Cryptocurrency has evolved from a mere speculative tool into a globally recognized asset, prompting countries like the United States, the United Kingdom, Dubai, Japan, and India to introduce new regulations by the fourth quarter of 2025. This article explores five of the most influential crypto regulations of 2025—ranging from taxation to digital asset privacy and security—that industry players, investors, and users need to understand to stay adaptive in the ever-changing crypto landscape.
Article Summary
🇺🇸 U.S. President Donald J. Trump has officially signed the GENIUS Act into law.
🇬🇧 Anyone engaging in crypto-related activities in the UK is required to obtain a license from the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA).
🔒 VARA licensing provides a clear regulatory framework for crypto companies operating in Dubai and the UAE.
🇯🇵 On-chain crypto transaction volume in Japan surged by 120% in the 12 months leading up to June 2025.
🇮🇳 In India, Capital Gains Tax (CGT) applies to crypto profits at a fixed rate of 30%, plus a 4% cess for health and education.
1. The GENIUS Act: U.S. Stablecoin Regulation

Cryptocurrency regulation in the United States remains one of the most complex and confusing in the world, largely due to the absence of clear federal standards. However, as of 2025, the regulatory landscape is beginning to shift. Lawmakers are showing a more open stance toward the crypto industry by revisiting key legislative proposals, including the Guiding and Establishing National Innovation for U.S. Stablecoins Act—better known as the GENIUS Act—as a concrete step toward greater legal clarity.
On July 18, 2025, U.S. President Donald J. Trump officially signed the GENIUS Act into law, marking a historic milestone in the regulation of digital currencies. This law positions the United States to become a global leader in the emerging stablecoin economy.
What Is a Stablecoin?
A stablecoin is a type of digital asset designed to maintain a stable value by being pegged to reserve assets, usually fiat currencies like the U.S. dollar. The main purpose of stablecoins is to enable fast, low-cost, and secure value transfers via blockchain technology. Their programmability also makes them widely used in smart contracts and decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystems.
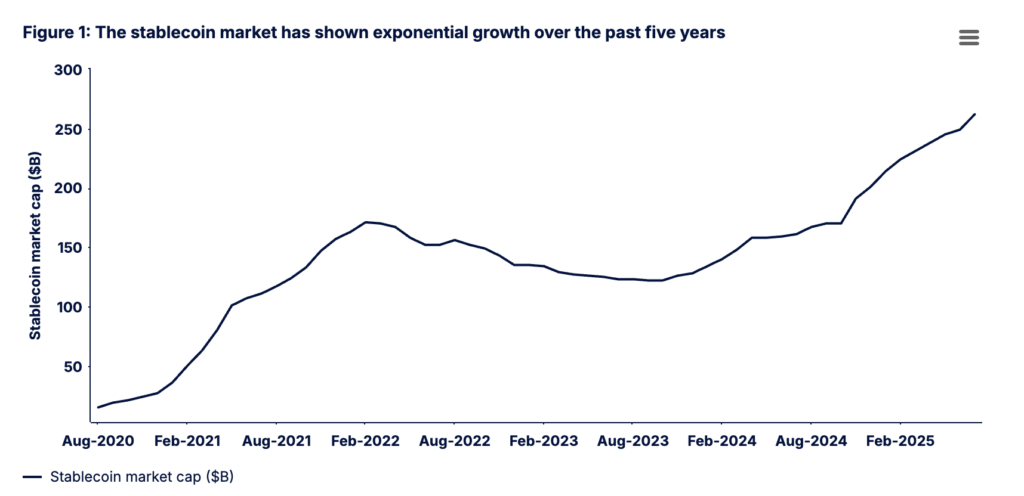
Over the past few years, stablecoins have evolved into a cash-like substitute within digital markets and are now heavily used for cross-border payments and other financial services. According to data from Artemis, the stablecoin market has grown at an average annual rate (CAGR) of 77% over the past five years, reaching over $250 billion by July 2025.
In 2024 alone, stablecoin transaction volume soared to $27.6 trillion, surpassing the combined volume of Visa and Mastercard. This explosive growth highlighted the need for a clear regulatory framework, which the GENIUS Act aims to deliver for dollar-backed stablecoin issuers in the U.S.
Key Provisions of the GENIUS Act
According to the official White House announcement, President Trump supported the GENIUS Act primarily because it is designed to protect consumers from bad actors in digital financial markets.
The law establishes a regulatory framework based on three main pillars:
- Licensing Requirements
- Reserve Standards
- Consumer Protections
The GENIUS Act creates a special licensing category for stablecoin issuers—entities that are exclusively authorized to issue payment stablecoins in the U.S. This exclusive licensing regime ensures that all issuers meet strict federal or state-level standards before entering the market.
Overall, the GENIUS Act introduces a comprehensive set of rules that govern the issuance and management of stablecoins, covering everything from reserve backing and transparency to compliance and consumer safety.
| Provision | Description |
|---|---|
| Authorized Issuers | Only licensed payment stablecoin issuers are allowed to issue or sell stablecoins. This includes subsidiaries of insured depository institutions, federally approved nonbank issuers, and state-licensed entities certified by the U.S. Department of the Treasury. |
| Reserve Requirements | Stablecoins must be fully backed by high-quality liquid assets—such as U.S. dollars, Treasury securities, or deposits held at the Federal Reserve—ensuring 1:1 redemption. |
| Transparency & Audits | Issuers must publish clear redemption policies, disclose reserve composition monthly, and submit monthly certifications. Issuers with market caps exceeding $50 billion are also required to undergo annual audits. |
| Compliance | Authorized issuers are treated as financial institutions under the Bank Secrecy Act and must comply with anti-money laundering (AML) regulations. |
| Regulatory Oversight | A dual-oversight model applies: issuers with over $10 billion in circulation fall under federal oversight, while smaller issuers may opt for state-level supervision if certified by the U.S. Treasury. |
| Consumer Protection | Custodians must segregate customer assets, prioritize customer claims in the event of insolvency, and ensure robust user protection measures are in place. |
| Legal Classification | Payment stablecoins are explicitly not classified as securities, bank deposits, or bank liabilities, and cannot pay interest or dividends. |
The Impact of the GENIUS Act on the Future of Cryptocurrency
The implementation of the GENIUS Act is expected to have a profound and long-lasting impact on the cryptocurrency landscape.
- Crypto Regulation Will Shift Toward Use-Case-Based Oversight
“This legislation is more than just stablecoin regulation—it’s a blueprint for how the U.S. will oversee digital assets moving forward,”
— Jagdeep Singh Sahota, Managing Director, Luminary Advisors
According to Sahota, the regulatory framework introduced by the GENIUS Act signals a shift from technology-based regulation to use-case-based oversight. For example, payment tokens will likely be regulated in a manner similar to banking services, while investment-focused digital assets will remain under the jurisdiction of the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC).
- A Surge in Stablecoin Issuance Is Likely
Matt Green, Chief Scientist at Cryptography Engineering LLC and a professor at Johns Hopkins University, believes regulatory scrutiny over digital assets will continue to grow.
“It’s becoming increasingly clear that traditional banks will play a much bigger role in digital assets, especially stablecoins,”
— Matt Green
This suggests that in the coming years, we may see more stablecoins issued by major banks, not just by traditional crypto-native companies as we do today.
- Paving the Way for Greater Regulatory Clarity
Nathan Dean, Senior Policy Analyst at Bloomberg Intelligence, sees the GENIUS Act as a foundational step toward establishing a clear regulatory framework for the broader crypto industry—especially after years of legal ambiguity.
“With the GENIUS Act, stablecoin issuers now finally have legal clarity—something the entire industry has long waited for—to grow and scale their products,”
— Nathan Dean
While this is a major win for companies like Circle and other stablecoin issuers, Dean emphasizes that the next major challenge is creating a comprehensive framework for the crypto market at large. To address this, the U.S. House of Representatives passed the CLARITY Act on July 17, 2025, and the Senate Banking Committee is currently reviewing a draft version of the bill.
Overall, the CLARITY Act aims to provide a well-defined regulatory structure for digital assets, set clear standards to determine whether an asset should be classified as a security or a commodity, and designate which authority has jurisdiction over each category.
2. Cryptoassets Order 2025 – United Kingdom

On April 29, 2025, the UK government released its long-anticipated draft regulation for cryptoassets: the Financial Services and Markets Act 2000 (Regulated Activities and Miscellaneous Provisions) (Cryptoassets) Order 2025. This Cryptoassets Order 2025 follows consultations led by HM Treasury since 2023, as part of the UK’s broader plan to establish itself as a global hub for the crypto industry.
The proposed regulation aims to provide a clear and robust framework for cryptoasset activities and gives formal authority to the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) to regulate a wide range of crypto-related services in the country.
Key Crypto Activities to Be Regulated in the UK
The draft amendments to the Regulated Activities Order (RAO) introduce several new categories of crypto-related activities that will fall under formal regulation. Once enacted, any company engaging in these activities will be legally required to obtain authorization from the FCA.
Below are the main activities covered under the new framework:
🔹 Issuance of Recognized Stablecoins
Any company issuing a stablecoin in the UK—whether offering it to the public, guaranteeing its value, or promising redemption into fiat currency—will be regulated under the new rules if the activity originates from within the UK.
🔹 Custody of Cryptoassets (for Third Parties)
Companies holding cryptoassets on behalf of clients, whether for investment purposes or when classified as securities, will fall under custody regulations. If a company controls and can transfer cryptoassets not owned by them, they are considered custodians and must be regulated accordingly.
🔹 Operating a Crypto Trading Platform
Any business running a trading platform where users can buy or sell cryptoassets—including platforms that match buyers and sellers for crypto-to-crypto or crypto-to-fiat transactions—will be subject to FCA oversight, much like traditional financial exchanges.
🔹 Dealing in Cryptoassets as Principal or Agent
This includes companies engaging in crypto lending/borrowing, buying or selling crypto on their own behalf, or acting as intermediaries in crypto transactions on behalf of others.
🔹 Crypto Lending Platforms
Platforms that facilitate crypto lending—connecting lenders and borrowers—are also included within the scope of regulated activities.
🔹 Staking Services
Firms offering staking services, where users lock up cryptoassets to help validate transactions on a blockchain (including liquid staking), must be authorized.
If a company issues tokens as a result of staking activities (like liquid staking tokens), it may also require additional licensing as a trading activity.
This regulatory move is a significant step forward in providing legal clarity for crypto businesses in the UK. It reflects the government’s commitment to balancing innovation with investor protection, and aligns the UK’s financial system with the evolving nature of digital assets.
3. Virtual Asset Regulatory Authority (VARA) – Dubai

Amid the rapid rise of the digital asset industry, Dubai has emerged as a global trailblazer by establishing a comprehensive regulatory framework that is now considered a benchmark at the international level.
At the heart of this progressive approach is the Virtual Assets Regulatory Authority (VARA), established under Law No. 4 of 2022. VARA is tasked with supervising all Virtual Asset Service Providers (VASPs) operating within Dubai, aiming to strike a balance between fostering technological innovation and ensuring financial system integrity and stability.
Key Provisions of VARA
VARA is a purpose-built, crypto-native regulator designed specifically to oversee the digital asset ecosystem. It grants licenses to a broad range of businesses directly involved in virtual asset activities—including exchanges, custodians, tokenization platforms, and staking service providers.
Below are some of the key provisions and principles underpinning VARA’s regulatory framework:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Regulatory Focus | VARA focuses exclusively on virtual assets and crypto-native business models, supporting innovation while positioning Dubai as a global crypto hub. |
| Licensing Structure | Employs a two-stage licensing process (initial approval, followed by full VASP licensing). Offers a sandbox-style MVP program for phased, supervised rollouts. |
| Client Base | Designed for both retail and institutional clients. VARA-licensed entities can serve the general public—not limited to professional investors. |
| Token Scope | Covers a wide range of tokens, including cryptocurrencies, utility tokens, NFTs, and tokenized real-world assets (RWAs)—thanks to its broad legal definition. |
VARA’s approach reflects Dubai’s ambition to lead in shaping the future of digital finance. Its clear, forward-thinking rules create a secure and innovation-friendly environment for crypto businesses, investors, and consumers alike.
Impact of VARA Licensing on Crypto Projects
🔹 Regulatory Clarity and Legal Certainty
VARA licensing provides a clear regulatory framework for crypto companies operating in Dubai or the broader UAE. This well-defined structure significantly reduces regulatory risk for market participants, making Dubai a more attractive destination for institutional investors and global crypto firms.
🔹 Boost in Institutional Interest and Liquidity
Being a licensed and regulated entity under VARA allows major crypto companies—such as custodians and exchanges—to operate with greater confidence in the region. This paves the way for larger capital inflows and higher trading activity.
Example:
- BitGo secured a broker-dealer license from VARA, enabling them to offer regulated services to institutional clients.
- Binance also received a VARA license, allowing it to serve retail clients, not just institutional investors.
🔹 Increased Investor Confidence and User Protection
The licensing framework enforces strict standards for compliance, anti-money laundering (AML), transparency, and auditing. This builds greater trust among users and helps ensure that crypto activities under VARA oversight are safer and more reliable for all stakeholders.
4. Financial Instruments and Exchange Act – Japan

Cryptocurrency is officially legal in Japan and operates within a well-defined and structured regulatory framework. The primary legal basis for crypto is the Payment Services Act (PSA), which mandates that all crypto asset exchange service providers must be registered and supervised by the country’s main financial regulator, the Financial Services Agency (FSA).
Additional oversight comes from the Financial Instruments and Exchange Act (FIEA) and various self-regulatory organizations (SROs), which impose further compliance requirements such as anti-money laundering (AML) procedures and consumer protection standards.
Proposed Crypto Tax Reforms in Japan
For years, Japanese crypto investors have faced one of the most burdensome tax systems in the world—with progressive rates reaching up to 55%. This has led many traders and businesses to relocate abroad.
However, in September 2025, the FSA submitted a significant proposal that could reshape the country’s crypto industry. The proposal seeks to reclassify cryptocurrencies from “means of payment” to formal financial products under the Financial Instruments and Exchange Act.
Most notably, the proposal includes a plan to cut the crypto tax rate from the current high of 55% to a flat 20%, aligning it with capital gains taxes for traditional assets like stocks. According to Cointelegraph, the tax reform is expected to come into effect in fiscal year 2026, pending parliamentary approval.
The reform also proposes introducing insider trading regulations, similar to those in traditional financial markets. These rules aim to prevent unfair advantages based on non-public information—such as token listings or protocol upgrades—thus improving transparency and fairness in the Japanese crypto market.
Impact of Crypto Tax Reform on Adoption in Japan
According to a recent Chainalysis report (September 24, 2025), Japan recorded the highest crypto growth rate among Asia-Pacific’s top five markets. On-chain crypto transaction volume in Japan grew 120% year-over-year by June 2025—outpacing Indonesia (103%), South Korea (100%), India (99%), and Vietnam (55%).
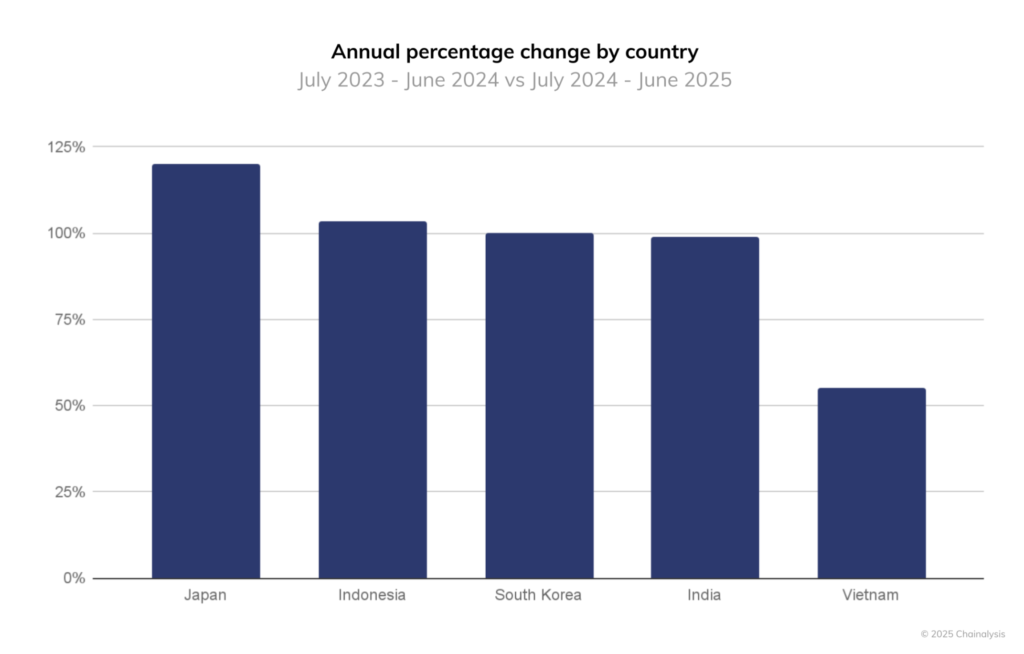
While Japan’s crypto market has remained relatively quiet in recent years compared to its neighbors, this surge coincides with positive policy shifts, including:
- Regulatory reforms recognizing crypto as investment instruments,
- The proposed tax overhaul, and
- The approval of the first yen-backed stablecoin license.
These changes signal Japan’s renewed commitment to becoming a major player in the global digital asset economy, with a regulatory environment that supports both growth and investor confidence.
5. High Capital Gains Tax on Crypto – India

As of 2025, India continues to enforce some of the strictest crypto tax regulations in the world. Whether you’re swapping Bitcoin or staking altcoins, a large portion of your gains is absorbed by taxes and transaction-related fees.
Types of Crypto Taxes in India
India taxes crypto based on the type of activity involved. Here’s a breakdown of the main tax categories:
1. Capital Gains Tax (CGT)
Applies when crypto assets are sold for a profit, such as converting Bitcoin into rupees.
- Flat rate: 30%
- Additional 4% cess for health and education
2. Income Tax
Applies to earnings from:
- Mining
- Staking
- Airdrops
- Salaries or payments in crypto
Rates follow India’s standard income tax brackets:
- 5% for income up to ₹2.5 lakh (~Rp47 million)
- Up to 30% for income over ₹15 lakh (~Rp283 million)
- Companies pay either 25% or 30%, depending on their structure
3. Tax Deducted at Source (TDS)
Since 2022, a 1% TDS applies to crypto transactions exceeding:
- ₹50,000 (~Rp9.4 million) for general users
- ₹10,000 (~Rp1.8 million) for certain categories (e.g. professionals or freelancers)
This tax is automatically deducted during each transaction on crypto platforms.
4. Other Taxes
In Budget 2025, the Indian government added new provisions:
- Hidden or undeclared crypto assets discovered during audits may be taxed at 60%, categorized as “undisclosed income.”
- No wealth or inheritance tax specifically for crypto holdings as of now.
According to reports from Indian crypto traders on X, as of July 2025, global exchange Bybit began implementing an 18% Goods and Services Tax (GST) on all crypto-related services for Indian users.
This followed a government clarification that all crypto platforms operating in or serving India must:
- Collect 18% GST on services like trading, staking, withdrawals, deposits, swaps, and platform fees
- Register under Indian GST law and report user activity to authorities
Though GST doesn’t directly impact trading profits, it adds an additional layer of cost to using crypto platforms. Nearly every service offered to Indian users now carries a tax burden, reducing profit margins—especially for active traders who frequently use advanced tools and services.
Crypto Tax Reporting & Compliance in India
In addition to high tax rates, India requires every individual and business involved in crypto to report their earnings to the Income Tax Department. Individuals must use ITR-2, while businesses use ITR-3. Since 2023, reporting must be done through a dedicated section called “Schedule VDA”, which tracks all gains from digital assets.
Taxpayers must record every transaction, including the date, amount, and rupee value, often using crypto wallets or apps. The filing deadline for individuals is July 31, and October 31 for audited businesses, based on the financial year ending March 31. Late submissions can result in fines ranging from ₹10,000 (~Rp1.8 million) to ₹2 lakh (~Rp37 million), and may lead to further scrutiny or penalties.
The Future of Crypto Taxation in India
Crypto taxation in India is likely to evolve after 2025. Starting April 2026, under Budget 2025 provisions, all crypto exchanges will be required to report detailed transaction data to the government—making it far harder to conceal any crypto activity.
According to Coinfomania, India continues to favor high taxes as a risk mitigation strategy, but may consider relaxing rules if other countries adopt more crypto-friendly policies.
Many in the community hope for lower rates or loss deductions, but for now, the government appears committed to strict oversight and maintaining high tax burdens on the sector.
Conclusion
2025 marks a pivotal year for global crypto regulation. As digital assets continue to mature, major economies are establishing clearer legal frameworks—either boosting growth or tightening control.
In the United States, the GENIUS Act lays the groundwork for regulating dollar-backed stablecoins and signals a shift toward use-based oversight, where crypto is regulated based on function, not just technology. The United Kingdom, through its Cryptoassets Order 2025, empowers the FCA to oversee key activities like custody, trading platforms, and stablecoin issuance—reinforcing its ambition to become a global crypto hub.
Dubai, via VARA, adopts a crypto-native model, offering licenses to exchanges, custodians, and staking providers. This approach enhances innovation while attracting institutional capital through regulatory clarity and consumer protection.
Meanwhile, Japan is reforming its harsh tax rules, aiming to reclassify crypto as financial products and reduce capital gains tax from 55% to 20%—a move that could reposition it as a leading crypto market in Asia. On the other hand, India maintains one of the world’s toughest regimes, with high taxes, strict reporting, and growing operational costs that may limit adoption.
Overall, these regulatory shifts highlight a new era of active global crypto governance. Countries that balance innovation with investor protection are likely to shape the future of digital finance.
References
- Bolder Group. A Breakdown of Key Global Crypto Regulations in 2025. Accessed on October 16, 2025
- Chainalysis. APAC Crypto Adoption Accelerates with Distinct National Pathways. Accessed on October 16, 2025
- Coinfomania. Crypto Taxation in India: A Complete Guide. Accessed on October 16, 2025
- Cointelegraph. From 55% to 20%? How Japan plans to fix its crypto tax rules. Accessed on October 16, 2025.
- Norton Rose. The UK Regime for Cryptoassets: Draft Rules and Legislation. Accessed on October 16, 2025.
- Onkar Singh. Crypto Tax in India: How Much You Actually Keep in 2025. Accessed on October 16, 2025.
- State Street. GENIUS Act Explained: What It Means for Crypto and Digital Assets. Accessed on October 16, 2025.
- TechTarget – Sean Michael Kerner. GENIUS Act Explained: How It Will Affect the Crypto Industry. Accessed on October 16, 2025.
- World Economic Forum. The GENIUS Act is Designed to Regulate Stablecoins in the US, but How Will It Work? Accessed on October 16, 2025.