In the blockchain world, a hard fork is a major update that changes the main structure of the network and is incompatible with previous versions. Every node and validator needs to update its system to stay in sync with the new protocol. In the context of Ethereum, the Fusaka Hardfork is not just a technical upgrade, but rather a strategic move to strengthen the network’s foundation through increased Layer-2 data capacity and operational efficiency. This article will take a closer look at what the Fusaka Hardfork is, its technical updates, its impact on the network and users, and the future outlook for Ethereum (ETH) price.
Article Summary
- ⚙️ Fusaka Hardfork is a major Ethereum upgrade focused on improving network infrastructure and efficiency.
- 🚀 Featuring two key technologies: PeerDAS for data efficiency and Verkle Trees for lightweight and fast verification.
- 💡 Increased blob capacity by 8x (from 6 to 48 per block), lowering Layer-2 transaction costs by 70%.
- Undergoes rigorous audits and a $2 million bug bounty program to achieve “trillion-dollar security” standards.
- 📈 Analysts predict ETH prices could rise 30-55% post-upgrade due to increased scalability and network adoption.
What is the Fusaka Hardfork?
The Fusaka upgrade is a major Ethereum update that focuses on improving the core infrastructure of the network. The goal is not to change the user experience, but rather to strengthen the foundation of the protocol to be ready for future growth.
Unlike the Pectra upgrade that adds new features such as account abstraction, Fusaka is designed to remain compatible with all existing dApps and smart contracts. That way, the transition process can be seamless with no risk of disruption for developers.
Learn more about What is the Ethereum Pectra Upgrade? Release Schedule, New Features, and Impact on Pintu Academy!
Fusaka’s role in the Ethereum 2025 Roadmap
Strategically, Fusaka is an important part of the Ethereum 2025 roadmap. This update marks an acceleration of the upgrade cycle to every six months. Fusaka continues the concepts of Dencun, particularly the development of blob transactions to increase data capacity and network efficiency.
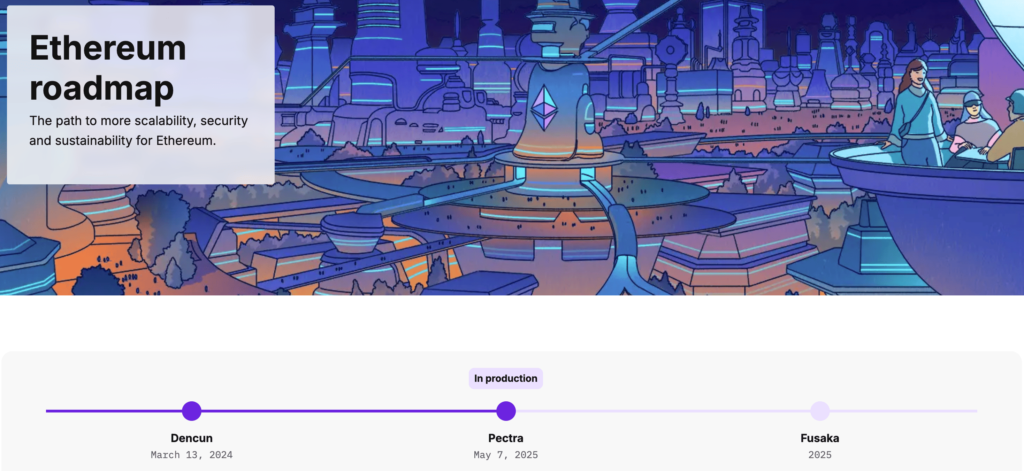
Fusaka is scheduled to go live on the mainnet on December 3, 2025. This update combines Osaka at the execution layer and Fulu at the consensus layer, with a focus on scalability, data availability(PeerDAS), as well as increased Layer-2 capacity without compromising decentralization.
Double Naming Tradition on Every Ethereum Upgrade
Ethereum names each upgrade with two names: one for the execution layer and one for the consensus layer. This tradition started after The Merge, when the network switched to a proof-of-stake system and the two layers were separated.
The names are usually taken from cities or locations that have meaning to the Ethereum community. For example, Dencun comes from “Deneb” and “Cancun”, while Fusaka from “Fulu” and “Osaka”. The goal is to make each upgrade easily recognizable and reflect the direction in which the network is developing.
Fusaka Technical Update
The Fusaka upgrade brings major updates on the Ethereum infrastructure side with 11-12 core proposals (EIPs) focused on efficiency, scalability, and security. The two main components in this update are PeerDAS and Verkle Trees.
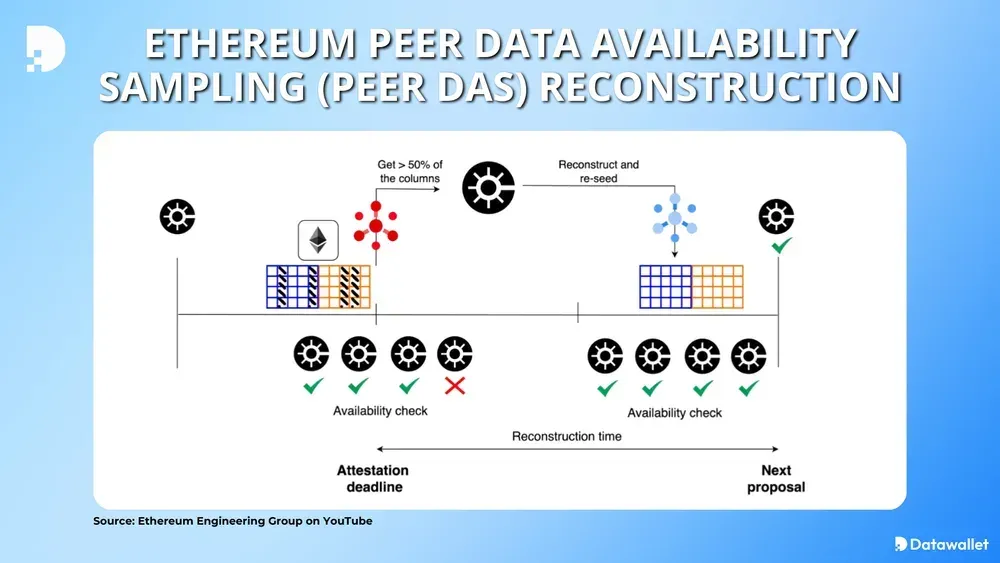
- PeerDAS (Peer-to-Peer Data Availability Sampling / EIP-7594) is at the core of Fusaka. This technology allows validators to verify data availability without having to download the entire block, simply by taking a small sample of the blob data. This approach saves bandwidth and storage, and makes the validation process more efficient and evenly distributed across nodes.
- Verkle Trees introduces a new data structure that makes verification proofs much smaller. The impact is great for users and developers, as it allows light clients to run lighter, even on mobile devices, without compromising network security.
Key Proposals in Fusaka
The Fusaka upgrade includes several Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIPs) that focus on improving Layer-1 scalability, Layer-2 data capacity, and smart contract development efficiency. According to a report by Christine Kim, Vice President of Research at Galaxy Digital, here’s a list of the major EIPs that are part of this update:
- EIP-7594 – PeerDAS (Peer-to-Peer Data Availability Sampling): Introduces a new protocol that allows consensus nodes to verify blob data without having to download the entire block. This is a key feature for Layer-2 scale-up.
- EIP-7892 – Blob Parameters Only Forks: Enables automatic adjustments to blob transaction parameters via lightweight updates(small forks) without the need to perform large network-wide hard forks.
- EIP-7692 – Mega EOF (Ethereum Object Format): Combines twelve updates at once to reorganize the way smart contracts are stored, validated, and executed inside the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM).
- EIP-7917 – Deterministic Proposer Lookahead: Determines block proposer scheduling several epochs in advance so that rollups and decentralized applications can optimize the order of transactions at Layer-2.
- EIP-7825 – Transaction Gas Limit Cap: Ethereum’s gas limit will increase from 45 million to 60 million through proposal EIP-7935, an increase of about 33%. This update complements EIP-7825, which limits gas to 30 million per transaction to maintain network efficiency.
- EIP-7918 – Blob Base Fee Bound: Keeps blob base fees in balance with execution fees, keeping the fee market stable and predictable – essential for Layer-2 efficiency.
- EIP-7762 – Minimum Blob Base Fee: Increase the minimum base fee for blob transactions to keep the data market stable and reduce the risk of extreme price spikes.
In addition, several other EIPs such as EXTCODETYPE (EIP-7761), PAY Opcode (EIP-5920), and Meter Contract Size Limits (EIP-7907) are also under discussion. Although not a major part of the scale-up, these proposals still play a role in improving EVM’s contract flexibility, execution efficiency, and internal operations.
Capacity Up 8x: From 6 to 48 Blobs per Block
Fusaka’s upgrade brings a major increase in Ethereum’s blob capacity, which is the data storage space essential to Layer-2 networks. After Dencun increased the blob limit to 6 per block, Fusaka will increase it by 8x to 48 blobs per block through PeerDAS technology.
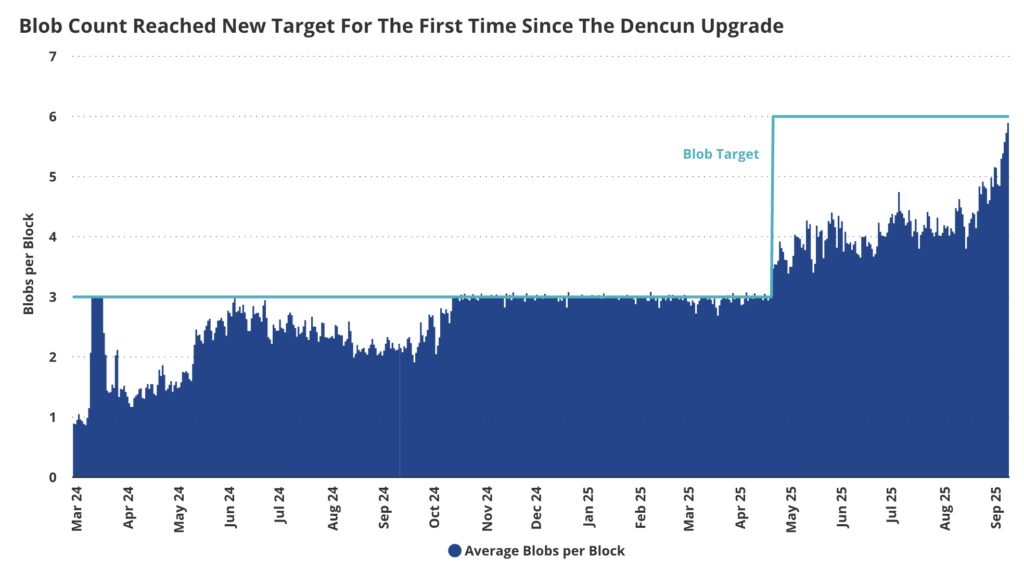
This mechanism allows nodes to verify data with a probabilistic sampling method without downloading the entire blob, resulting in drastically reduced bandwidth and storage requirements. This approach allows for increased data throughput without compromising security, while providing the foundation for subsequent incremental improvements through Blob Parameter Only (BPO) forks.
Importance of Fusaka Upgrade
Ethereum now powers thousands of decentralized applications (dApps) and the majority of its growth depends on Layer-2 rollups. Fusaka addresses these challenges with three main focuses:
- Scalability: PeerDAS and increased blob capacity make the network capable of processing more transactions at a lower cost.
- Decentralization: Validators don’t need to process all the data, so more participants can run nodes.
- Future readiness: Fusaka is the foundation for the next upgrade with faster block times and more sophisticated execution models.
In a post on his X account, @VitalikButerin emphasized that security is a top priority in the Fusaka upgrade, especially in the core PeerDAS feature. He explained that this technology allows each node to randomly verify data without having to download the entire block, thus improving efficiency without compromising security.
Vitalik also emphasized that core developers are being very careful in testing because the technology is new and complex. He added that the blob count will be increased incrementally, as Fusaka becomes a key factor in driving Layer-2 scalability and efficiency of the Ethereum network in the future.
Gas Limit Increases 33%, Per Transaction Limit Set at 16.78 Million Units
The Fusaka Upgrade introduces a per-transaction gas limit of 16.78 million units to improve block efficiency and support Ethereum’s transition to parallel execution. This update is already active on the Holesky and Sepolia test networks, with the goal of preventing a single transaction from consuming the entire block capacity that could previously reach 45 million gases. This step is important to maintain network stability and prevent potential denial-of-service.
Through a post on his X account, @sassal0x shared that before the Fusaka Upgrade launches in early December 2025, Ethereum’s gas limit will be raised from 45 million to 60 million based on the EIP-7935 proposal, an increase of about 33% from the current limit.
Fusaka Upgrade Timeline
The Fusaka upgrade will be rolled out gradually through several test phases before being released to the mainnet. This process starts with testing on the testnet network to ensure system stability and performance are on track. Here is the schedule of the phases:
- Holesky testnet: scheduled to go live on October 1, 2025
- Sepolia testnet: scheduled to go live on October 14, 2025
- Hoodi testnet: scheduled to go live on October 28, 2025
- Mainnet: targeted for release on December 3, 2025 (schedule subject to change based on testing results)
Each testnet phase serves to test performance, detect potential bugs, and ensure all components are working optimally before an official update is deployed on the main Ethereum network.
Impact on Network and Users
The Fusaka upgrade has far-reaching effects across the Ethereum ecosystem, with different impacts for different parties:
For Users
The Fusaka upgrade makes the transaction experience on Ethereum smoother and more efficient. Users will experience more stable and predictive gas fees, with better transaction speeds, especially when the network is congested. The ultimate goal is to make Ethereum more accessible and affordable for everyday use.
For Layer-2 Networks
The Fusaka upgrade increases Ethereum’s blob capacity and data throughput by up to eight 8x through PeerDAS, making verification more efficient without burdening validators. As a result, Layer-2 transaction fees can drop by up to 70%, making transactions faster and cheaper, and strengthening ETH’s position as the center of the Ethereum ecosystem and a key driver of DeFi growth.
For Developers
With the increased gas limit through EIP-7935, developers can now build more complex and functional applications within a single block. All dApps and smart contracts remain compatible, so no major changes are required. The development environment becomes more stable, giving more room for innovation.
For Validators and Node Operators
PeerDAS technology reduces bandwidth and storage load, making the validation process more efficient. However, increasing block size also demands more powerful hardware and more storage capacity. This could potentially lead to the dominance of large staking providers, making maintaining a balance between efficiency and decentralization an important challenge post-Fusaka.
For Network Security
Fusaka underwent a thorough audit and a $2 million bug bounty program to ensure the system’s robustness before its release to the mainnet. The developer’s goal is to achieve the “trillion-dollar security” standard, a level of security capable of protecting trillions of dollars worth of assets and transactions. This move confirms Ethereum’s commitment to remaining the most secure and trusted network in the Web3 world.
Ethereum Price Analysis and Community Response to Fusaka Upgrade
Fusaka’s upgrade received mixed responses from the crypto community on X, especially about its impact on Ethereum’s scalability and prospects.
Market Optimism for Ethereum’s Fusaka Upgrade
In a post on his X account, @MerlijnTrader, a popular crypto trader and analyst with over 400K followers, expressed his optimistic views on the Ethereum Fusaka upgrade. He wrote that Vitalik Buterin has confirmed the launch of the Fusaka Upgrade on December 3, 2025, which will open a new era of massive scalability for Ethereum.
In his tweet, Merlijn emphasized that $ETH is now entering an era of performance, with the prospect of more users, lower transaction fees, and increased demand – signaling the market’s confidence in Ethereum’s future post-upgrade.
ETH Price Predicted to Reach $5,000 – $10,000
Through a post on his X account, @xCryptoParadise, said that two major Ethereum (ETH) upgrades will occur on December 3, 2025 and January 7, 2026 through the launch of Fusaka hard forks. In his tweet, he highlighted that these updates will increase scalability, strengthen network security, and lower transaction fees without causing downtime.
He added that the success of this upgrade could strengthen Ethereum’s dominance in the DeFi and stablecoin sectors. In addition, he projected the potential for ETH prices to reach $5,000 as a major momentum for altcoins, and $10,000 as a major inflection point for the crypto market.
ETH Price Predicted to Rise 30% – 55% After Fusaka Upgrade
Through a post on his X account on August 9, @HOSS_ibc, a crypto market analyst, shared the results of his technical analysis for ETH for the period August 2025 to August 2026. In his tweet, he estimated that the ETH price, which is currently around US$4,178, has the potential to rise to the range of US$5,500-US$6,500, or an increase of around 30-55% in a year.
According to him, the main factor driving this potential increase is the Fusaka upgrade. The implementation of Verkle Trees and PeerDAS technology is believed to significantly improve the efficiency and scalability of the Ethereum network.
ETH at Critical Point: Between Breakout Toward $4,800 or Further Consolidation
Through a post on his X account, @CryptoWinkle, a crypto technical analyst, said that Ethereum (ETH) is currently consolidating below the $4,000 level, forming a symmetrical triangle pattern around $3,800 that has the potential to determine the direction of the next big move. He thinks that if the price manages to break the resistance area, ETH could head towards the target of $4,560 to $4,800.
In terms of fundamentals, the Fusaka Upgrade is said to improve network scalability but raises concerns regarding the centralization of validators. In addition, the potential approval of the Ethereum ETF and changing staking dynamics are also important factors influencing market direction. According to him, ETH is now at a tipping point – where a breakout could open a new upside phase, while a rejection below $4,000 could extend the consolidation phase.
Start Crypto Investing at the Pintu
Now that you understand the major Fusaka Hard Fork update and its impact on the Ethereum ecosystem, you can start exploring the growing number of Ethereum and Layer-2 projects on the Pintu app. All in one secure, easy-to-use app that’s suitable for beginners and experienced investors alike.
Here’s how to buy crypto assets on Pintu:
- Enter the Pintu homepage.
- Go to the Market page.
- Search and select the crypto asset that you have analyzed before.
- Enter the amount you wish to purchase, and follow the rest of the steps.
Conclusion
The Fusaka Hardfork upgrade is an important milestone in Ethereum’s development, bringing PeerDAS and Verkle Trees technologies that increase data capacity, efficiency, and scalability without compromising security. With eight times the blob capacity and higher verification efficiency, Fusaka paved the way for a faster and cheaper Layer-2 and DeFi ecosystem.
From a market perspective, this update is seen as a catalyst for ETH price increases, with projections of a 30-55% rise to $10,000 thanks to increased adoption and network efficiency. Fusaka is not just a technical upgrade, but a strategic move that strengthens Ethereum’s position as Web3’s primary infrastructure.
Disclaimer: All articles from Pintu Academy are intended for educational purposes and do not constitute financial advice.
Reference:
- Binance Academy. Ethereum Fusaka Upgrade: All You Need to Know. Accessed October 27, 2025
- Bitget. Ethereum Fusaka Upgrade: What You Need to Know. Accessed October 27, 2025
- Data Wallet. Ethereum Fusaka Upgrade & EIPs Explained. Accessed October 27, 2025
- LBAnk. A Deep Dive Into the Ethereum Fusaka Upgrade. Accessed October 27, 2025
- VanEck. VanEck Crypto Monthly Recap for September 2025. Accessed October 28, 2025
