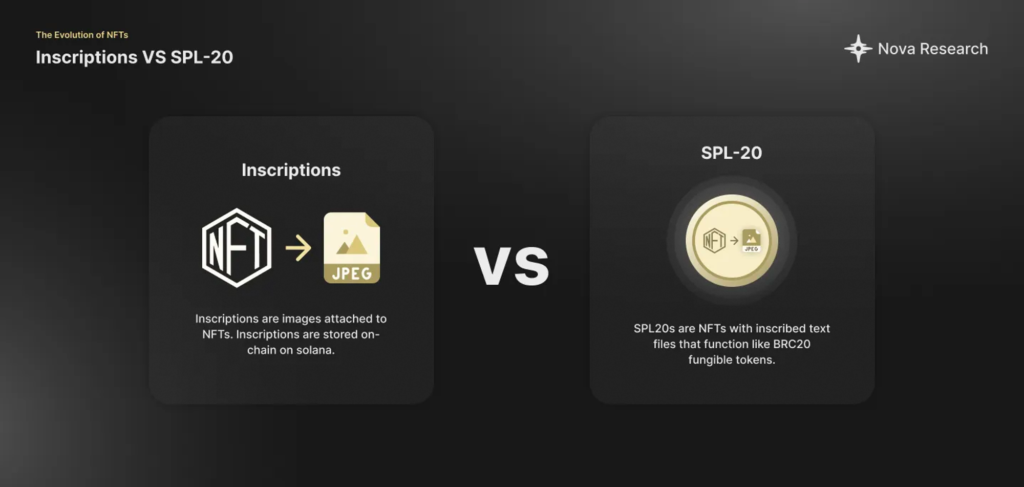
Solana has emerged as a prominent ecosystem alongside Bitcoin and Ethereum. In the realm of inscriptions, Solana employs a comparatively intricate approach. Solana’s inscriptions adhere to the Libreplex protocol, which entails establishing a Program Derived Address (PDA) interconnected with an NFT that houses digital content like images or JSON metadata. SPL-20 tokens, defined through JSON, encompass each operation, functioning as NFT minting, with each action being assigned a specific order number.
SPL-20 inscriptions are unique Solana addresses that contain images stored directly on the Solana blockchain.
When creating inscriptions with the SPL-20 standard, there are two concepts of immutability in NFTs: mutable imprints and immutable artefacts.
- Mutable Imprints as Reserved Spaces: When users create mutable inscriptions, Solana’s inscriptions serve as mutable and reserved spaces on the blockchain. Essentially, users secure digital space on the Solana blockchain. Users can change NFT characters as Solana supports upgradeable contracts that allow using new functions for NFT games.
- Immutable Artifacts: Once immutable, Solana inscriptions become permanent records as immutable digital artefacts. These inscription tokens become a lasting proof of ownership for the creators and are recorded permanently on the Solana blockchain.
Examples of projects that support inscriptions in Solana:
- SOLS: The first token to implement the SPL-20 standard with LibrePlex inscriptions. Within hours of its launch on November 23, 2023, there were already 21,000 SOLS tokens inscribed by users.
- Blockrons: The first PFP NFT stored entirely on the Solana blockchain. The entire Blockrons NFT collection is immutable with 0 royalties.
- Magic Eden: A popular NFT marketplace that integrates its system with the inscriptions technique. Users can mint NFT inscriptions on LibrePlex and then list them on Magic Eden.
Inscriptions on EVM Blockchains
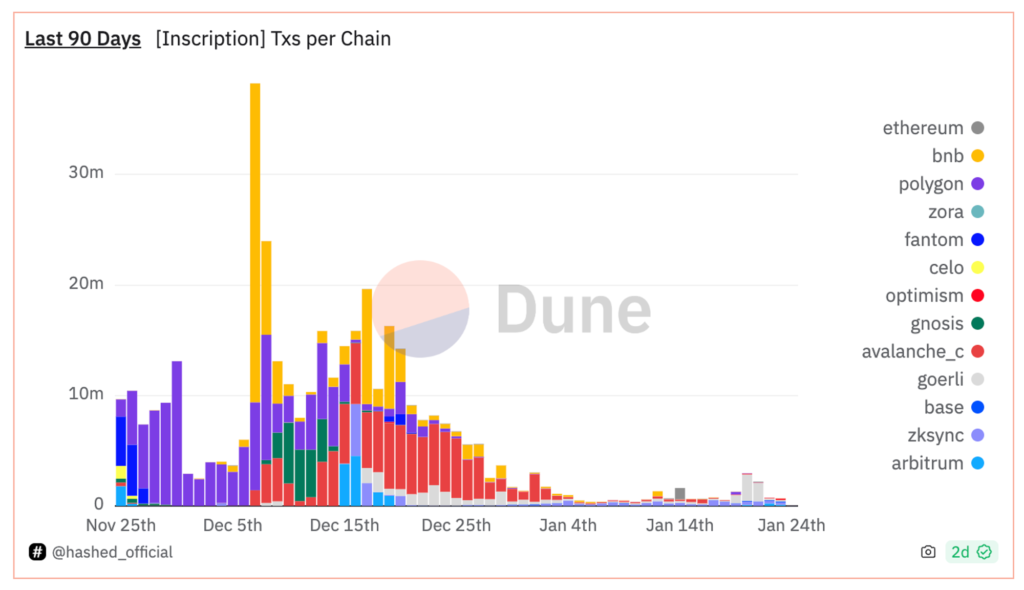
EVM blockchains are compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). They include Polygon, Arbitrum, Avalanche, ZkSync, and others. The technique of inscriptions on the EVM blockchain is similar to the method used in Ethscriptions, which embeds arbitrary data in the calldata area.
Analyzing the provided image, it’s clear that there was a substantial increase in inscription transaction activity in early December 2023. While all operating on the EVM, each blockchain displayed distinct effects in response to the surge in inscription transactions.
1. Arbitrum
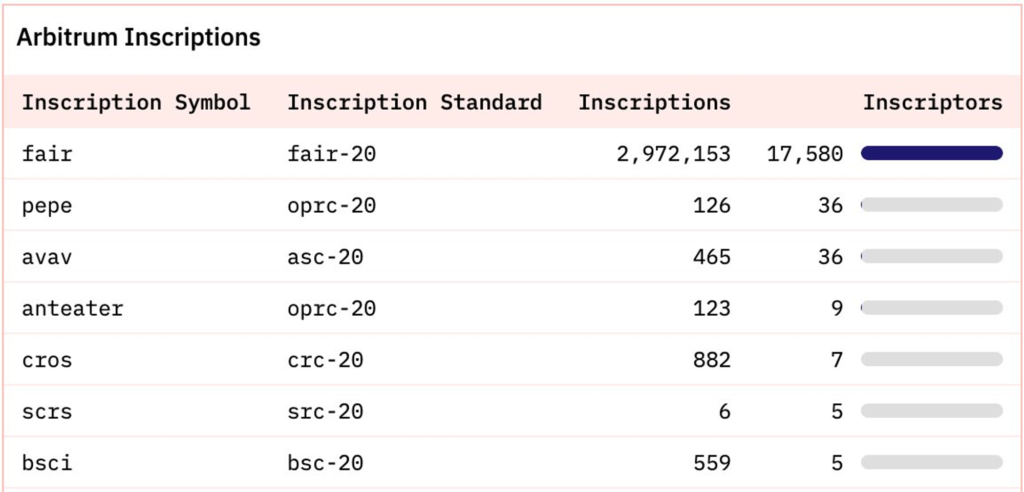
Network activity on Arbitrum One experienced a significant increase due to the inscription of the FAIR token, which is the FAIR-20 standard token for inscriptions. There were around 8 million transactions, with 90% coming from inscription transactions in December 2023.
Unfortunately, this transaction surge caused network congestion, causing Arbitrum to stop the transaction process for 1.5 hours on December 15, 2023. After 4 hours, Arbitrum announced that the network was operating normally and continued to find out about the incident so that it would not be repeated.
Examples of projects that support inscriptions on Arbitrum:
- FAIR: FAIR-20 standard token that supports the first inscriptions on the Arbitrum network.
- Nova Inscriptions: A platform facilitating the creation of NFT inscriptions within the Arbitrum Nova network, offering a pool of 2,100,000 NFTs available for printing and trading on OpenSea.
2. Polygon
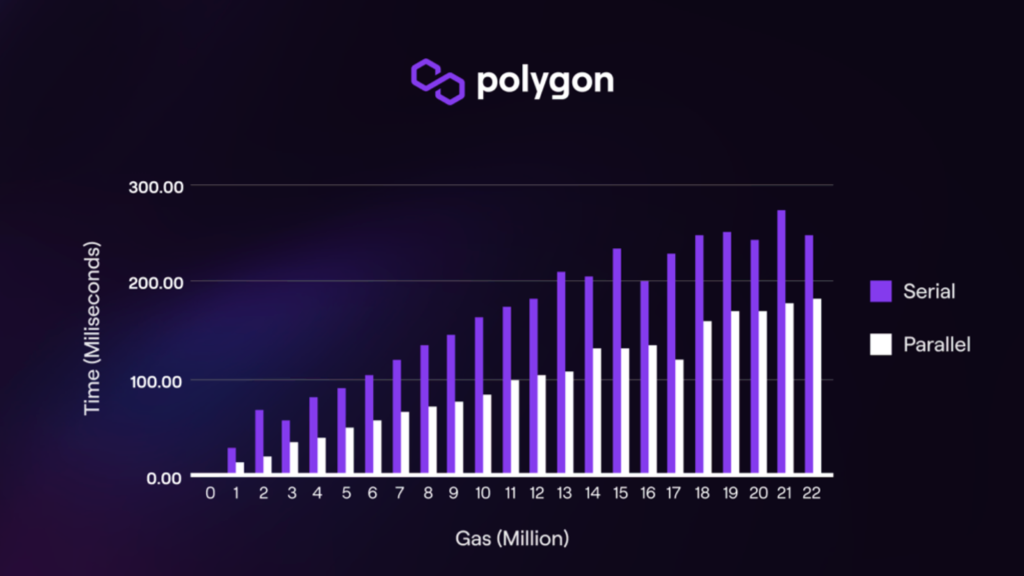
On November 14, 2023, the transaction volume on Polygon increased from 2.8 million to 6 million transactions. As activity related to PRC-20 token inscriptions rose, transactions on the Polygon PoS network also surged.
In contrast to Arbitrum, which faced network congestion, Polygon PoS encountered no disruptions and witnessed no substantial rise in gas fees. This resilience can be attributed to its utilization of Block STM-based parallel EVM technology, an approach to parallel transaction confirmation.
The integration of Block STM, derived from Aptos Labs and implemented by Polygon since July 2023 through the Indore Fork Update, has empowered Polygon PoS to handle a surge in inscription transactions smoothly without encountering intricate challenges.
Examples of projects that support inscriptions in Polygon:
- POLS: POLS is the first inscription token on the Polygon network.
- Glypher: The first marketplace to support all types of inscriptions on the Polygon network (PRC-20). The platform allows users to inscribe and trade PRC-20 easily.
3. Avalanche
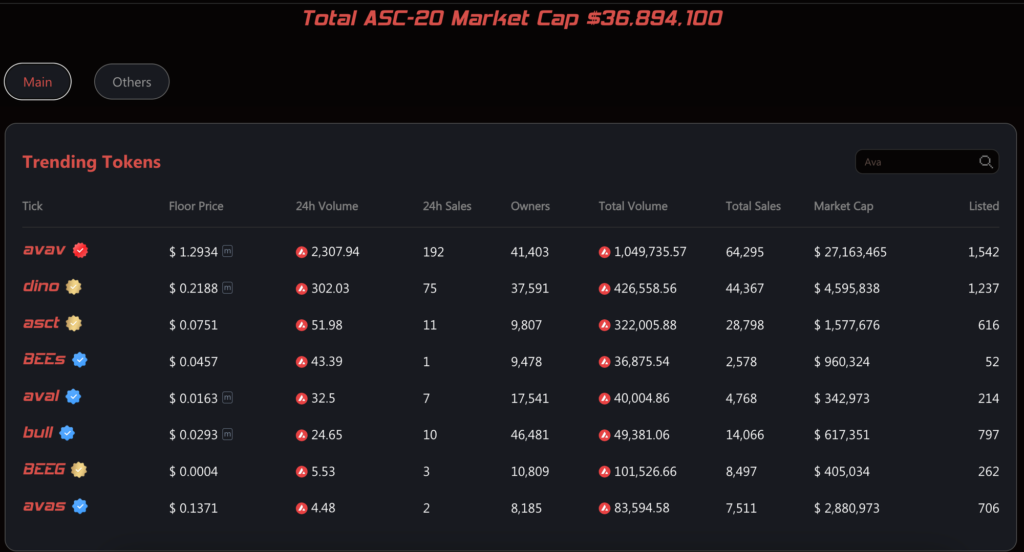
Like other EVM blockchains, Avalanche also experienced a rise in transactions related to inscription activity on its network, Avalanche C-Chain. Avalanche C-Chain reached an all-time high of 6.3 million transactions in November 2023, of which 97% came from Avalanche inscriptions.
In December 2023, Avalanche inscription transactions reached 95 million, with 85% revenue from ACS-20 standard token inscriptions. Avalanche’s inscription process is primarily through Avascriptions.
On December 19, 2023, Kevin Sekniqi, co-founder of Ava Labs, said that Avalanche C-Chain reached 977 TPS, which is quite a contrast to when some other blockchains experienced crashes. Sekniqi emphasized that inscriptions have been a significant ‘stress test’ of the current infrastructure, highlighting the need for subnets to handle the additional load.
According to Cointelegraph, partial outage on several blockchains occurred due to spikes in inscriptions on Arbitrum, zkSync, Cronos, and Celestia.
Examples of projects that support inscriptions on Avalanche:
- AVAV: An ASC-20 standard token that supports inscriptions by embedding JSON data into the Avalanche blockchain.
- DINO: Similar to AVAV, DINO is the second most popular ASC-20 token after AVAV in the Avalanche ecosystem.
Get to know the Avalanche ecosystem in the article Navigating the Avalanche Ecosystem: Thriving in the NFT, DeFi, and Gamefi Sectors.
Inscriptions on Cosmos Hub
Cosmos Hub is the largest Cosmos blockchain by market cap. However, it does not support the implementation of smart contracts, NFTs, or fungible tokens. Cosmos Hub is like a powerful global computer or Layer 0 and can process thousands of transactions per second and build blockchains on top of it.
Recently, a platform named Asteroid has surfaced, allowing the implementation of inscription techniques on Cosmos Hub. Asteroid offers a framework for constructing protocols based on inscriptions atop the Cosmos SDK blockchain.
Asteroids have two metaprotocols: The Cosmos Inscriptions Specification and the Cosmos Fungible Token (CFT-20) Standard.
- The Cosmos Inscriptions Specification: Inscriptions in Cosmos detail how to embed arbitrary data similar to the Ordinals process in Bitcoin. However, the Cosmos SDK differs from other blockchain implementations regarding message validation. One field that is quite suitable for inscriptions is the “memo” field. Memos are used in transfers to CEX and IBC-Hooks. Another field for embedding arbitrary data into the blockchain is through non_critical_extension_options (NCXO).
- Cosmos Fungible Token (CFT-20) Standard: The CFT-20 token standard allows for creating, minting, and transferring fungible tokens using the Asteroid metaprotocol framework. The standard relies solely on the URN in the memo field, except for an optional logo that can be specified when creating tokens that use Asteroid inscriptions.
Examples of projects that support Cosmos Hub inscriptions:
- ROIDS: An Asteroid platform token that supports the CFT-20 token standard. ROIDS is not just a token; it is also a validator with printing capabilities on the Asteroid Protocol.
- Leap Wallet: Users can use Leap Wallet to store inscriptions (CFT-20) tokens such as ROIDS, JKWON, ADB, and others.
The Potential and Future of Inscriptions
The heightened interest in inscriptions, particularly across networks beyond Bitcoin, indicates a speculative and enthusiastic element in the market. The term “inscriptions craze” indicates the robust sentiment among market participants, potentially fostering positive momentum for its value and popularity.
While Inscriptions demonstrate high levels of activity, concerns persist regarding their utility. Tokens with inscriptions, limited to on-chain text, provide minimal real-world usefulness. The issuance of numerous inscription tokens across various networks has yet to translate into significant active trading, indicating a need for increased market adoption and activity.
The sustainability and continued evolution of inscriptions will be significantly impacted by the blockchain ecosystem’s and community’s responses and efforts in addressing the challenges and opportunities that emerge.
Conclusion
In early 2023, the concept of inscriptions was introduced with the Ordinals protocol on the Bitcoin blockchain. Later, Ethscriptions on Ethereum and widespread adoption on the EVM blockchain brought about the popularity of inscriptions. The surge in inscription transactions, especially on EVM, led to significant consequences such as increased gas fees and transaction processing time.
Despite attracting significant interest, the adoption and utility of inscription tokens pose challenges. The future and potential of inscriptions will be shaped by how the blockchain ecosystem responds to emerging opportunities and challenges.
Buy Inscription Token on the Pintu App
You can buy inscription tokens and other assets such as ORDI, SATS and others without worrying about fraud on Pintu. In addition, all crypto assets on Pintu have passed a rigorous assessment process and prioritize the principle of prudence.
The Pintu application is compatible with various popular digital wallets, such as Metamask, to facilitate transactions. Download the Pintu app on the Play Store and App Store! Your safety is guaranteed because Pintu is regulated and supervised by Bappebti and Kominfo.
In addition to making transactions on the Pintu app, you can learn more about crypto through various Pintu Academy articles that are updated weekly! All Pintu Academy articles are created for educational and knowledge purposes, not as financial advice.
References
- William M. Peaster, The Inscriptions Craze ✍️, Bankless, accessed 25 January 2024.
- 100y, Inscriptions Everywhere, Four Pillars, accessed 25 January 2024.
- Tim Copeland, BRC-20 style tokens are spreading to chains beyond Bitcoin. But why? The Block, accessed 25 January 2024.
- Wayne Jones, Surge in Inscriptions on EVM Chains: Etherscan Reports, Crypto Potato, accessed 25 January 2024.
- Martin Young, Inscriptions push 9 EVM chains to reach yearly transaction highs, Cointelegraph, accessed 26 January 2024.
- Delphi Labs, Experimental new “Asteroid” inscriptions protocol brings tokens and NFTs to Cosmos Hub, Delphi Labs, accessed 26 January 2024.
- Nova Research, The Evolution of NFTs with Solana Inscriptions, Medium, accessed 26 January 2024.