Chainlink is a platform that uses decentralized oracle services to securely connect real-world data to smart contracts in the blockchain industry. By using Chainlink, you can ensure the integrity and reliability of the data being used in your smart contracts. To learn more about Chainlink and its features, you can read the following article.
Article Summary
- 🌐 Chainlink is a platform that provides oracles services that enable smart contracts to communicate securely with real-world data and services outside the blockchain network.
- 🌟 The primary purpose of Chainlink is to overcome the inability of smart contracts to interact with real-world data outside the blockchain, such as weather data, sports results, stock prices, and even data from other blockchains.
- 🤝Some industries that use data from Chainlink oracles include the DeFi industry, NFT, gaming, insurance, enterprise systems, supply chain, government, and others.
What is Chainlink (LINK)?
Chainlink is not a blockchain but a platform that provides oracle services for smart contracts on the blockchain. Oracles are distributed data provider networks that provide real-world data to blockchain networks. In short, Chainlink is a middleware that can connect blockchain to real-world (off-chain) data, such as weather, sports scores, stock prices, and even data from other blockchains, like crypto asset prices.
The primary purpose of Chainlink is to overcome the inability of smart contracts to access off-chain data. In addition, the available oracles are still centralized and have security concerns (a single point of failure). Therefore, it is necessary to provide data from decentralized trusted parties. Thus, Chainlink, an extensive decentralized oracles network, supports developers build more robust and diverse blockchain applications using available data.
Chainlink was founded in 2017 by Sergey Nazarov and Steve Ellis. Previously, they founded SmartContract, a San Francisco-based blockchain company which is now developing the Chainlink ecosystem. In the same year, Chainlink managed to raise funds through an ICO or initial coin offering of 32 million US dollars in ETH and they used the collected money to develop the Chainlink ecosystem. In 2019 Chainlink officially launched its main network on the Ethereum blockchain.
Here’s a Chainlink introduction video.
Chainlink is not affiliated with Oracle Corporation, a computer technology company that specializes in providing data. Chainlink refers to itself as a decentralized oracle network (DON) with oracle nodes as intermediary data providers.
Read also: Understanding Nodes and Their Functions in Blockchain.
How Does Chainlink Work?
In connecting smart contracts on the blockchain to real-world data, Chainlink utilizes a decentralized oracle network and the Application Programming Interface (API) of the data to be retrieved. The architecture has two primary components: an on-chain and an off-chain infrastructure.
When the smart contract creator request data, smart contracts on the blockchain allow a component to integrate them with non-blockchain applications. They also help in the selection and creation of oracles. Once done, the off-chain data is executed outside the blockchain, then reported back to the blockchain infrastructure. Chainlink Core equips Chainlink’s off-chain architecture.
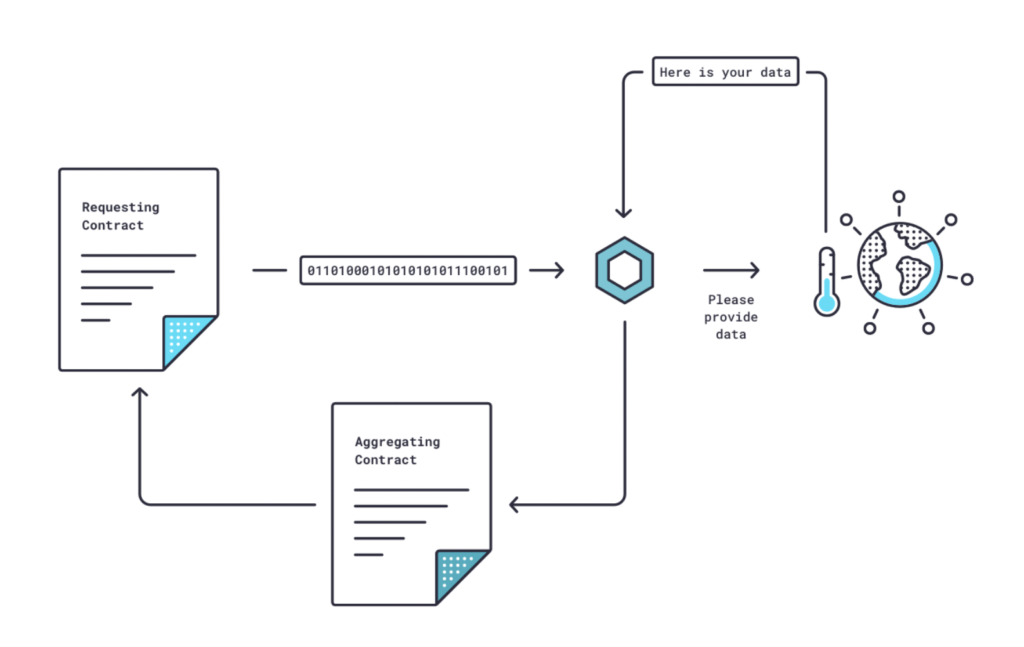
On-Chain Operation
Chainlink’s on-chain architecture builds on the Ethereum blockchain and contains smart contract oracles. These oracles receive and process user requests for off-chain data sent to the network using smart contracts. The following contracts are involved in processing data on the protocol.
- Requesting contract: The process starts on the blockchain when the smart contract creator requests off-chain information data.
- Service Level Agreement (SLA) contract: To obtain the off-chain data, the Chainlink protocol registers this request as an “event” and generates a smart contract called SLA contract on the blockchain.
The SLA contract then generates three sub-contracts, as follows:
- Reputation contract: functions to select an oracle by assessing the authenticity of the oracle based on how accurate the oracle provider’s performance results in presenting data.
- Order-matching contract: functions to determine the number of nodes to be used. It sends a requesting contract to the oracle nodes and then takes bids from the oracle nodes. Then it chooses the appropriate number and type of nodes to fulfill the request. The larger the number of nodes, the more secure it will be.
- Aggregating contract: functions to retrieve data from the selected oracle nodes and validate the data accuracy. For example, to retrieve data, there are ten oracle nodes available. Seven nodes deliver the same data, while three nodes deliver different data. The aggregating contract will recognize the three nodes’ wrongs and eliminate them.
The on-chain operation is divided into three parts: oracle node selection, data collection, and result aggregation. The choice of oracle nodes is organized by the platform/user or smart contract creator to determine the data needed through the requesting contract. After that, the Chainlink software will issue and use the SLA contract to select the appropriate oracle nodes to provide the data.
The selected oracle nodes then interact with external data sources to obtain off-chain data. And then, the oracle nodes processes the data. Finally, all the data is aggregated to the aggregation contract for selection and validation and submitted to the user/platform.
Off-chain Operation
The off-chain architecture is a great feature of Chainlink, containing oracle nodes outside the blockchain but still connected to the Ethereum network. These nodes are responsible for collecting and bringing off-chain data into the blockchain.
Chainlink utilizes Chainlink Core software technology to connect data requests from requesting contracts (on-chain) to real-world data (off-chain) and then send the off-chain data back to the blockchain.
Chainlink Core translates the programming language of the on-chain data request to the off-chain programming language so that the real world can understand and vice versa.
The translated language (off-chain) is then forwarded to an API that collects data from that source. Once the data is collected, it is translated back into the on-chain language through Chainlink Core and sent back to the aggregating contract. The data is then reported to the user or creator of the smart contract.
LINK Token
LINK is Chainlink’s native token with ERC20 standard. This token has two functions in the Chainlink ecosystem:
- Payment token: LINK is used to pay incentives to operator oracle nodes that have provided data such as off-chain data retrieval, data formatting into the blockchain, and off-chain computation.
- Work token: LINK is used as collateral for operator nodes to provide oracle services by staking LINK tokens.
The amount of LINK tokens staked as collateral can affect the selection rate of operator oracle nodes as the selected data provider to fulfill data requests. Once selected, they are responsible for entering the data into the blockchain. They will also receive rewards in the form of LINK tokens. The amount of rewards depends on the prevailing market conditions and the market demand for data. However, the system will reduce the operator nodes’ stake if they act dishonestly or make mistakes.
The LINK token staking system is a new feature of Chainlink's total update called Chainlink Economics 2.0. The LINK staking system is currently in version 0.1 with very limited features. Chainlink has long-term plans for this.
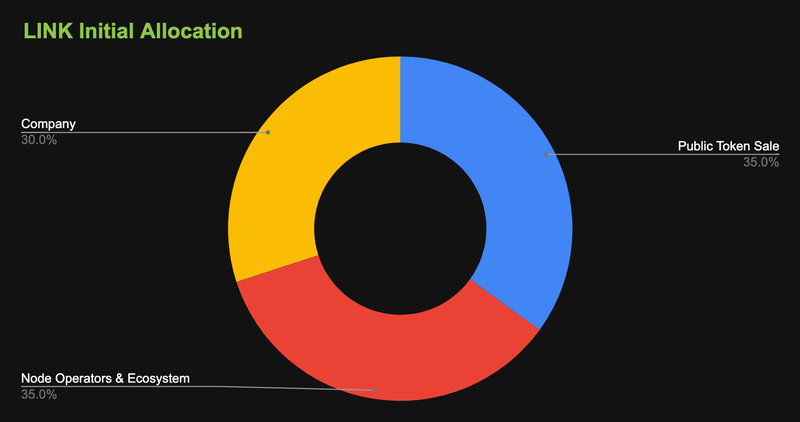
At the time of the LINK token launch in 2017, Chainlink had a maximum supply of 1 billion LINK tokens. From the diagram above, you can see that it allocates 35% of its tokens to public sales, 35% to incentivize operator nodes and ecosystem development, and 30% to the company.
Use Cases of Chainlink
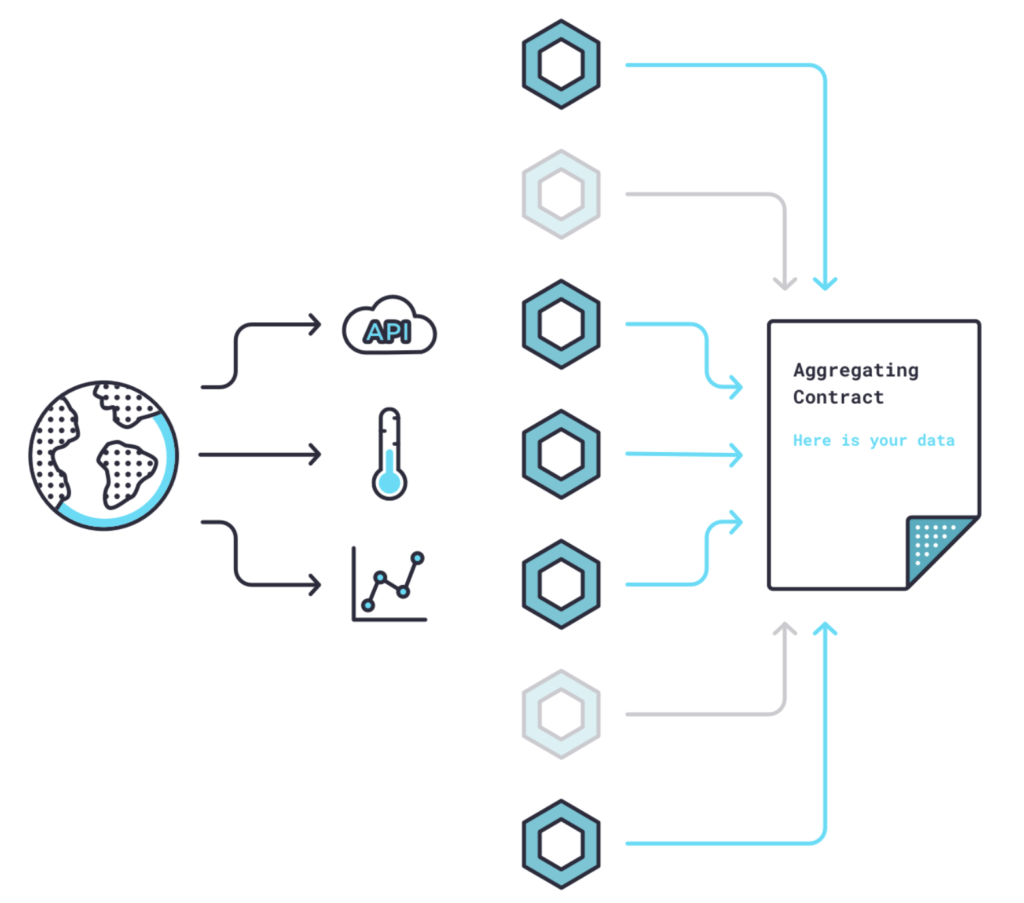
Chainlink is not one oracle network but an ecosystem of many decentralized oracle networks running simultaneously. With this decentralized network, developers can connect smart contracts to off-chain data with various APIs to fulfill the data needed.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Many DeFi applications integrate their system to Chainlink. They use this platform to access data related to crypto asset prices, access interest rates, verify collateralization, and more.
Chainlink's price feeds are the fastest access to connect DApps smart contracts to the real-world market prices of assets with a high level of security.
In addition, the DeFi applications use Chainlink to protect funds in the liquidity pool from hacker attacks. One of the reasons the system can be breached is the use of centralized price feeds. The Chainlink system is different, it leverages a decentralized oracle network. So, it can increase the security of the DeFi system.
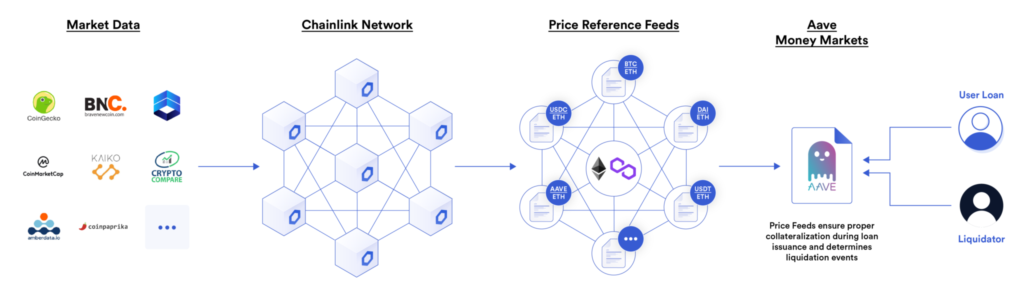
Aave, Compound, and Liquity are examples of DeFi that use Chainlink’s price feeds to retrieve crypto asset data from various blockchains. With real-time price data, these lending and borrowing applications can calculate the value of their users’ collateral and debt to determine when liquidations should be initiated. It ensures the availability of collateral to protect users’ deposits.
Game
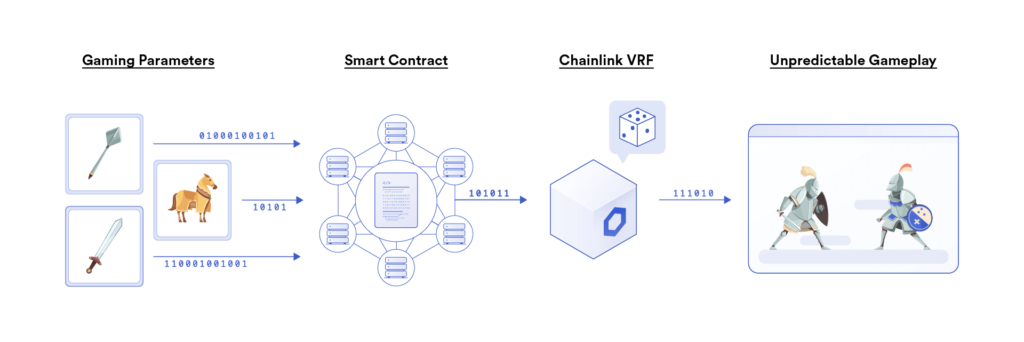
Randomness is an essential component of blockchain-based gaming applications. It can make things unexpected and be used to create random gameplay and rare NFTs. In random gameplay, a game becomes more interesting when surprising things happen. Also, the player becomes more curious about what he will face in the next game level. However, creating safe and reliable randomness is difficult, so Chainlink developed the Chainlink Verifiable Randomness Function (VRF). Chainlink VRF provides smart contracts by generating on-chain cryptographic proof to prove that randomness has not been manipulated or altered.
Cited from Hybrid, "Randomness has the capability to provide variety, diversity, quantity, and essentially makes the game less boring. Minecraft worlds, for instance, are always unique and infinite; no two world's seeds are the same. Draws in card games also ensure that matches play out differently."
Game developers can utilize Chainlink VRF to ensure unpredictable game events that create challenging and exciting scenarios for players. They can create gameplay scenarios that include map generation, critical hit probability (a randomized aspect of the game), matchmaking (playing multiplayer game with randomized people), card draw order, and others.
Sport
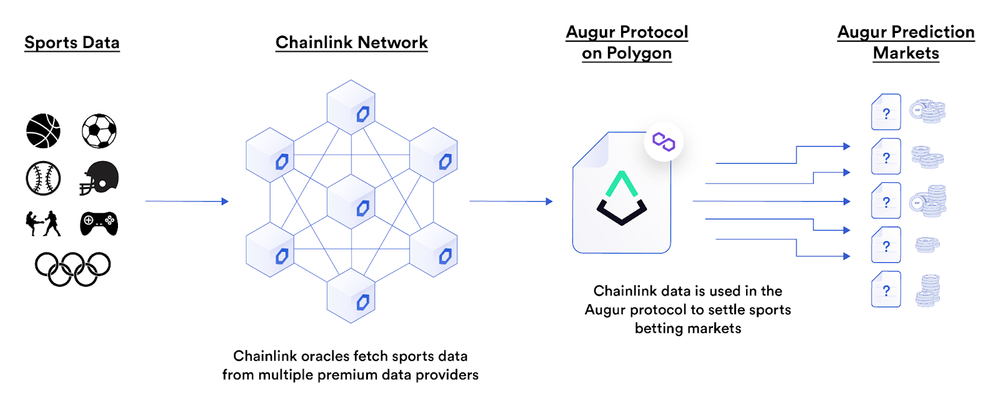
Chainlink’s smart contracts also contain sports data such as the winning team, final score, man of the match, top score, etc. With a decentralized oracle network, Chainlink is able to verify sports results by collecting data from web APIs. Sports betting markets can leverage this data.
One of the blockchain-based betting markets that use Chainlink’s oracles is Augur. Augur users can speculate on various sports-related subjects such as basketball (NBA), baseball (MLB), martial arts, and Olympic. Match results can be settled quickly after the market closes using a decentralized network of oracles that provide real-world (off-chain) data.
Weather
Chainlink’s decentralized oracle network can be beneficial to the weather industry, one of which is AccuWeather. AccuWeather is a weather forecasting company based in the United States. The company can supply and sell high-quality weather data directly to smart contract applications on various blockchains. The accurate data from its meteorologist team include temperature, wind speed, rainfall, tropical storm category, and other data.
The smart contracts can also cryptographically sign the data to let users know that the data came directly from the AccuWeather API. AccuWeather offers several APIs based on location, forecasts, current conditions, indices, weather alerts, satellite images, and many others.
Is Chainlink a Good Investment?
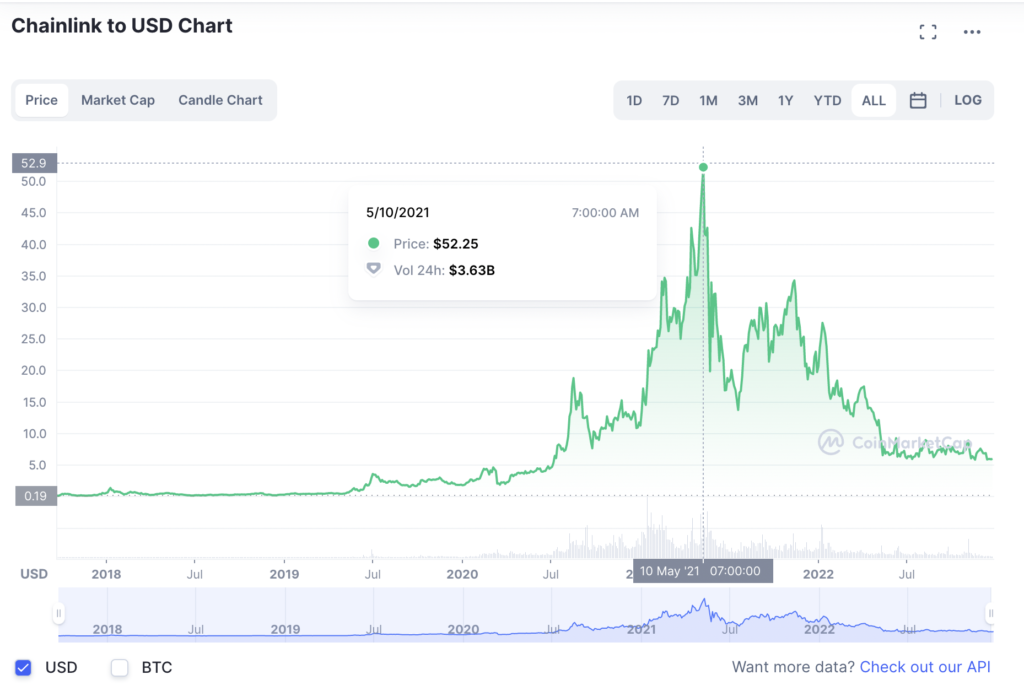
The price of LINK at the time of writing (December 27, 2022) is $6.01, with a trading volume of 136.128.450 US dollars in 24 hours. LINK reached an all-time high on May 10, 2021, by hitting 52.25 US dollars and a trading volume of 3.63 billion US dollars in 24 hours.
According to Coinmarketcap, Chainlink ranks 21st with a market cap of over 3 billion US dollars. LINK’s high market cap closely correlates with Chainlink’s extensive market share in the oracle industry. Major crypto projects that utilize this platform include Aave, Uniswap, Synthetix, Curve, Nifty Royale, Coti, Cardano, NBA, dYdX, and others.
Regarding Chainlink’s performance as a decentralized oracle network, Chainlink Labs reported that during the third quarter of 2022, the ecosystem expanded to more than 1.500 projects across 15 blockchains. Chainlink has also provided 4.2 billion data and 8 million randomness requests.
Then, the presence of former Google CEO Eric Schmidt is a good factor for Chainlink to have his insight and experience in building a global software platform. He joined Chainlink in 2021 and served as a strategic advisor in charge of assessing Chainlink’s performance and researching Chainlink’s operational systems.
However, Chainlink allegedly experienced problems with the sale of LINK tokens by its developers in August 2020, causing a 16% drop. Reports from Trustnodes showed on-chain activity of multiple wallets addresses moving 500.000 LINKs every week, valued at 40 million US dollars at the time.
Conclusion
Chainlink has many use cases that can support the development of an application and guarantee security equivalent to the blockchain. Some industries that utilize this platform include the DeFi industry, NFT, gaming, insurance, enterprise systems, supply chain, government, and others.
Then, you can see Chainlink’s prospects from the Chainlink 2.0 roadmap, which includes increasing security and reducing the operational costs of its oracle services. In addition, Chainlink is developing a staking feature for LINK token holders and node operators to earn rewards while securing the oracle network. From the above fundamental analysis, it is possibly going to be one of the most important projects.
However, like other crypto assets, Chainlink (LINK) tokens also have high price volatility. Therefore, before investing in LINK tokens, you should consider the benefits and risks.
Read also: 7 Things to Know Before Investing in Crypto Assets.
How to Buy LINK on Pintu
You can start investing in LINK by buying it in the Pintu app. Here’s how to buy crypto on the Pintu application:
- Create a Pintu account and follow the process of verifying your identity to start trading.
- On the homepage, click the deposit button and top up the Pintu balance using your preferred payment method.
- Go to the market page and look for LINK.
- Click buy and fill in the amount you want.
- Now you have LINK as an asset!
In addition, the Pintu application is compatible with various popular digital wallets such as Metamask to facilitate your transactions. Go and download the Pintu cryptocurrency app on Play Store and App Store! Pintu is regulated and supervised by CoFTRA and Kominfo.
You can also learn more crypto through the various Door Academy articles which are updated every week! All Pintu Academy articles are for educational purposes, not financial advice.
References
- Steve Ellis, Ari Juels, and Sergey Nazarov, Chainlink Whitepaper, Chainlink, accessed 26 Desember 2022,
- Chainlink Team, What Is Chainlink? A Beginner’s Guide, Chainlink Blog, accessed 26 Desember 2022
- Blockchain Council Team, What Is Chainlink? The Most Comprehensive Guide Ever, Blockchain Council, accessed 26 Desember 2022.
- Steve Walters, Chainlink Review: Smart Contract Solutions for any Blockchain, Coinbureau, accessed 26 Desember 2022.
- Crispus Nyaga, Is Chainlink a Good Investment? 5 Reasons We Think It Is, Coin Journal, accessed 26 Desember 2022.
- Coin Telegraph Team, What is Chainlink: A beginner’s guide to the cross-chain interoperability protocol, Coin Telegraph, accessed 26 Desember 2022.
- Blockchain 101 Team, Chainlink for Beginners, Blockchain 101, accessed 29 Desember 2022.
