Value investing is an equity investment strategy that focuses on buying a company’s shares at a market price below its fair value. This approach emphasizes fundamental analysis to assess business quality, financial performance, and long-term prospects, so that investors can benefit when the stock price again reflects its intrinsic value.
Unlike strategies that chase short-term price increases, value investing relies on patience and discipline in valuing a company as a business. Concepts such as undervalued stocks, margin of safety, and the use of financial ratios are the main foundations of this strategy, making it a popular approach among long-term investors.
Article Summary
📊 Value Investing in Stocks: Value investing is afundamental analysis-based investment strategy that aims to buy stocks at a price lower than their intrinsic value. This approach sees stocks as a representation of business ownership, not just a trading instrument.
📐 Value Investing Key Indicators: Valuation of company value is done using financial ratios such as price to earnings ratio (P/E), price to book ratio (P/B), return on equity (ROE ), debt to equity ratio (D/E), and free cash flow (FCF) to measure valuation, profitability, and financial health of the company.
🛡️ Margin of Safety and Undervalued Stocks: The concept of margin of safety is key to reducing risk by buying stocks at prices far below their estimated fair value. Undervalued stocks generally arise due to short-term market sentiment, rather than a decline in business fundamentals.
📈 Value Investing vs Growth Investing: Value investing focuses on cheap prices relative to value, while growth investing pursues high earnings growth despite expensive valuations. Both are characterized by different risks and time horizons, but can complement each other in a portfolio.
🏦 Legendary Investor’s Long-Term Strategy: Value investing emphasizes long-term investing, patience, and understanding financial statements. This strategy is mostly applied to blue chip stocks and defensive sectors that have stable cash flows and clear business models.
What is Value Investing and its Basic Definition
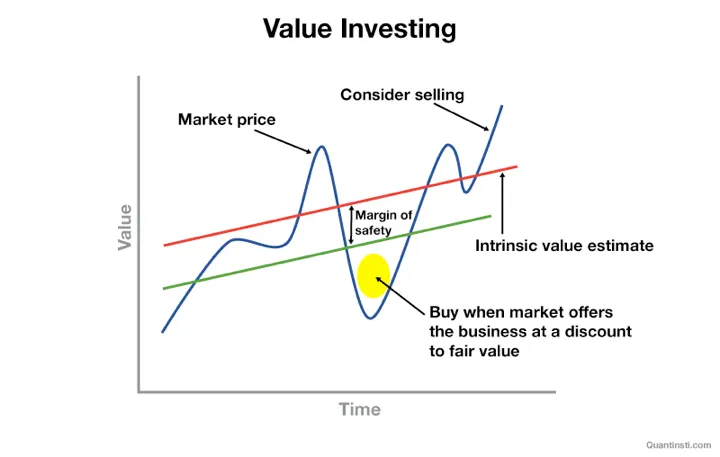
What is value investing is an equity investment strategy that focuses on buying stocks at market prices below their fair value. In the definition of value investing, investors seek to find undervalued stocks, which are stocks that fundamentally perform well but are undervalued by the market.
This approach is closely related to fundamental stock analysis, as investment decisions are based on the company’s financial statements, business performance and long-term prospects. The ultimate goal is to make a profit when the stock price again reflects the trueintrinsic value of the stock.
Basic Principles of Value Investing
The basic principle of value investing stems from the assumption that markets are not always efficient. Stock prices may deviate from their fair value due to sentiment, economic cycles, or investor psychological factors.
One of the key concepts in this strategy is the margin of safety, which is the difference between a stock’s intrinsic value and its purchase price. The larger the margin of safety, the lower the risk of loss if the intrinsic value estimate is not completely accurate.
Intrinsic Value of Shares and How to Calculate It
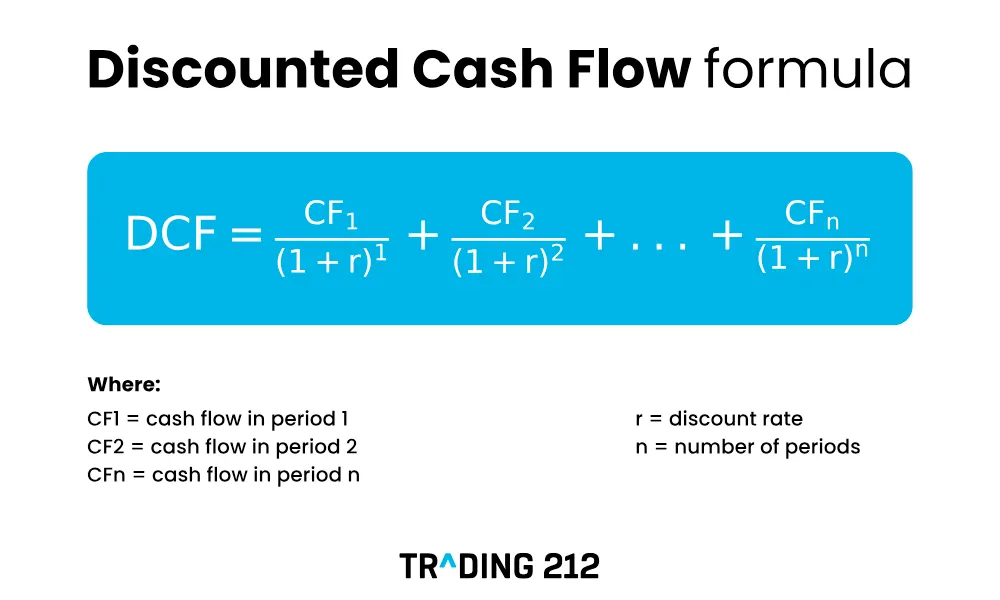
How to calculate the intrinsic value of a stock is generally done with valuation approaches, such as discounted cash flow (DCF) based free cash flow (FCF). This method calculates the present value of future cash flows generated by the company.
In addition to DCF, investors also use a relative approach by comparing the company’s financial ratios to the industry average. This approach helps assess whether a stock is undervalued or overvalued.
Key Indicators in Value Investing
Several key indicators are used in value investing to assess whether a stock is undervalued while having sound fundamentals. These indicators help investors understand how the market values a company’s performance, assets and risks more objectively before making an investment decision.
- Price to Earnings Ratio (P/E Ratio) Measures how many times a company’s net income is valued by the market through its share price. A relatively low P/E is often associated with value stocks, although it still needs to be compared to sector averages and the company’s business conditions.
- Price to Book Ratio (P/B Ratio) Compares the share price to the book value of the company. This indicator is particularly useful for assessing companies in asset-intensive sectors, such as banking and manufacturing, to see if the stock is trading below its net asset value.
- Return on Equity (ROE) shows the company’s ability to generate profits from the capital invested by shareholders. A consistent and high ROE reflects management’s efficiency in managing equity.
- Debt to Equity Ratio (D/E Ratio) Measures the level of debt utilization compared toequity. A D/E that is too high may indicate greater financial risk, especially during economic downturns.
Additional Indicators to Look Out for
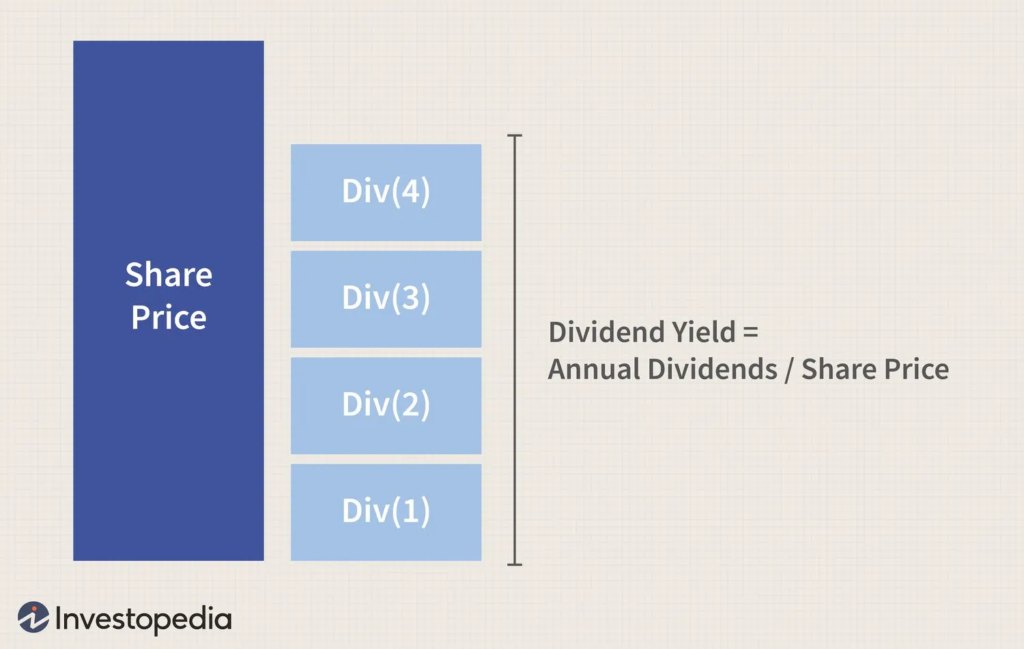
In addition to the basic valuation ratios, a stock’s dividend yield is often considered by value investors because it reflects regular income. Stable dividends usually come from companies with healthy cash flow.
Another critically important factor is free cash flow (FCF), as accounting earnings do not always reflect real cash. Companies with positive and consistent FCF generally have better financial flexibility.
Difference between Value Investing vs Growth Investing
The main difference between value investing and growth investinglies in their investment focus. Value investing emphasizes buying stocks at relatively low prices relative to their fundamentals, while growth investing focuses on companies with high revenue and profit growth, despite their relatively expensive valuations.
In terms of risk, value investing faces the risk of misjudging intrinsic value or changes in company fundamentals. Growth investing , on the other hand, is more vulnerable to failure to meet growth expectations, especially when valuations are already high.
In practice, these two approaches are not mutually exclusive. Many investors combine value and growth strategies according to market conditions, investment horizon, and risk profile.
Warren Buffett’s Value Investing Strategy

Warren Buffett’s value investing strategy emphasizes buying quality businesses at fair prices, not just cheap stocks. Buffett also values long-term competitive advantage, solid management, and cash flow consistency.
This approach makes value investing a long-term strategy. Investors do not focus on daily price fluctuations, but rather on the growth in value of a business over many years.
How to Screen Value Investing Stocks
The value investing stock screening process aims to filter out potentially undervalued stocks based on fundamental indicators. The initial stage usually uses financial ratio filters to narrow down the selection from hundreds of stocks to a few candidates worthy of further analysis.
The steps for screening value investing stocks can be done as follows:
- Determine initial valuation criteria Choose stocks with relatively low price to earnings ratio (P/E) and price to book ratio (P/B) below the industry average as an initial indication of undervalued stocks.
- Selection of company profitability Ensure that the company has a stable and consistent return on equity (ROE), signaling the ability to generate profits from shareholders’ capital.
- Evaluate the debt structure Use the debt to equity ratio (D/E) to ensure that the debt level is still under control and does not overburden the company’s financial condition.
- Check the quality of cash flow Analyze free cash flow to see if the company is able to generate enough cash from its operating activities.
- Use stock screening tools Make use of free value investing stock screening tools to speed up the screening process, such as the financial ratio and industry sector filter features.
- Perform further analysis Screening results need to be complemented with analysis of financial statements, business models, and industry prospects to make investment decisions more comprehensive and measurable.
Stocks and Sectors Suitable for Value Investing

What stocks are suitable for value investing generally come from established companies with clear business models. Sectors suitable for value investing include banking,consumer goods, energy and infrastructure.
For the domestic context, investors often look for examples of undervalued stocks in Indonesia from the category of defensive or cyclical stocks that are in the bottom phase of the cycle. The best blue chip stocks for value investing 2026 are usually judged by earnings consistency, healthy balance sheets, and good governance.
Common Mistakes and Investment Timing
Beginner mistakes when value investing include only looking at the cheap ratio without understanding the quality of the business. Cheap stocks are not necessarily valuable if their fundamentals are structurally deteriorated.
The best time to buy value investing stocks is usually when the market is pessimistic, but the fundamentals of the company remain solid. Discipline and patience are the keys to this strategy.
How to Buy Tokenized US Stocks on the Pintu App

You can start investing in tokenized stocks like Tesla, Nvidia, Apple, and Microstrategy right on the Pintu app, the steps are very simple:
- Open the Doors app.
- Go to the Market section and search for the stocks you want to buy (TSLAx), (AAPLx), (NVDAx), (MSTRx).
- Enter the amount you wish to purchase after logging in.
- You can follow the same steps to buy other tokenized stocks in the Pintu app.
Pintu is also compatible with popular digital wallets such as Phantom and MetaMask, making your transactions even easier. Download Pintu app now on Play Store or App Store! Your safety is guaranteed, as Pintu is supervised by OJK (Financial Services Authority) and CFX.
In addition to trading, Pintu also allows you to learn more about crypto through various educational articles on Pintu Academy which are updated weekly. All articles published on Pintu Academy are for educational purposes only and are not financial advice.
FAQ
How long does it take to see results from value investing in stocks?
Value investing is generally medium to long-term oriented, often taking several years for the intrinsic value to be reflected in the stock price.
What blue chip stocks or sectors are best suited for a value investing strategy?
Blue chip stocks with stable cash flows and defensive sectors such as banking, consumer and energy are often the top choices of value investors.
What are the main differences between value investing and dividend investing?
Value investing focuses on the difference between price and intrinsic value, while dividend investing focuses on regular dividend income, although the two are often complementary.
Reference
- Makmur.id. Understanding the Basic Principles of Value Investing ala Warren Buffett. Accessed January 15, 2026
- Stockbit Snips. Value Investing: Strategies and Examples. Accessed January 15, 2026