The Bitcoin blockchain is known for its high security but it does not support many features, such as smart contracts like Ethereum. However, along with technological developments, deploying smart contracts on the Bitcoin blockchain through Stacks is possible. So, what is Stacks, how does it work, and what projects are in it? Let’s take a look at the following article.
Article Summary
- 🔗 Stacks (STX) is a layer 2 blockchain that aims to enhance Bitcoin’s capabilities by implementing smart contracts and allowing developers to build decentralized applications (dApps) on the Bitcoin blockchain.
- 💻 Stacks uses a proof of transfer (PoX) consensus mechanism. This mechanism leverages the security of the proof of work (PoW) system of the Bitcoin blockchain. STX miners use Bitcoin to compete and add new blocks to the Stacks chain. In return, they receive STX block rewards.
- ⚡ Stacks combines the advantages of the Bitcoin blockchain with the smart contract blockchain. With Stacks, the capabilities of the Bitcoin blockchain are increased, the transaction process is faster, the programming language is easy, and also the level of security is high.
What is Stacks (STX)?
Stacks is a layer 2 blockchain that connects with Bitcoin through a Proof of Transfer (PoX) consensus mechanism accross two chains (Stacks and Bitcoin). Stacks aims to enhance the Bitcoin blockchain by enabling the implementation of smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps) on the Bitcoin platform. In addition, Stacks also aims to turn BTC from a passive asset into a productive one.
Bitcoin and Stacks are two different blockchains, but they work together. Stacks works by anchoring its system on Bitcoin, so it has the security and stability of the Bitcoin network. Likewise, the smart contracts that Stacks brings to the Bitcoin blockchain do not change any of Bitcoin’s features.
Developers can create innovative features using Stacks’ open and modular nature for dApps. It also has a separate ledger to store data outside the Bitcoin blockchain called Gaia. It allows developers to build dApps just like on Ethereum or Solana.
Read also What is Bitcoin?
Creators and Origins of Stacks
In 2013, Muneeb Ali and Ryan Shea founded Blockstack, which changed its name to Stacks in 2020. They developed Blockstack technology at Princeton University’s Computer Science Department to solve problems related to today’s websites and smartphone apps.
The platform’s focuses are to replace the reliance on centralized cloud service providers and applications that require storing user information on these services for operation.
After years of research and technology development, in 2017, Blockstack launched the alpha version of the Blockstack browser and decentralized data storage system.
In 2018, under Blockstack PBC, the project expanded into the blockchain world and launched its main network, Stacks 1.0.
A year later, Hiro PBC (formerly Blockstack PBC) secured up to US$75 million in funding from an initial coin offering (ICO) and investors. Stacks investors include USV, Lux Capital, Zhen Fund, HashKey, Recruit Holding, SNZ, Digital Currency Group, Y Combinator, Foundation Capital, Winklevoss Capital, and over 4,500 other entities and individuals.
The Blockstack team worked closely with the SEC for almost a year to qualify for the STX token sale. They successfully made an SEC-qualified STX sale in July 2019.
In January 2021, the development team launched the Stacks 2.0 mainnet. This network allows developers to build smart contracts and DeFi on the Bitcoin blockchain. In addition, this upgrade also supports the settlement of transaction processes using STX on the Bitcoin blockchain.
How does Stacks work?
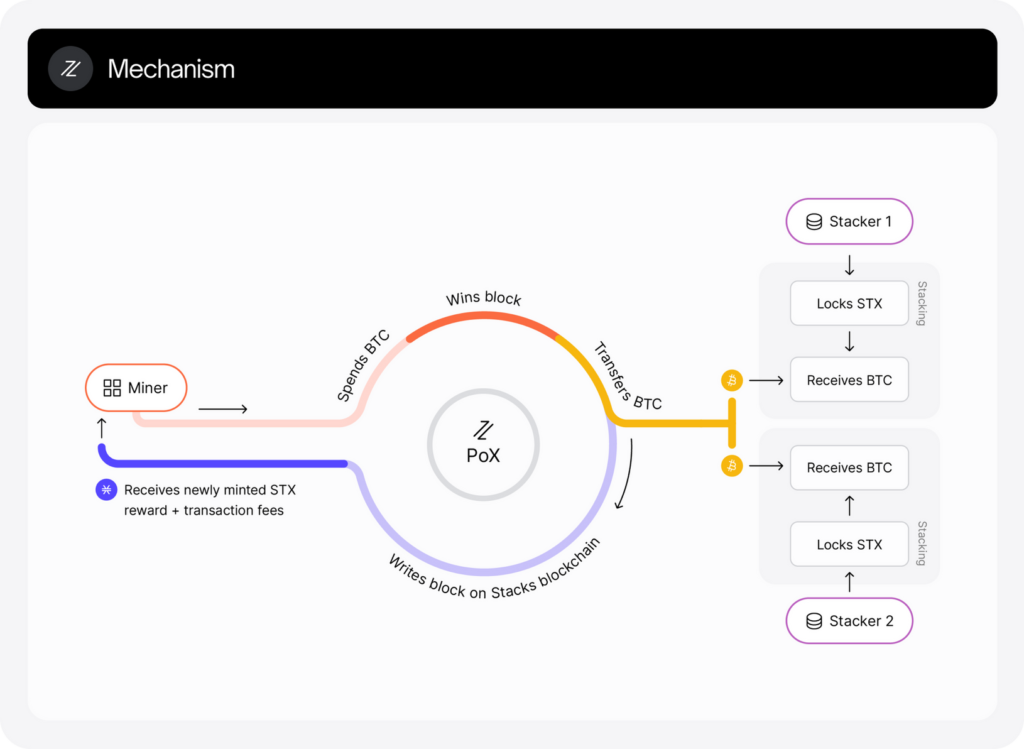
As you can see in the illustration above, Stacks operates by the interaction between two parties: the STX miner and the stacker, which is governed by a unique consensus mechanism called Proof of Transfer (PoX).
Proof of Transfer (PoX) is a modification of Proof of Burn (PoB) and is conceptually similar to Proof of Work (PoW). PoX requires miners to spend Bitcoin to participate in miner elections and create the new block on the Stacks blockchain.
PoX is connected to Bitcoin with a 1:1 block ratio, allowing all activity on the Stacks blockchain to be verified on the Bitcoin blockchain. The PoX system does not use electricity like PoW because PoX uses minted Bitcoin as a “proof of computation”. Miners then show their mining fees using Bitcoin directly. In other words, PoX requires using Bitcoin instead of electricity for the mining competition.
The unique aspect of PoX is that Bitcoin miners do not burn the BTC that has been used as a proxy for computing resources. Instead, they send it to STX token holders who have locked their tokens, a process known as “stacking”.
STX Mining
Participation in STX mining involves an open membership system that requires miners to verify STX transactions and maintain the Stacks network. The mining process requires a resource of recognized value (Bitcoin) to ensure transparency.
As explained in the ‘How does Stacks Work’ section, STX mining requires miners to spend a certain amount of Bitcoin to mine a Stacks block. Miners who successfully mine a block will get STX tokens as a reward. The probability of winning a block is proportional to the amount of Bitcoin spent per block by the miner.
To start mining STX, you must run as both a Bitcoin node and a Stacks node. Then, you also need to set up a Bitcoin wallet and a Stacks wallet. Bitcoin wallet is used to prepare your BTC balance to compete with other miners to generate Stacks of blocks. Meanwhile, the Stacks wallet holds rewards in the form of STX when miners successfully generate STX blocks.
STX Stacking
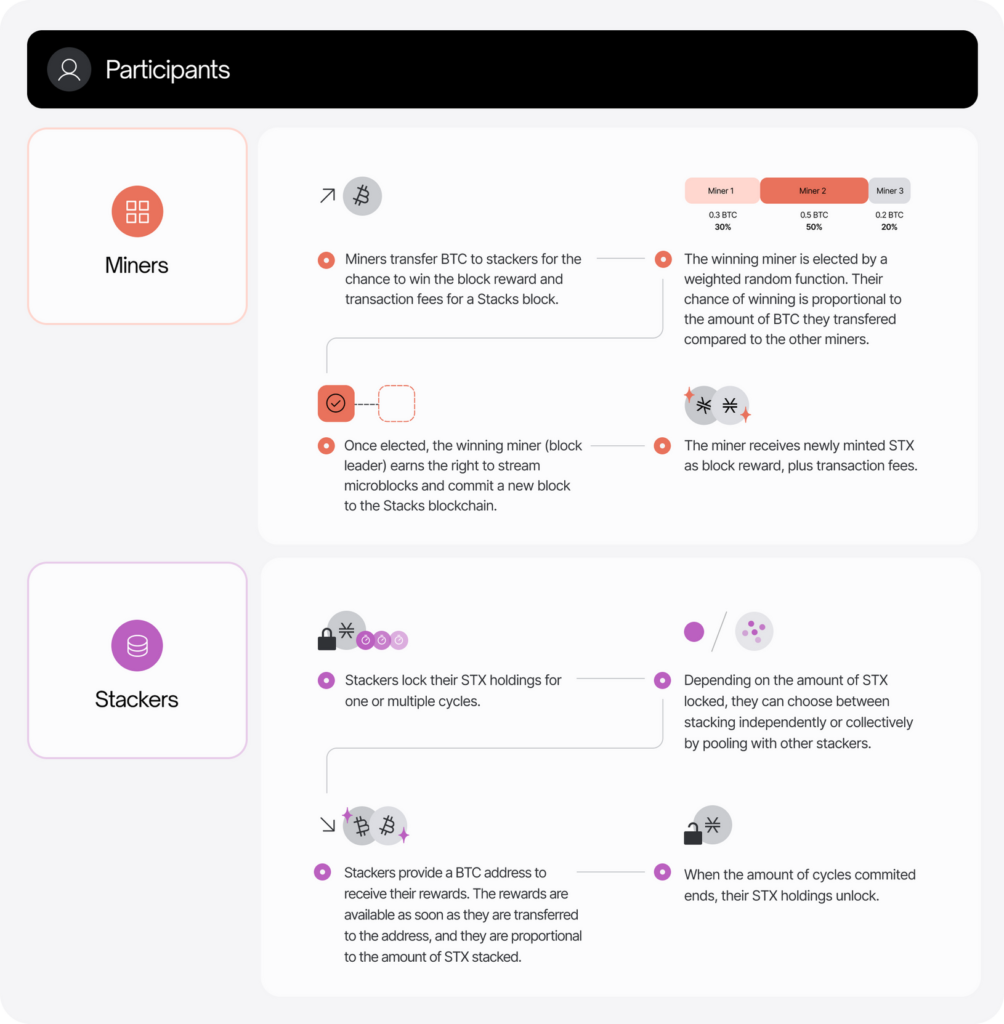
Stacking is a simplified process involving STX token holders locking up their tokens in exchange for Bitcoin rewards from STX miners. In other words, you can support the Stacks blockchain and earn BTC simply by buying and locking STX tokens.
Additionally, stackers encourage STX miners to be honest and not create conflicting forks on the network. While stacking can help improve network security, it does not fully secure PoX.
STX stacking works in two ways: private and collective stacking through stacking pools. To run as a private stacker, you need 110,000 STX. However, you can participate in a stacking pool if you have less than that amount of STX. OkCoin is currently the official provider of collective stacking.
Clarity Programming Language
Stacks uses the Clarity programming language to support the writing of smart contracts on the Bitcoin network. The primary difference between Clarity and some other programming languages is that it can be interpreted and displayed on the blockchain without any changes.
Clarity smart contract code is human-readable, making it easy to check the information. You know what the program will do from the code itself.
To build dApps on top of the Bitcoin blockchain, Stacks allows dApps developers to build dApps with a modern and secure programming language.
What Makes Stacks Different?
- Bitcoin Blockchain Security System
Stacks leverages Bitcoin’s high level of security because confirmation of Stacks transactions is settled in Bitcoin. After 100 Bitcoins or about a day of confirmation, the transaction that occurred on the Stacks layer will be secured by the entire hash power of Bitcoin.
- Proof of Transfer Consensus Mechanism
Stacks uses a proof of transfer (PoX) consensus mechanism by reusing Bitcoin’s proof of work (PoW) system. It makes Stacks highly scalable and decentralized without causing further environmental damage due to Bitcoin mining.
- Fast Transaction Processing
It utilizes microblocks to process transactions faster, despite it operating at the same block time as Bitcoin. Dividing blocks into microblocks can reduce transaction processing time from minutes to seconds.
- Bitcoin Naming Service
Stacks is designed with an integrated naming service, the Bitcoin Name Service (BNS). The concept is the same as Ethereum Name Service (ENS).
Learn more about ENS here.
Projects on Stacks
This platform is on a mission to bring smart contracts to the Bitcoin blockchain. It gives the Bitcoin blockchain more use-cases in supporting DeFi and NFTs, such as Ethereum.
Some DeFi projects on the Stacks protocol include ALEX, a decentralized application (DEX) like Uniswap. Then Arkadiko, a lending platform that is comparable to MakerDAO.
In addition, some of the other DeFi projects on the network are Stackswap, Zest Protocol, LNSwap, and Liquidium (a lending platform with NFT collateral).
From the NFTs space, Stacks is connected to Gamma, the largest NFT marketplace on the Stacks platform, which also contains several NFT Ordinals collections. In the future, it is expected that users will be able to trade NFT Ordinals on the marketplace.
Find out more about What Are Ordinals? Bitcoin NFT Innovation.
In addition, there is Trade Port, an NFT aggregator connected to several marketplaces on the Stacks, NEAR and Aptos blockchains. Then Hey Layer, an NFT marketplace that can be likened to SuperRare.
Buying Cryptocurrencies in Pintu
Currently, STX tokens cannot be traded through Pintu yet. Therefore, stay tuned to Pintu’s channels for further information regarding the listing of STX tokens. In the meantime, you can invest in various crypto assets such as BTC, ETH, SOL, and others safely and easily.
Pintu is also compatible with popular wallets such as Metamask to facilitate your transactions. Download Pintu app on Play Store and App Store! Your security is guaranteed because Pintu is regulated and supervised by Bappebti and Kominfo.
In addition to executing transactions, in the Pintu Apps, you can also learn more about crypto through various Pintu Academy articles which are updated every week! All Pintu Academy articles are made for knowledge and educational purposes, not as financial advice.
References
- Stacks Team, Stacks: A Bitcoin Layer for Smart Contracts, Stacks, diakses 1 Maret 2023.
- Stacks Team, What is Proof of Transfer? (PoX), Onstacks, 1 Maret 2023.
- Messari Team, Overview of Stacks, Messari, diakses 1 Maret 2023.
- Rahul Nambiampurath, What Is Stacks? The Defiant, diakses 1 Maret 2023.
- Katelyn Peters, Blockstack (Stacks), Investopedia, diakses 1 Maret 2023.
