The Internet continues to shape our social lifestyles on a daily basis, and currently, we find ourselves immersed in a world where activities like social media, online shopping, and search engine browsing dominate, known as Web 2.0. However, as cryptocurrencies, blockchain technology, and the Internet of Things (IoT) gain prominence, we are transitioning into a new era called Web 3.0, which is already impacting our daily lives. In this article, we will explore the definitions of Web 2.0 and Web 3.0 and delve into the fundamental differences between these two generations of the Internet, providing a comprehensive analysis.
Article Summary
- 👀 Web 2.0 facilitates user-generated content that can be shared and viewed by millions of people worldwide, exemplified by social media platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, and YouTube. According to a report by We Are Social and Hootsuite, the global social media user base will reach 4.76 billion by January 2023.
- 🌐 Web 3.0, often referred to as the “Semantic Web,” is characterized by a decentralized structure that offers enhanced security and transparency, where all content and authority is under the full control of each individual who accesses it.
- 🆕 Web 3.0 has the potential to disrupt many industries, including finance, the arts, health care, and more. However, Web 3.0 also has many shortcomings, namely the complexity of use due to its novelty and the high volatility of its assets.
- 💸 Both Web 2.0 and Web 3.0 have the potential to shape the future of the Internet in their own unique ways and have a positive impact on our lives. Those who can adapt and harness the power of both Web 2.0 and Web 3.0 will gain a significant competitive advantage in the digital world.
What is Web 2.0?

Web 2.0 is the Internet generation that emerged in the early 2000s. As quoted by Investopedia.com, Web 2.0 represents a paradigm shift in Internet usage, where the monotonous Web pages of Web 1.0 were replaced by interactivity, social connectivity, and user-generated content in the first two decades of the 21st century. Web 2.0 allows users to create content that can be shared and viewed by millions of people around the world.
In essence, Web 2.0 has revolutionized the Internet industry by enabling anyone to collect, generate, and distribute vast amounts of content to a global network with a single click. The widespread use of social media such as Instagram, Twitter, Facebook, YouTube, blogs, podcasts and other social media platforms exemplify the capabilities of Web 2.0 platforms.
Web 2.0 technologies and applications include:
- 🌐 Web browsers: Web 2.0 has led to significant improvements in web browsers, enabling the creation of more interactive and dynamic websites.
- 📱 Social media: Platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn have revolutionized the way we communicate and share information online.
- 🛒 E-commerce: Online shopping is a technology brought about by Web 2.0 that catalyzed the growth of e-commerce platforms and marketplaces such as Amazon, eBay, Tokopedia, Blibli, Shopee and others that connect sellers and consumers in online buying and selling activities.
- 📲 Web-based applications: Web 2.0 also gave birth to various innovative web applications such as photo editing applications, video streaming, blogs and more, enriching the user experience while navigating the digital world.
Web 2.0 has changed the way we interact with the Internet, opening up new opportunities from communication to commerce. Web 2.0 represents an era in which users play an active role in creating and sharing content, and participate in rich online communities on a global scale. However, we are now entering a new phase of evolution from the Web 2.0 world, Web 3.0.
What is Web 3.0?

Web 3.0, also known as Web3, is the subsequent phase in the evolution of the web or internet, possessing the potential to shift the centralized paradigm of Web 2.0. Web 3.0 is built on the concept of decentralization, openness, and enhanced user agency.
Web3 is also known as the “Semantic Web,” the next generation of the internet that is continuously under development. One of the key features of Web3 is its ability to connect and exchange data with other devices and systems in a decentralized manner. Unlike Web 2.0, which depends on centralized servers and systems to store and process data, Web3 employs distributed ledger technology, such as blockchain, to store and process data in a decentralized fashion. This undoubtedly adds value in terms of enhanced security, transparency, and interoperability.
Technologies and applications of Web 3.0 include:
- Blockchain: Web3 uses blockchain technology to store and process data in a decentralized manner. Blockchain technology has revolutionized the way transactions and value exchange occur online.
- Decentralized Applications (dApps): The Web3 world allows for the development of dApps built on blockchain technology and operate in a decentralized manner. Full control is not centralized, unlike in Web 2.0.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Web3 has the potential to integrate smooth communication between devices with IoT systems, thus enabling greater automation and efficiency.
The potential impact of Web3 on the internet and society is quite substantial. Web3 has the potential to transform the way people conduct online transactions and value exchanges, as well as how they store and process data. Web3 also enables integration and communication with IoT devices and systems, which can lead to increased automation and efficiency across various industries.
Differences between Web2 & Web3
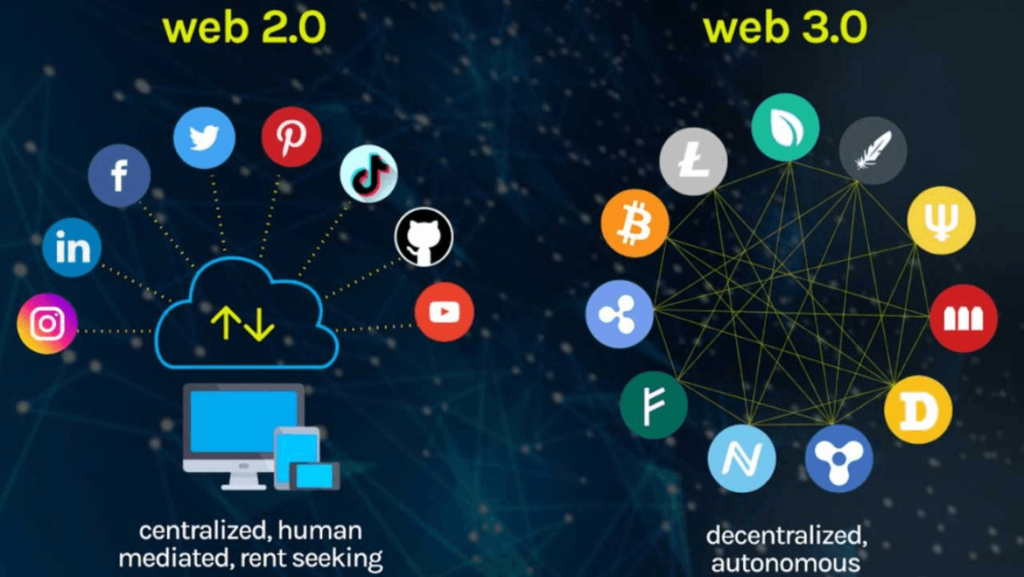
After understanding the basic definitions of Web 2.0 and Web 3.0, it’s necessary to dig deeper and compare the two to understand the key differences between them.
| Web2 | Web3 | |
|---|---|---|
| Adoption | Wide adoption | Limited adoption |
| Ease of Use | Easy to use | Complex |
| Maturity | Mature and stable | Early stage |
| Security | Vulnerable | Secure |
| Transparency | Opaque | Transparent |
| Interoprability | Siloed | Interoperable |
| Innovation | Limited | Potential for innovation |
| Mass Adoption | Yes | Potential for mass adoption |
| Volatility | Stable | Volatile |
The most obvious difference between Web 2.0 and Web 3.0 lies in their approach to data storage and processing. Web 2.0 relies on centralized servers and systems for data storage and processing, while Web 3.0 uses distributed ledger technology, such as blockchain, for decentralized data storage and processing. This divergence has many implications for data security, transparency, and interoperability.
Another difference between Web 2.0 and Web 3.0 is the degree of control and ownership users have over their data. In Web 2.0, user data is primarily controlled and owned by a centralized entity, such as a social media platform or search engine. In contrast, in Web 3.0, users retain full control and ownership of their data. This is possible because all data is stored on the blockchain and can be accessed and managed directly by the user, without the need for permission or approval from a third party.
Uniqueness and Weaknesses of Web2 & Web3
| Web2 | Advantages | Weakness |
|---|---|---|
| Mass adoption | Vulnerable | |
| Easy to use | Lack of transparency | |
| Mature and stable | Siloed | |
| Web 3 | Decentralized | Complex |
| Full control of ownership | Limited adoption | |
| Innovations are growing | Volatile asset | |
| Potential for mass adoption | ||
| Transparent |
Both Web 2.0 and Web 3.0 have unique strengths and limitations. Web 2.0, being more mature, shows widespread adoption with technologies and applications that are widely accepted by the majority. However, Web 2.0 is vulnerable to security threats and is often criticized for its lack of transparency and interoperability. These issues can potentially be addressed by Web 3.0 technologies and applications that provide users with enhanced security, transparency, and interoperability. However, it’s important to note that Web 3.0 is still in its early stages of development and requires extensive user education due to its complex and volatile characteristics.
The application of Web 2.0 and Web 3.0 technologies depends fundamentally on the specific needs and goals of each individual. If you are looking for a proven solution with widespread adoption, Web 2.0 may be a better alternative. On the other hand, if you are willing to take risks and are ready to delve into the complexities associated with newer technologies, Web 3.0 could offer myriad benefits in terms of security, transparency, and innovation.
The Future of Web 2.0 and Web 3.0
After comprehending the differences between Web 2.0 and Web 3.0, what could we speculate about their respective futures? As we’ve discerned, both Web 2.0 and Web 3.0 boast their unique strengths and weaknesses, making it challenging to predict with accuracy which technology will ultimately dominate in the long run. However, there is a variety of expert opinions, with many believing that Web 3.0 technologies and applications will eventually supplant those of Web 2.0, while others opine that Web 2.0 and Web 3.0 will coexist and mutually enhance each other.
Web 2.0 undeniably excels in terms of massive adoption, as evidenced by the considerable uptake of internet usage and social media worldwide. Quoting data from the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), the number of internet users worldwide reached 5.3 billion in 2022, signifying that around 66% of the global population are internet users. Meanwhile, according to a report by We Are Social and Hootsuite, the number of social media users worldwide as of January 2023 was approximately 4.76 billion, equivalent to 59.4% of the total current global population.
It can be posited that Web 2.0 technologies and applications have had a head start and currently possess a substantial user base and infrastructure. Hence, any potential full-scale transition from Web 2.0 to Web 3.0 seems unlikely to be a complete replacement, as it would require a significant shift in the way individuals and businesses utilize the internet.
On the one hand, despite many concerns about the complexity and volatility of Web 3.0 technologies, the fact remains that their adoption has been able to grow rapidly in a relatively short period of time. According to data from TripleA, a Singapore-based blockchain company, the number of crypto users worldwide is estimated to reach over 420 million by 2023, and this number is bound to increase with continued innovation and rising adoption rates.
Web 3.0 continues to show robust progress, offering technological novelties and providing extensive benefits across various sectors, including:
- 💵 Finance: The emergence of Decentralized Finance (DeFi) technologies refers to a range of financial products and services that operate without the need for centralized authorities such as banks. This decentralization is enabled by blockchain technology and smart contracts, which are at the core of Web 3.0.
- 🎨 Art: Through Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) that can be integrated into Web 3.0. As blockchain tokens, NFTs allow creators to transparently prove ownership of various assets such as digital art, music, data, in-game assets, and more.
- 🏥 Healthcare: In the healthcare sector, an interesting application of blockchain technology can address the problem of counterfeit drugs and securely store medical records. Another example is securing patient data through zero-knowledge proof systems, which allow patients to authenticate their identity to healthcare institutions without disclosing sensitive information.
Numerous other industries can be disrupted by the advent of Web 3.0, and in the future, it is conceivable that Web 3.0 technologies and applications will become increasingly mainstream. This is due to the multitude of benefits they offer compared to traditional Web 2.0 technologies.
For instance, the decentralized nature of Web 3.0 technologies can foster enhanced security and transparency, thereby attracting greater adoption rates. Additionally, the potential for innovation in Web 3.0 could lead to the development of new and exciting applications capable of disrupting traditional industries.
Both Web 2.0 and Web 3.0 hold the potential to shape the future of the internet in their respective ways, yet the impact they produce is significantly influential in our lives. Companies or individuals capable of adapting and harnessing the strengths of both Web 2.0 and Web 3.0 are likely to secure substantial advantages in the digital landscape.
Conclusion
Web 2.0 and Web 3.0 are in two distinct phases of internet evolution. Web 2.0, known as the “social web,” is characterized by the emergence of centralized platforms and applications such as Facebook and Google, which have revolutionized the way humans communicate and share content online.
On the other hand, Web 3.0 represents a shift towards decentralization and the use of blockchain technology, potentially bringing about significant changes in fields such as data privacy, security, and ownership.
The future of the internet will be shaped by advancements and adoption of Web 2.0 and Web 3.0 technologies. Therefore, it’s essential for us to stay updated and adapt to these changes to remain relevant and competitive in the digital world.
References
- Frisco D’anconia, How to transition from Web2 to Web3, Guardian.ng, accessed on 19 May 2023.
- Kinza Yasar, What is Web 3.0 (Web3)? Definition, guide and history, Techtarget.com, accessed on 19 May 2023.
- Binance Academy, Web2 vs. Web3: Which Is Better?, Binance.com, accessed on 19 May 2023.
- Margaret James, Web 3.0 Explained, Plus the History of Web 1.0 and 2.0, Investopedia.com, accessed on 19 May 2023.
- Nic Chong, Web2 vs. Web3: Understanding the Evolution of the Internet, Medium.com, accessed on 19 May 2023.
- Bernard Marr, Web3, NFTs, And The Future Of Art, Forbes.com, accessed on 19 May 2023.
- Sophia Moscovis, How Web3 and the metaverse are changing healthcare, Forbes.com, accessed on 19 May 2023.
- Cindy Mutia Annur, Pertumbuhan Melambat, Jumlah Pengguna Media Sosial Global Capai 4,76 Miliar hingga Awal 2023, accessed on 19 May 2023.
- Shilvina Widi, Jumlah Pengguna internet di Dunia Mencapai 5,3 Miliar pada 2022, Dataindonesia.id, accessed on 19 May 2023.