Bitcoin’s high energy consumption often sparks debate about the importance of efficiency efforts in the bitcoin mining process. According to data from the Cambridge Center for Alternative Finance (CCAF), Bitcoin currently consumes around 110 Terawatt Hours per year or approximately 0.55% of global electricity production. This is roughly equivalent to the annual energy consumption of small countries like Malaysia or Sweden.
But can we justify the Bitcoin energy consumption? Is it true that this energy consumption can damage the environment? Here is our explanation.
Bitcoin energy consumption is used to secure the Bitcoin network
Bitcoin or gold requires energy to produce and circulate them to the market. In the gold mining industry, energy is required to extract gold from the earth, run machinery, and relocate it. If in the gold mining process energy is used to turn rock into a valuable commodity, then in Bitcoin mining is the process of turning complex math into a valuable asset. Both of them require electrical energy.
First of all, we have to understand how Bitcoin works. Bitcoin energy consumption is used to secure the Bitcoin network by the miners. Miners need a high-powered computer to solve difficult mathematical problems to secure bitcoin transactions. The result of this process is newly minted bitcoin that is published into the system and rewarded for the miners.
Miners sell bitcoin to pay for the electricity bills. Obviously, they will try to find the most efficient way to mine bitcoin to get a higher profit margin. So how do they do this? By looking for renewable energy sources that are available in large quantities.
Bitcoin mining uses energy that is difficult for other industries to use
Because the cost to run Bitcoin mining operations is high, and a large portion of the cost goes for electricity to run mining machines (such as ASICs), Bitcoin miners are looking for more options of energy-efficient resources. One of the options is to use leftover energy that cannot be used anymore. For example, in the United States, some miners use natural gas flares. When oil is extracted, a by-product of petroleum is usually formed into natural gas. This gas can pollute the environment. Since the location of oil rigs is usually in remote areas, extracting energy from this gas is not effective for traditional industries. Bitcoin miners from North Dakota to Siberia are using this opportunity to extract natural gas from petroleum by-products and use that energy to run Bitcoin mining.
In China, hydroelectric energy is the largest renewable electrical energy in the world. During the rainy season in Sichuan and Yunan, this hydro energy is usually left unused. Their energy production in the rainy season exceeds local demand from China. Not to mention their battery technology is advanced enough to accommodate this energy. Therefore, it is not surprising that 50% of global Bitcoin mining occurs in this area during the rainy season. This energy is cheap, redundant, and wasted if it is not used for bitcoin mining.
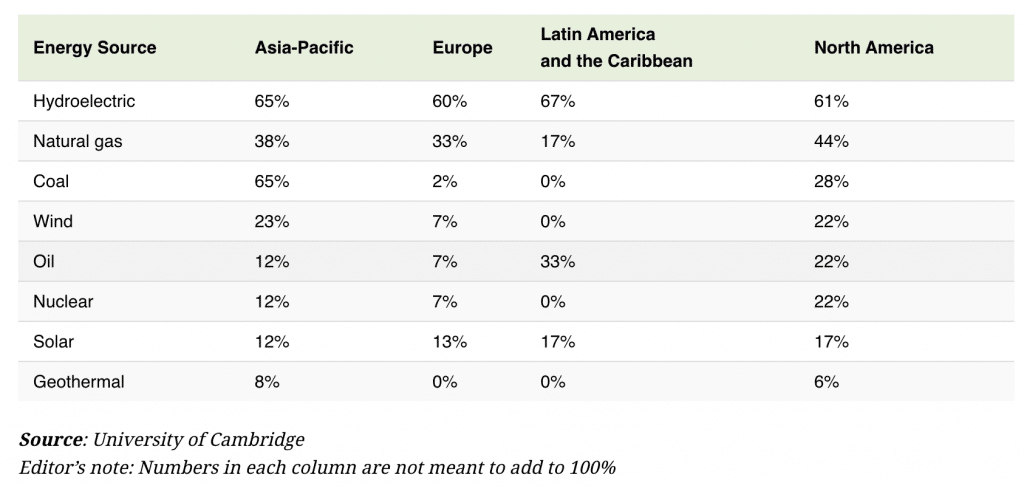
Based on data from Cambridge University, here are the energy sources for bitcoin mining. Hydroelectric power is the largest energy source, and natural gas ranks second. Although in Asia Pacific coal power is still utilized for bitcoin mining, in other areas, the proportion is very small.
It’s difficult to calculate Bitcoin carbon emissions
To calculate carbon emissions first we must know the energy mix of the industry how much uses non-renewable energy is compared to non-renewable energy. The carbon emissions from the Bitcoin industry that uses hydropower are much less than those using coal energy. Based on data from Coinshare 74.1% of Bitcoin miners use renewable and environmentally friendly energy.
The carbon footprint is calculated based on how much greenhouse gas emissions (CO2 and Methane) are emitted by the actions we take. According to research conducted by Joule, Bitcoin is claimed to produce 22 metric tons of CO2 annually. Joule’s research uses carbon emission calculations based on the assumption of energy usage on the location of large miners. But Joule doesn’t take into account that large miners usually operate through a method known as mining pools–the miners will combine the capabilities of their machines to have a greater chance of earning Bitcoins. The members of mining pools are scattered all over the world. Not to mention that most miners usually like to move from one place to another, making it difficult to track their locations. This causes the calculation of carbon emissions from cryptocurrencies to be very difficult.
Can we justify Bitcoin’s energy consumption?
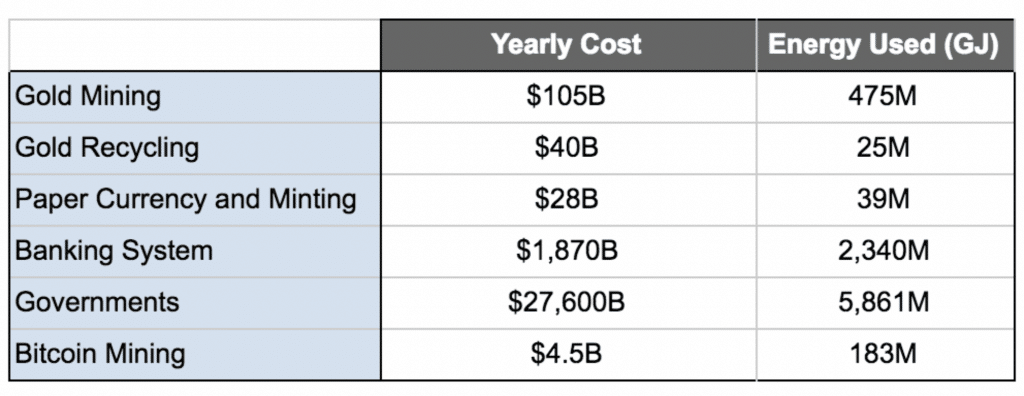
Bitcoin indeed consumes energy, but Bitcoin energy consumption is much less compared to other energy consumption such as gold or banking industry.
Bitcoin mining incentivized the growth of renewable, widely available and environmentally friendly energy. Bitcoin mining is similar to aluminum mining. To produce aluminum, bauxite must be converted into aluminum and this process is very labor-intensive. A country like Iceland produces more electricity per capita than any other country in the world. Almost all of its energy comes from glacier rivers or geothermal. About four-fifths of Iceland’s electricity is currently used to smelt aluminum. With a lot of energy required to smelt aluminum, this remaining energy is exported to other regions and industries.
In Iceland, for example, leftover aluminum smelters are used to run data center industry. The same thing we can expect from Bitcoin mining. Bitcoin uses and consumes a lot of energy but just like aluminum, Bitcoin can export the energy it produces for other industries.
Bitcoin mining is run through the concept of a free market, meaning that anyone can participate or leave as they will. In contrast to gold mining where permanent losses are resulting from the excavation of soil and the process of turning gold ore into gold bars. The land reclamation process is also very costly and closing a gold mine also requires a lot of planning and cost. Unlike bitcoin mining, which can be moved easily. Some miners operate by using containers so that they can move from one place to another with cheap energy.
Conclusion
Bitcoin mining uses a lot of energy but much less energy when compared to running the banking or gold industries. Bitcoin mining has a positive impact on the environment as it encourages the shift to renewable energy. While the development of renewable energy is usually very dependent on the government, Bitcoin provides incentives through the free market to develop renewable and environmentally friendly energy.
