In the early days of Bitcoin and the crypto world, buying and selling crypto were done using conventional order book mechanisms like stocks and other assets. In this system, all buying and selling require a third party to arrange and match the two parties who want to sell or buy an asset. All major crypto exchanges still use this system. However, the decentralized crypto industry also requires a decentralized trading system. Automated market maker (AMM) is the crypto world’s answer to conventional order book problems. Now, this system has become a crypto industry standard. So, what are automated market makers? What is its role and function in the crypto world? This article will dissect in full about AMM.
Article Summary
- 📠 Automated Market Makers is a mechanism that utilizes computer algorithms to enable the automation of digital asset exchange. AMM utilizes a decentralized liquidity pool to allow users to buy and sell crypto without a third party to manage transactions.
- ️ ⚖️ The AMM mechanism is specifically made for buying and selling digital assets such as cryptocurrencies. AMM allows for decentralized and automated exchange of assets without the need for an intermediary to monitor the order book.
- ⛲ All cryptocurrency exchanges on a DEX platform using AMM require a liquidity pool. It acts as a source of liquidity for crypto-asset pairs to prevent high slippage. Liquidity providers are an important part of the automated market makers mechanism because they work as constant suppliers of crypto assets for trading.
- 🏦 The AMM system and the DEX platform that uses it have their own advantages and disadvantages. These platforms are usually perfect if you want to invest in new and less popular crypto assets. However, you need to pay attention to the transaction volume and the depth of the liquidity pool to avoid slippage and transaction failures.
What are Automated Market Makers (AMM)?
Automated Market Makers is a mechanism that utilizes computer algorithms to enable the automation of digital asset exchange. AMM utilizes a decentralized liquidity pool to allow users to buy and sell crypto assets without the need for a third party to manage transactions.
Basically, the AMM system is a program that automatically matches two parties who wish to exchange their assets. Almost all decentralized crypto exchanges (DEX) use the AMM system to allow trading on their platforms.
The automated market makers system can only be applied to blockchain networks that have smart-contract capabilities such as Ethereum and Binance. In the AMM system, anyone can become a liquidity provider as long as he fulfills the requirements of the automated market makers algorithm. Some of the most popular AMM examples are Uniswap, Balancer, and Curve.
How Does AMM Work?
The automated market maker or AMM mechanism is specifically made for buying and selling digital assets such as cryptocurrencies. AMM allows for decentralized and automated exchange of assets without the need for an intermediary to monitor the order book. This mechanism was first utilized by DeFi products such as DEX. Uniswap, one of the earliest and most popular DEX platforms, first used the automated market makers mechanism to build a large liquidity pool that could be used by multiple users.
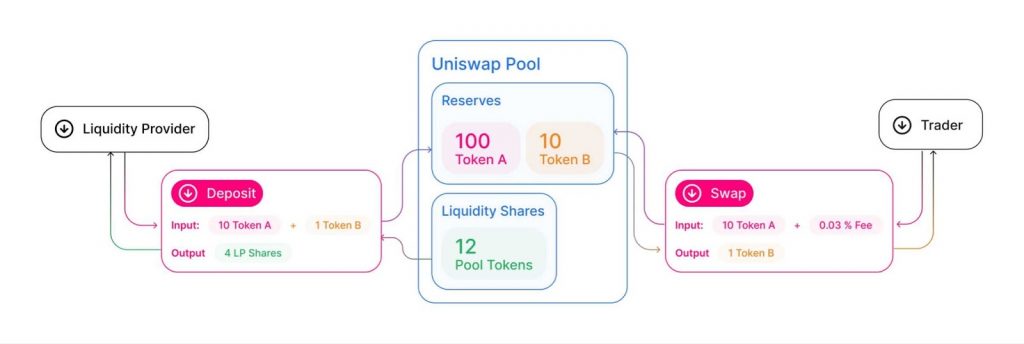
The automated market makers algorithm regulates all aspects of asset exchange that occurs through smart contracts. It displays market prices that are always updated and carries out all trading. However, another important part of determining the mechanism of automated market makers is the liquidity pool and its liquidity providers.
One of the most important technical aspects of an AMM is ensuring the balance of each liquidity pool so that it does not affect the pricing of the assets within. AMM does this by using a mathematical calculation. UniSwap and other major DEXes use a simple x*y=k equation. X is the crypto asset A and y is crypto asset B while K is a constant number. Essentially, the goal is to always rebalance assets A and B whilst keeping the value of K the same.
Liquidity Pool
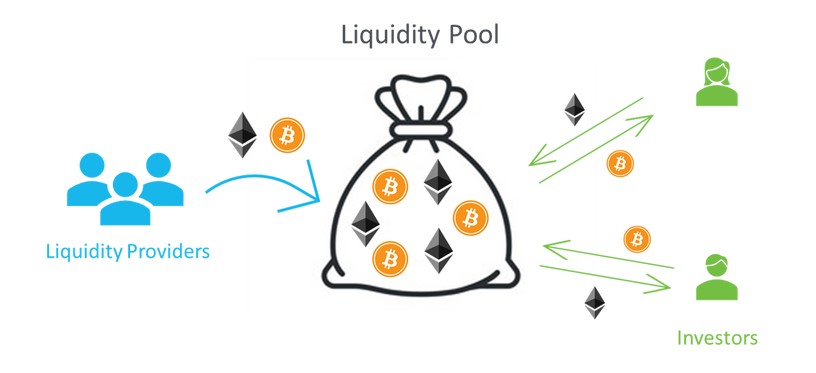
The liquidity pool is an important pillar of the AMM system. All decentralized cryptocurrency exchanges that use AMM require a liquidity pool. It acts as a source of liquidity for crypto-asset pairs in a DEX and prevents high slippage. The liquidity pool is basically a place where all asset exchanges take place.
All trades occur by entering and withdrawing assets from the pool. People who provide assets into the pool for a certain period of time are referred to as liquidity providers. Liquidity providers play an important role because the more assets are stored in the pool, the smaller the slippage that occurs, reducing losses for users.
💡 Slippage
is the difference between the market price of an asset and the price of the asset we get when we trade. For example, we see the FTM price at 2.2 US dollars but when we trade an asset, we get the price FTM at 2.21 US dollars. This is the result of slippage that occurs but is still ideal because the difference is still small.
DEX wants each asset pair (Bitcoin-FTM) to have deep liquidity so that users do not suffer losses. DEX platforms offer various incentives to encourage their users to become liquidity providers. They incentivize liquidity providers by sharing a portion of the transaction fees collected by the platform.
Becoming a Liquidity Provider
As already explained, liquidity providers are an important part of the automated market makers mechanism because they work as suppliers of pairs of crypto assets to be traded. The DEX will reward liquidity providers with a percentage of the transaction fees that the platform earns or with their protocol tokens.
In addition, several DEX platforms also provide an opportunity for liquidity providers to do yield farming of the LP tokens they get. From here, they can get additional financial benefits from yield farming. Yield farming is a DeFi product where you lock your tokens to earn interest. Examples of DEXs that do this scheme are PancakeSwap and SpookySwap.
However, there is a risk of becoming a liquidity provider, especially if you store it on a platform with low transaction volume and liquidity. You also need to understand the concept of impermanent loss. Impermanent loss is a temporary loss commonly experienced by liquidity providers as a result of price fluctuations of crypto assets in the liquidity pool. This concept is referred to as ‘impermanent’ because you will not incur a loss unless you withdraw the asset from the liquidity pool. So, you can wait until the value of your asset returns to avoid impermanent loss.
Advantages and Disadvantages of AMM on a DEX platform
Advantages
- 💻 Decentralized: DEX is a decentralized exchange platform that utilizes smart-contract programs to carry out trades and other activities such as being a liquidity provider. Some DEXs also have their own governance system where platform users can vote on various DEX policies such as transaction fee percentages and so on.
- ⚡ Non-Custodial: All DEX platforms are non-custodial which means they do not store and hold your assets while you use their services. In a centralized exchange or CEX, all your assets are temporarily stored and the exchange has the right to freeze assets in the event of a serious violation such as a criminal offense.
- 🪙 A wider selection of crypto assets: DEX is usually the first choice for the launch of new crypto assets. In fact, some DEXs have a dedicated section of tokens that are new or about to be launched. Therefore, it is the right platform if you want to invest in new and less popular crypto assets.
Weaknessess
- 🌊 Depth of liquidity: All DEX platforms use an AMM system that relies on liquidity providers to function optimally. A DEX requires large liquidity so that all transactions can be carried out quickly at the appropriate market price. If you use a DEX with too little liquidity, your transaction may not be processed or even fail.
- 💸 Transaction volume and slippage: The DEX platform also requires stable transaction volume to avoid high slippage rates. Using DEX with a small transaction volume will result in the price of your purchase is different from the market price.
- 🤑 Limited purchase types: Currently, major crypto exchanges are able to offer various types of buy orders besides spot such as limit orders, OCO, and stop limit. Unlike CEX, most DEXs only support purchases at market price or spot buy.
Some of the Most Popular AMM Protocols in Crypto

- Curve: Curve is one of the most popular DeFi apps specially created for creating multiple liquidity pools. The curve platform has succeeded in attracting a large number of users who want to become liquidity providers because it provides flexible incentives according to the investment preferences of the users. It is the largest AMM protocol with a TVL of $9,65 billion dollars.
- AAVE: AAVE is a DeFi application for lending that utilizes the AMM system. It is the second AMM protocol with a TVL of $9,1 billion dollars.
- UniSwap: UniSwap is a DEX platform on the Ethereum network. He was also one of the first DEXs to popularize the AMM system. In addition, UniSwap is a DEX platform with the largest TVL compared to others ($5,89 billion dollars).
- Balancer: Balancer is a DeFi application that acts as an asset manager using a smart-contract system. This protocol uses AMM for all trading and swap activities on its platform. It has a TVL of $2,01 billion dollars.
Buying Cryptocurrency
You can buy various cryptocurrencies on the Pintu app such as ETH, TBC, FTM, and SOL. Through Pintu, you can buy cryptocurrency in a safe and convenient way.
In addition, the Pintu application is compatible with various popular digital wallets such as Metamask to facilitate your transactions. You can download the Pintu app on Play Store and App Store! Your security is guaranteed because Pintu is regulated and supervised by Bappebti and Kominfo.
You can also learn more about crypto through the various Pintu Academy articles which are updated every week! All Pintu Academy articles are made for educational purposes, not financial advice.
References
- Andrey Sergeenkov, What Is an Automated Market Maker? – AMMs Explained, Coin Desk, accessed on 11 May 2022.
- Marko Mihajlović, What Is An AMM (Automated Market Maker) | A Beginner’s Guide to Decentralized Finance (DeFi), Shrimpy, accessed on 12 May 2022.
- Fernando Martinelli, What Is an Automated Market Maker (AMM)? | by Fernando Martinelli | Balancer Protocol, Medium, accessed on 13 May 2022.
- What are Automated Market Makers Like Uniswap, The Defiant, accessed on 14 May 2022.
- Rahul Rai, The Past, Present, and Future of Decentralized Exchanges, Messari, accessed on 16 May 2022.