Crypto prices move very dynamically, even for major assets like Bitcoin. These fluctuations present opportunities, but also risks that cannot be ignored. One of the strategies used to minimize risk is hedging. This article will explain what hedging is, the strategies and types involved, and the advantages and disadvantages of using hedging in crypto futures trading.
Article Summary
🛡️ Definition of Hedging: A strategy used by investors or traders to protect the value of assets from volatile price movements.
⚖️ Types of Hedging: There are several types of hedging, such as partial hedge, full hedge, and cross hedge. Each can be adjusted according to your needs and risk tolerance.
📊 Risk Management in Hedging: Avoid over-hedging, manage your margin wisely, and evaluate positions regularly to ensure your hedging strategy remains effective and doesn’t introduce new risks.
Definition of Hedging in Crypto Futures Trading
Hedging in crypto futures trading is a strategy used by investors or traders to protect the value of their assets from volatile price movements. Although it may sound technical, the concept of hedging is something we often encounter in daily life.
One example is when someone buys a car and also gets it insured. With insurance, if an unexpected event like an accident occurs, the car owner is protected through compensation, minimizing the losses incurred.
In the context of crypto futures trading, this technique is implemented by opening a position opposite to the asset we hold.
For example, you buy 1 ETH on the spot market and anticipate the market might weaken. To protect your asset, you can open a short ETH position in the futures market with the same size. That way, if ETH price drops, the profit from the short position helps offset the loss on your spot asset. Conversely, if ETH price rises, the loss from the short ETH position in futures can be covered by the gain on the ETH held in your spot wallet.
Hedging becomes an effective strategy to help reduce the potential loss of assets held in the spot market. However, its effectiveness depends on how balanced the size of the futures position is. Keep in mind that hedging doesn’t always cover losses entirely if price movements don’t align with expectations, it’s meant to limit losses, not eliminate them.
In general, this technique focuses on minimizing loss rather than maximizing potential gains.
Types of Hedging in Crypto Futures Trading
Hedging strategies in the futures market can be approached in various ways, depending on how much risk exposure you want to reduce and how you manage your assets. Here are several commonly used types of hedging:
Partial Hedge
Partial hedge is a strategy that protects only a portion of the crypto asset’s value, not the entire amount. It is typically executed by opening a short position in futures that is smaller than the total amount held in the spot market. This strategy suits traders who want to reduce the risk of a price drop but still want exposure to potential gains if the price rises.
Example:
You hold 1 ETH on the spot market. To reduce downside risk, you open a 0.5 ETH short position in the futures market. If ETH price drops, the loss on the spot side is partly covered by the profit from the futures position. However, if the price goes up, you still gain from the 0.5 ETH that isn’t hedged.
Full Hedge
Full hedge means opening an opposite position in the futures market equal in size to your spot asset. The goal is to completely lock in the portfolio’s value regardless of market movement. This strategy is commonly used when a trader wants to be neutral toward the market, such as before a major event that’s difficult to predict.
Example:
You hold 0.5 BTC in your spot wallet. To protect the asset’s value from price fluctuations, you open a 0.5 BTC short position in the futures market. This way, any change in Bitcoin's price will have little to no impact on your total portfolio value, since the spot and futures positions offset each other.
Cross Hedging
Cross hedge involves opening a hedge position using a different asset than the one you hold in your main portfolio. This strategy is usually chosen when traders identify a strong correlation between certain crypto assets.
Example:
Say you hold a portfolio of altcoins whose price movements tend to follow Bitcoin. To reduce risk in case the market drops, you can open a short BTC position in the futures market. The size of the short position is adjusted to match the total valuation of your altcoins. So if your altcoins drop in value, the profit from the BTC short can help offset that loss.
Risk Management and Effective Hedging Strategies
Hedging in futures trading can be an effective way to reduce risk and protect portfolio value, as long as it’s executed with careful planning. However, if not managed properly, this strategy could actually cause losses especially if you ignore important factors such as leverage and margin. To ensure your hedging remains safe and effective, here are several key risk management practices to consider:
1. Choose the Right Crypto Asset
Asset selection plays an important role in the success of a hedging strategy. Avoid assets with low float, potential supply shocks from token unlocks, or those currently under heavy negative sentiment, as their price movements are often unstable and unpredictable. On the other hand, assets with high liquidity, market cap, and trading volume like BTC or ETH are more suitable as hedge assets due to their relatively stable behavior and reliability in managing portfolio risk.
2. Select the Appropriate Hedging Type
There are various hedging strategies available to protect asset value. The first step is to evaluate your portfolio, then choose the type of hedging that best fits your investment objectives and risk tolerance. Don’t rush, make sure the strategy you choose is relevant to your current portfolio condition.
3. Avoid Over-Hedging
While hedging aims to secure your portfolio, that doesn’t mean you need to cover all your exposure. Over-hedging can eliminate profit potential and add costs such as funding fees, transaction fees, and liquidation risks. Determine the portion of assets that truly need protection and size your positions based on calculated risk.
4. Manage Margin Wisely
Since futures hedging uses margin and leverage, managing your margin wisely is crucial to avoid liquidation. Don’t use your entire available margin for one position. Always leave room to adapt to unexpected price movements so your hedge remains safe and doesn’t endanger your portfolio.
5. Monitor and Evaluate Hedge Positions
A hedge may give peace of mind during market volatility, but it shouldn’t be left unmanaged. Continuously monitor your hedge positions, especially if market conditions shift drastically or your initial plan is no longer valid. Don’t hesitate to resize, revise, or close your hedge if it’s no longer necessary. Flexibility is key to keeping your hedging strategy effective and under control.
Pros and Cons of Hedging in Futures Trading
It’s important to understand that futures hedging strategies still carry risks and may not be suitable without proper risk management. But if used correctly, hedging can be an effective tool for keeping your portfolio stable amid market volatility. Here are the advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages of Hedging
1. Reduces Risk from Market Volatility
Hedging helps mitigate the negative impact of extreme price movements, especially during bearish conditions.
2. Protects Portfolio Value
It helps maintain stable portfolio value even during major market corrections. This is especially useful for long-term holders who want short-term protection.
3. Flexible
There are various hedging strategies to match your trading style. Whether it’s full hedge, partial hedge, or cross hedge, they can all be adjusted based on your risk profile and investment goals.
Disadvantages of Hedging
1. Not Completely Risk-Free
Hedging reduces potential loss, but it still carries risk. If the position size, entry timing, or hedge price isn’t right, it can still result in losses. Even a 1:1 hedge ratio can be ineffective if entered at the wrong price compared to the spot position. So hedging isn’t a guaranteed win, it’s a risk control tool that must be applied carefully.
2. Requires Technical Knowledge
This strategy isn’t just about opening an opposite position and forgetting about it. Hedging requires a deep understanding of how futures work, such as margin mechanics, leverage, and liquidation risk. You also need to know how to calculate your portfolio exposure accurately to avoid missteps that can increase your overall risk.
Step-by-Step Guide to Hedging with Pintu Futures
Here’s a practical example of how to apply a hedging strategy using Pintu Futures with a total capital of 250 USDT. In this example, 125 USDT is allocated to purchase BTC as your main investment asset, while the remaining 125 USDT is used to open a hedge position in the futures market.
1. Open the Pintu app.
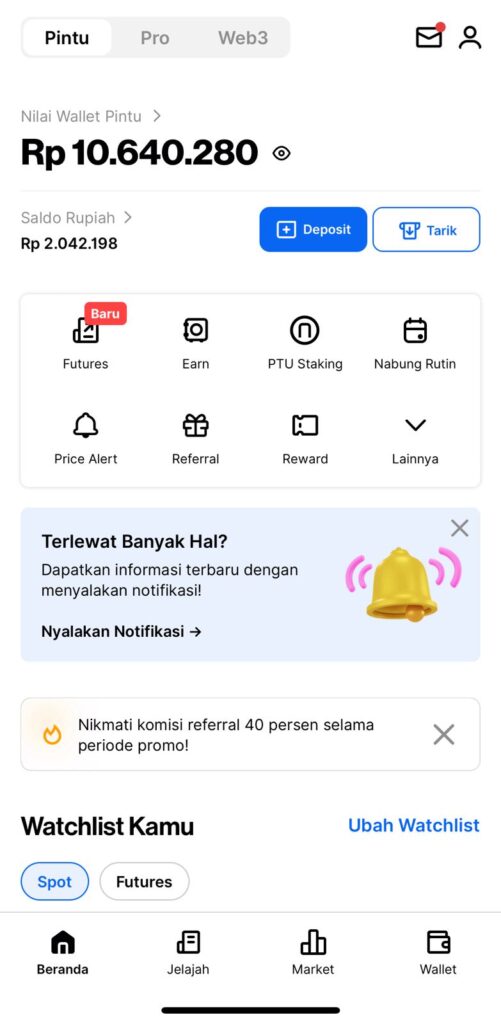
2. Tap on “Pintu Pro.”
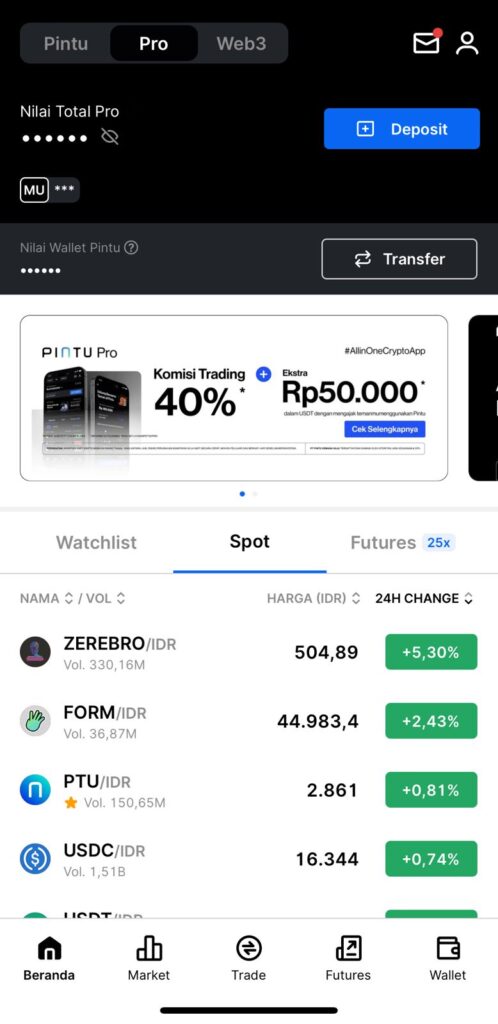
3. Select “Transfer” and move your USDT from Pintu to Pintu Pro Spot for both investment and hedging purposes. The transfer process is free of charge.
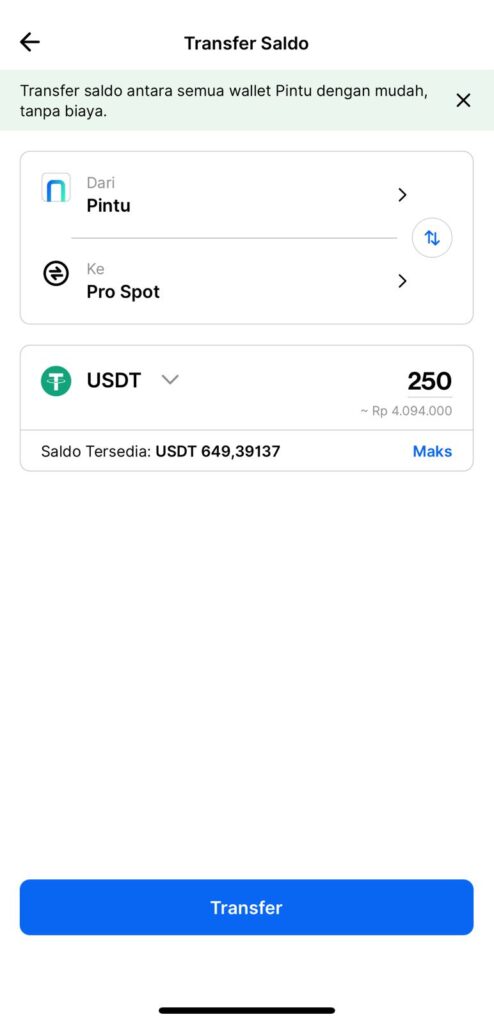
4. Sell half of your USDT for IDR by selecting “Sell USDT.”
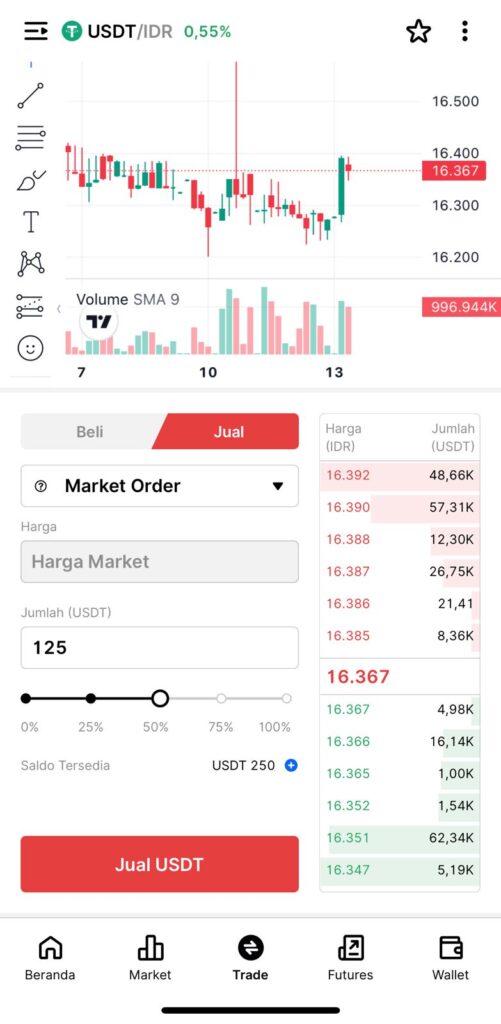
5. Once you have IDR, use it to purchase your investment asset. In this example, we’re buying 0.001 BTC at the price of IDR 1,713,853,000. Tap “Buy BTC” and wait for the order to be executed. Once completed, congratulations! you’ve invested in BTC!
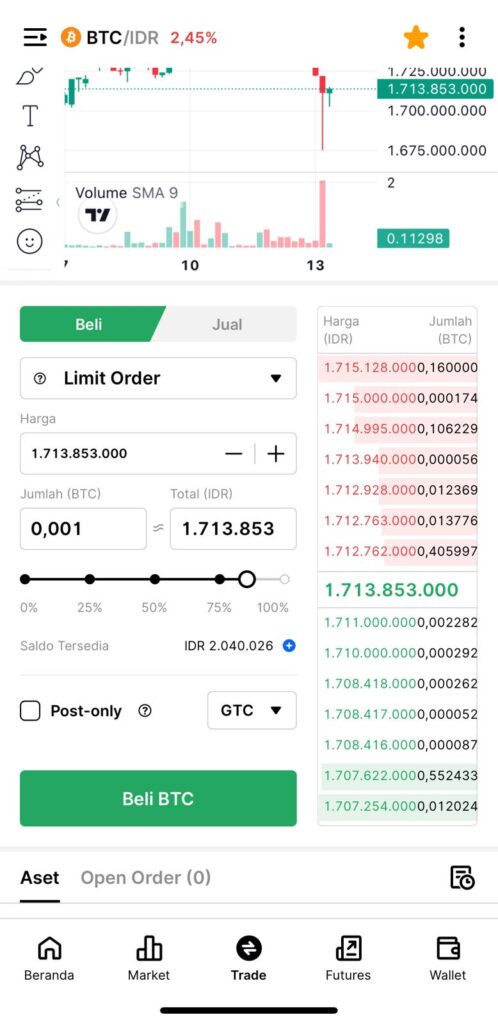
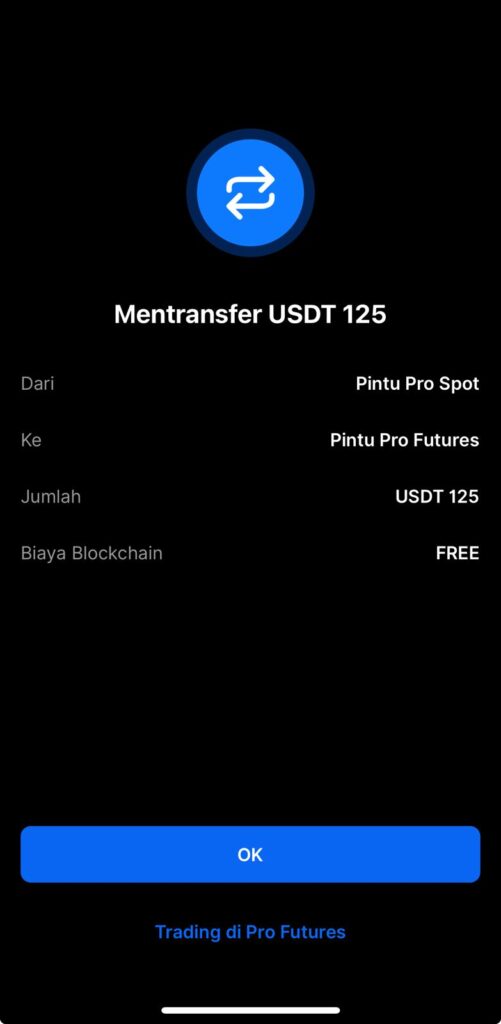
6. Now, transfer the remaining 125 USDT from Pintu Pro Spot to Pintu Futures.
7. In the futures market, choose “BTCUSDT-PERP,” then set your position size and entry price to match your spot BTC holding. In this example, the margin required is just 4.81 USDT less than 5% of the total hedge allocation. Tap “Sell (Short).”
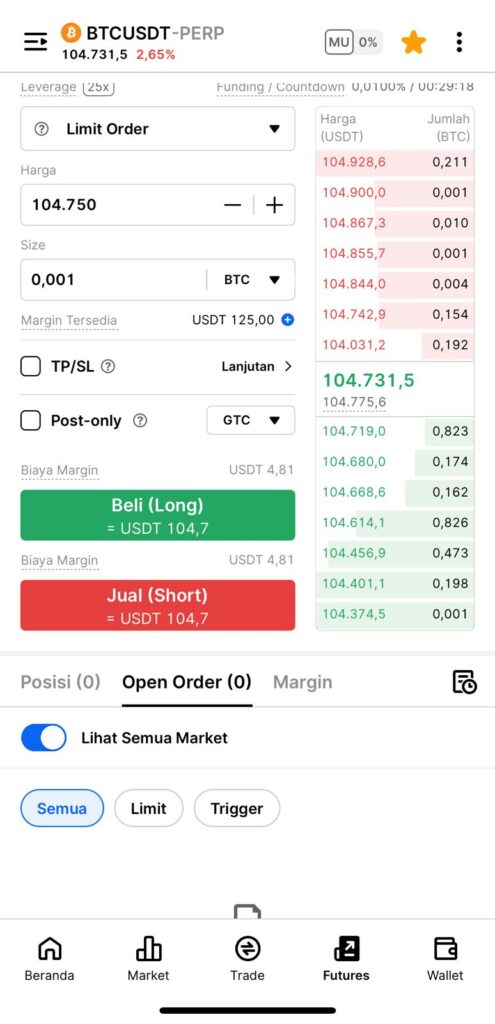
8. Wait for the order to be successfully filled.
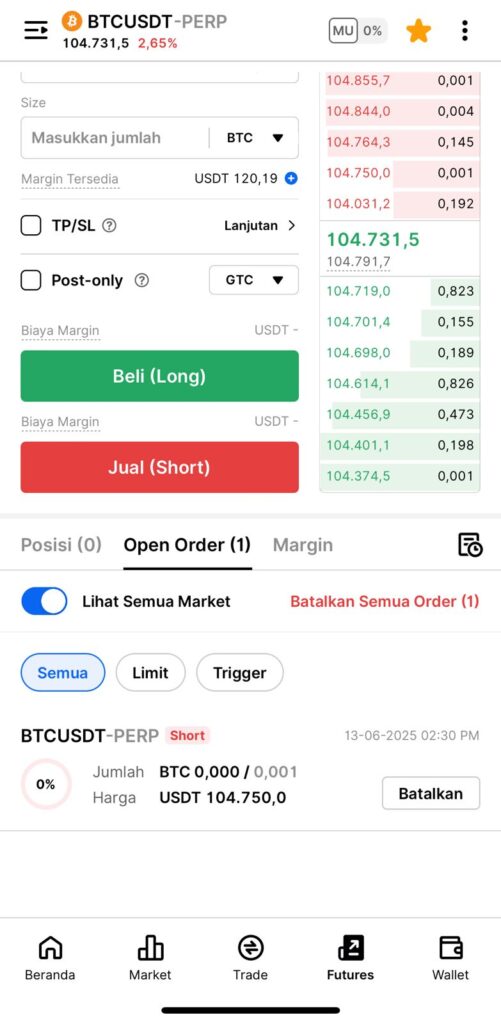
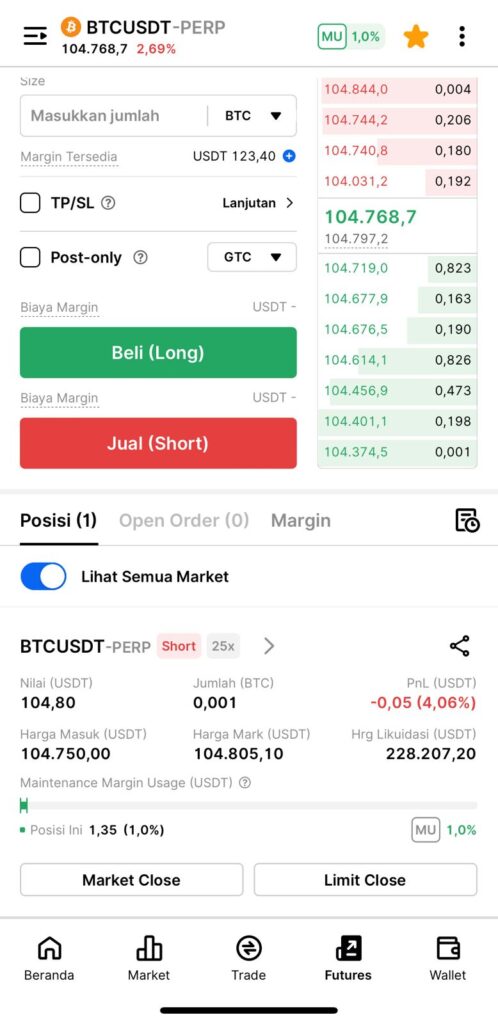
9. Once executed, congrats! You’ve successfully set up a hedge using Pintu Futures.
The Pintu app is also compatible with popular digital wallets such as MetaMask, making your transactions even more convenient. Go ahead and download the Pintu app on the Play Store or App Store today! Your security is guaranteed, as Pintu is regulated and supervised by OJK and CFX.
In addition to trading, Pintu also allows you to learn more about crypto through a wide range of articles on Pintu Academy, updated weekly!
Disclaimer: All articles from Pintu Academy are intended for educational purposes only and do not constitute financial advice.
Conclusion
Hedging in crypto futures trading is a valuable strategy for managing risk and protecting your portfolio during volatile market conditions. By opening an opposite position in the futures market, traders or investors can offset potential losses from their spot holdings. However, this strategy is not risk-free. Without careful planning and a solid understanding of futures mechanics, hedging can backfire and lead to losses. Make sure you understand how the futures market works before using it as a risk management strategy for your portfolio.
References
- The Investopedia Team, “[Beginner’s Guide to Hedging: Definition and Example of Hedges in Finance](https://www.investopedia.com/trading/hedging-beginners-guide/#:~:text=Hedging techniques generally involve the,a gain in a derivative.)”, Investopedia, accessed on June 12, 2025.
- The Investopedia Team, “Hedge: Definition and How It Works in Investing”, Investopedia, accessed on June 13, 2025.
- Peter Gratton, “How Are Futures Used to Hedge a Position?”, Investopedia, accessed on June 13, 2025.