One of the words that are starting to turn into jargon in the crypto world is interoperability. Interoperability is the ability of a blockchain or crypto asset to communicate and interact with other blockchain networks. This capability is important for crypto assets to exist in an interconnected network. Therefore, several crypto projects are building interoperability capabilities into their foundations. The two crypto projects that do this are the Cosmos and Polkadot networks which share the same principles but different implementations. Then, what is Polka dot (DOT)? How does it apply the principle of interoperability? Should you invest in DOT tokens? This article will explain the Polkadot network.
Article Summary
- 🌐 Polkadot (DOT) is a blockchain network created to connect a set of other blockchains in one unified ecosystem. Polkadot is designed as a multi-chain decentralized network in which each small network within it exists independently.
- ⚛️ Polkadot’s main architecture consists of a relay chain that acts as the core of the network and a parallel system of blockchains called parachains. Polkadot’s relay chain network acts as a security provider for the entire ecosystem by setting up validators and processing all transactions. Each parachains is flexible and can be tailor made according to its owner.
- 💻 Parachain is an important part of the Polkadot ecosystem because each parachain has a smart-contract capability and can create its own application or blockchain. Each parachain is auctioned with a 2-year extendable contract. The project that will get a parachain slot is chosen by DOT owner in a voting system.
- 🤑 Messari’s research shows that Polkadot is one of the most widely owned crypto assets by institutional investors. This shows that investors with large funds believe in the long-term potential of the Polkadot ecosystem. However, this does not guarantee that DOT price movements in the short to medium term can provide financial benefits.
What is Polkadot Network?
Polkadot (DOT) is a blockchain network created to connect a set of other blockchains in one unified ecosystem. Polkadot is a multi-chain decentralized network in which each small network within it exists independently. The native crypto asset of the Polkadot network is DOT.
The developers can create their own applications and blockchain on top of the Polkadot network using parachain. Think of the relationship between the Polkadot network and parachain as a parent company having multiple subsidiaries in a decentralized ecosystem. These small parachain networks are useful for various purposes, including creating a new blockchain.
According to CoinMarketCap, the Polkadot network is the 11th largest crypto asset in the world with a market cap value of $22 billion dollars. Meanwhile, the price of 1 DOT is $22 dollars (4 April 2022) without a maximum supply with 987 million DOT already circulating in the market.
Who created Polkadot?
The Polkadot network comes from the mind of Gavin Wood, the co-founder of Ethereum and the main developer who created Solidity (Ethereum programming application). In 2016, Gavin Wood left Ethereum and wrote a whitepaper on the Polkadot network. Wood also founded the company Parity Technologies which is responsible for manufacturing Polkadot technology infrastructure and Substrate, a programming application-specific to Polkadot.
The Polkadot network was successfully launched in August 2020 with all its features up and running and the parachains auction can start. Polkadot has a dedicated page explaining the Polkadot launch process and the current phase status. Currently, Polkadot is in the process of auctioning parachain to developers. Apart from that, the page also describes two important upcoming updates, Cross-Consensus Message Format (XCM), and parathreads.
Read: Whitepaper of Polkadot Network
How does Polkadot work?
The Polkadot network use Substrate, a programming application made especially for Polkadot and all its features. Substrate for Polkadot is similar to the Cosmos SDK for the Cosmos ecosystem, ensuring that all applications and blockchain in the Polkadot ecosystem can interact and connect with each other via the same application programming.
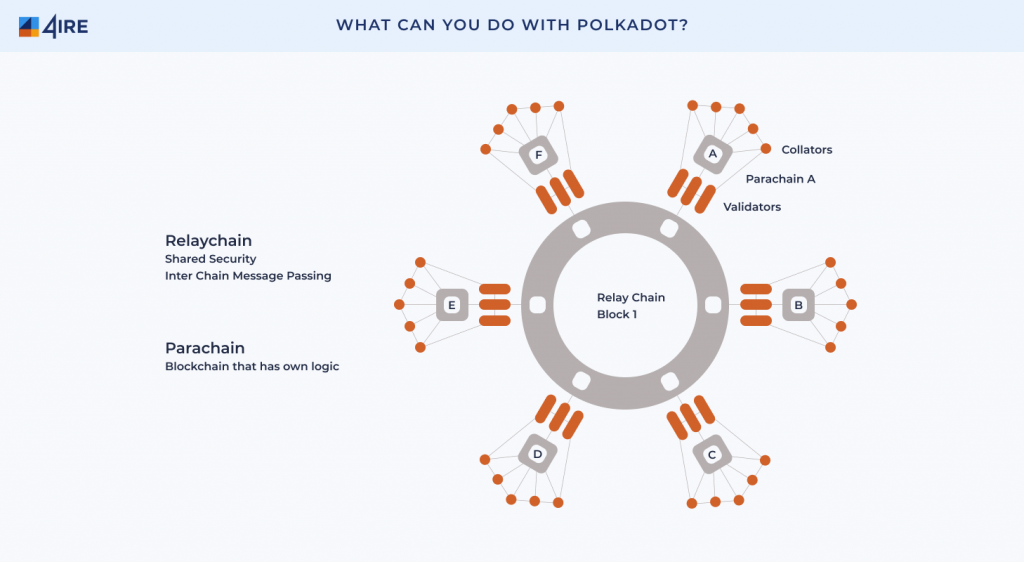
Polkadot’s main architecture consists of a relay chain that acts as the core of the network and parallel blockchains called parachains. The Polkadot relay chain network acts as a security provider for the entire ecosystem by setting up validators and processing all transactions. So, each blockchain in the Polkadot network does not need its own validator. The relay chain also manages all inter-chain communication and ensures all transactions are successful. Basically, the relay chain has limited functionality so it can focus on managing overall network security.
Consensus Mechanism
Polkadot is a proof-of-stake (PoS) network that utilizes a staking scheme to validate transactions. It uses a variation of the PoS system called a Nominated Proof-of-stake (NPoS). In NPoS, there are several roles:
- Validator: The validator secures the Relay Chain by staking tokens (DOT). If selected as active validators, they validate transactions by taking information from collators on parachains and generating blocks on Relay Chain.
- Nominators: Nominator contributes to network security by staking DOT to validators so they can be selected by the network.
- Collator: Collator collects parachain transactions and provides information for validators in Relay Chain. They can also send and receive messages from other parachains using cross-chain message passing (XCMP).
- Fishermen: Fishermen monitor the network and report bad behavior to validators.
Also read: What is proof-of-stake (PoS) and how does it work?
Parachain dan Parathreads

Parachain is an important part of the Polkadot ecosystem because each parachain has smart-contract capabilities. The name parachain itself comes from two words, namely parallel and chain. Each parachain works independently and simultaneously, just like the Cosmos ecosystem. However, all parachains rely on validators and security from the core relay chain network.
This allows application and blockchain developers to focus on their network without having to worry about developing their own validator ecosystem. Each parachain also has XCM or Cross-Consensus Message Format capability which enables inter-chain communication similar to the IBC protocol of the Cosmos ecosystem.
Also read: What is the Cosmos ecosystem?
The Polkadot ecosystem currently only supports 100 parachains operating simultaneously. This makes each parachain slot extremely valuable and Polkadot does something unique. Each parachain is auctioned with an extendable 2-year contract. DOT holders have the power to choose
💡 There is one unique type of parachain called common good parachains. Common good parachains are basically parachain slots reserved for protocols that benefit the Polkadot ecosystem as a whole. The first common good parachains is statemint that allows the creation of various assets such as NFT.
Meanwhile, parathreads is a service offered by Polkadot to blockchains who want the security provided by parachains without having to participate in the auction process. Projects wishing to take advantage of parathreads pay a transaction fee to the Polkadot network based on processed blocks. Therefore, parathreads can be a temporary economical option for small developers.
So, every blockchain that leverages Polkadot’s Substrate app has 3 options:
- Independent blockchain with connecting bridge into the Polkadot ecosystem
- Participating in parachain auction
- Choose to use parathread
What makes Polkadot unique?
- 🌐 Ecosystem: Polkadot allows for the creation of an ecosystem of interconnected and interacting blockchains. This ecosystem creates unrestricted interoperability between all crypto assets on the Polkadot network.
- 🛡️ Shared security: The Polkadot network utilizes a shared security system where the core relay chain network is responsible for the security of the entire ecosystem. This system allows each blockchain to focus on its own project without worrying about security.
- 🏦 Unique governance system: In the Polkadot ecosystem, whoever owns the DOT has great power to determine various aspects of the network such as voting in parachain auctions and selecting parachain common goods. DOT is a special commodity of the Polkadot ecosystem
- 🏎️ Transaction speed and fees: Polkadot offers the same speed and transaction fees as other PoS networks (Cardano, Fantom, Solana, etc.)
What can you do with Polkadot (DOT)?
Using blockchain in the Polkadot ecosystem
- Moonbeam
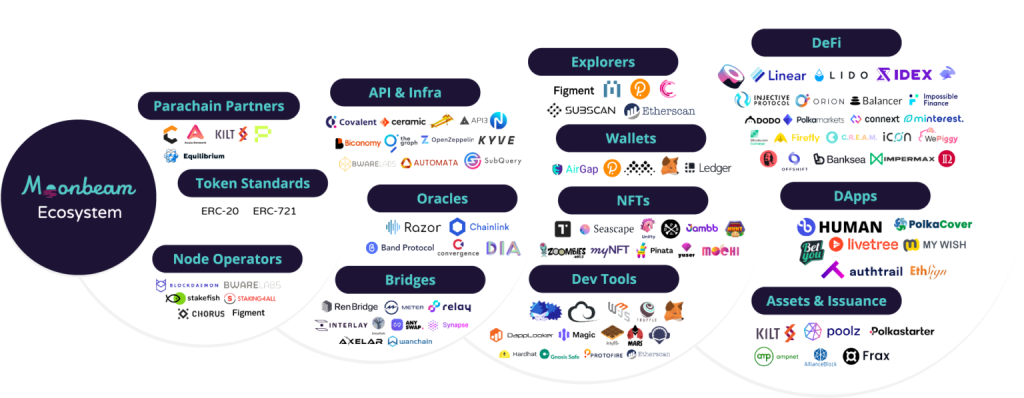
Moonbeam is a blockchain with smart contract capabilities for building a decentralized ecosystem on top of the Polkadot network. The native token of Moonbeam is Glimmer (GLMR). Moonbeam also has compatibility with the Ethereum network because it has EVM (Ethereum virtual machine) capabilities. So, Moonbeam is simultaneously connected to the Polkadot ecosystem as well as Ethereum.
Developers who don’t have the financial strength to create their own parachain can leverage Moonbeam to build apps on its ecosystem. In addition, Moonbeam also has a special blockchain for testing new features, products, or applications called Moonriver. Moonriver is useful for developers who want to test their application before launching it on Moonbeam.
- Kusama
Kusama is a blockchain with an almost identical architecture, codes, and basic capabilities as the Polkadot network, making it a blockchain cousin or canary network (a term that means a testing ground). Kusama’s main goal is to serve as a testing platform for various features and updates that will later be implemented on Polkadot.
More than that, Kusama also serves as a testbed for various developers and blockchains because it is cheaper than the Polkadot network. Kusama has the same features as Polkadot at a cheaper price more suitable for small and new projects. So, many apps and blockchains started on the Kusama network before moving to Polkadot.
Although it utilizes a relay chain with the same architecture as Polkadot, Kusama’s security is one level below Polkadot. The flip side of this is that all the security updates that Polkadot will have must be applied first on the Kusama network.
- Acala Network

Acala Network is a Decentralized Finance (DeFi) platform that wants to create a stablecoin (aUSD) ecosystem. The aUSD stablecoin system uses a model similar to DAI by leveraging the collateral of various assets on the Polkadot network to maintain its value to the dollar. The Acala Ecosystem also has specially modified EVM compatibility so that Ethereum DApps can directly add Acala to their application network.
The Acala Network was the first parachain to successfully passed the auction at Polkadot. Today, Acala has TVL worth $744 million dollars, one of the largest in Polkadot. Currently, Acala DEX, Acala Swap, and liquid staking are already functional.
Using DApps in the Polkadot ecosystem
- Reef Finance: The Reef Finance network is a DEX application that also functions as a DeFi ecosystem. In Reef, you can do staking and become a liquidity provider.
- HydraDX: The HydraDX app is a protocol providing cross-chain liquidity that leverages all assets on Polkadot. It also utilizes a brand-new model of Omnipool where the liquidity of all existing assets is combined into Lerna tokens (LRNA). Simply put, liquidity providers will be rewarded with transaction fees every time an asset is purchased from the LRNA pool of funds. HydraDX is still in the testing phase and has not yet launched.
- Parallel Finance: Parallel Finance is a DeFi application that focuses on a money market that allows you to save, borrow, and stake. The Parallel Finance network has 3 main products, a DEX, AMM, and money market.
DOT as investment
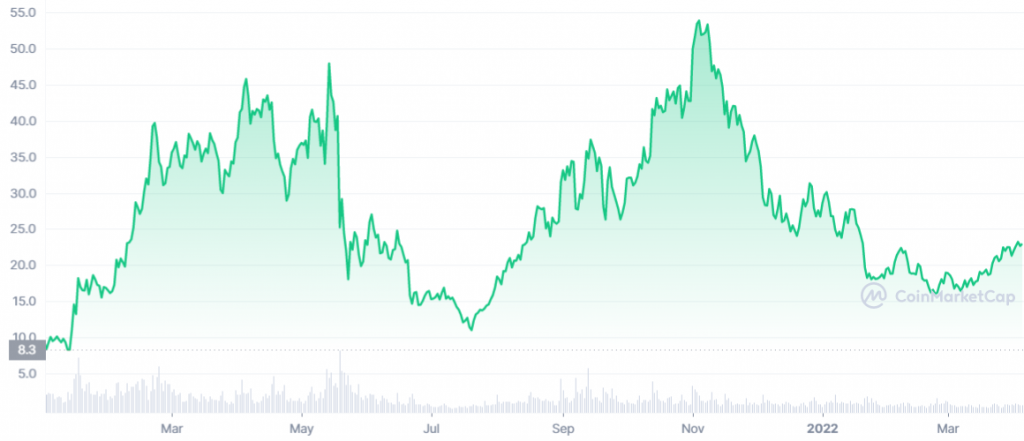
The Polkadot (DOT) price chart above shows the DOT coin has just experienced a recovery since the downtrend that occurred in November 2021. The DOT price trend from July 2021 to March 2022 is highly correlated to Bitcoin movements. One of the most basic indicators to see the strength of an altcoin is whether it managed to avoid the low price in the bear market in July 2021. In the case of the DOT, it managed to avoid the low of $12 dollars in July 2021 and hit a low of around $15 dollars in March 2022. This shows that investors are still interested in buying and holding DOT tokens instead of selling them.
Also read: What is Technical Analysis and how do you do it?
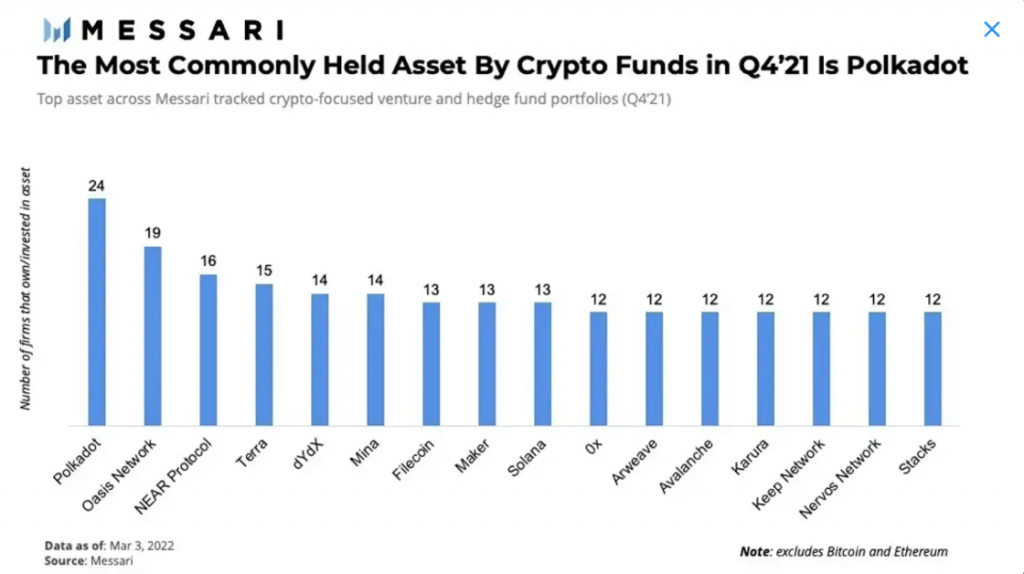
Messari’s research also shows that Polkadot is one of the most widely owned crypto assets by institutional investors. This shows that investors with large funds believe in the potential of the Polkadot ecosystem. This ownership also signifies the long-term potential of DOT. However, in the short to medium term, we cannot be sure that the Polkadot price movement will be profitable.
This led to concerns about the price movement of DOT in 2022. Since the beginning of the year, DOT has continued to experience a downward trend in price which was just broken in mid-April 2022. Meanwhile, other tokens such as LUNA, FTM, and NEAR have experienced rally several times since 2022. Although the macroeconomic conditions in Q1 2022 were not conducive, the downward trend in DOT is a point of concern that needs to be evaluated by investors.
💡 Polkadot Roadmap 2022: Polkadot network will continue to auction the remaining parachain slots and update its inter-blockchain communication system (XCM). In addition, an update for parathreads is in development.
The DOT coin needs a catalyst to create demand for DOT. The catalysts we can hope for can only come from various blockchains or applications launched from parachain auctions. Projects such as Efinity and HydraDX can generate demand for DOT tokens and drive the growth of the Polkadot ecosystem in 2022. Always do your own research (DYOR) before investing in any crypto asset.
DYOR: All information about the Polkadot network is on the study page on the Polkadot website.
Buying cryptocurrencies
You can start investing in cryptocurrencies in the Pintu app. Through Pintu, you can buy cryptocurrencies such as LUNA, BTC, etc in an all-in-one convenient application.
Pintu is also compatible with popular wallets such as Metamask to facilitate your transactions. Download the Pintu app on Play Store and App Store! Your security is guaranteed because Pintu is regulated and supervised by Bappebti and Kominfo.
You can learn more about cryptocurrencies through the various Pintu Academy articles that we update every week! All Pintu Academy articles are made for educational purposes only, not financial advice.
References
- Adriana Hamacher and Daniel Phillips, What Is Polkadot? | The Beginner’s Guide, Decrypt, accessed on 7 April 2022.
- What is Polkadot? (DOT), Kraken, accessed on 7 April 2022.
- What is Polkadot (DOT): A beginner’s guide to the decentralized Web 3.0 blockchain, Coin Telegraph, accessed on 7 April 2022.
- Ashwath Balakrishnan, What’s Up With Polkadot?, Delphi Digital, accessed on 8 April 2022.
- Polkadot and Cosmos · Polkadot Wiki, accessed on 8 April 2022.
- Parathreads · Polkadot Wiki, accessed on 11 April 2022.
- Common Good Parachains · Polkadot Wiki, accessed on 11 April 2022.
- Moonbeam Project FAQ | Frequently Asked Questions, accessed on 11 April 2022.
- Moonbeam Network, accessed on 12 April 2022.
- Nicolas Garcia, Polkadot Ecosystem Overview, Messari, accessed on 12 April 2022.
