Blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies play an important role in creating a secure decentralized financial ecosystem. Blockchain has become the foundation for new sectors such as decentralized financial applications (DApps). However, one of the major drawbacks of blockchain is that it cannot directly connect to external networks. This brings limitations to applications that require external data sources. Blockchain oracles are protocols that solve this problem. So, what are blockchain oracles? How do blockchain oracles work? We will discuss it in detail.
Article Summary
- 🧠 Blockchain technology has the significant drawback of not being able to interact with external data and systems, which limits its potential in various applications.
- 🔮 Oracles like Chainlink and Pyth Network retrieve and display external data into the blockchain ecosystem, enabling the execution of smart contract-based functions with precise and secure data.
- ⛓️ Chainlink is the largest blockchain oracle that provides decentralized solutions for off-chain data integration and offers a range of innovative products such as VRF and smart contract automation.
- ⚖️ Pyth Network provides a decentralized solution built using the Solana codebase, enabling faster and more cost-efficient off-chain data feed.
- 🚀 In the context of an ever-evolving crypto ecosystem, blockchain oracles are a critical element that enables applications such as DEX to function with accurate and secure real-time data.
What is Blockchain Oracles?
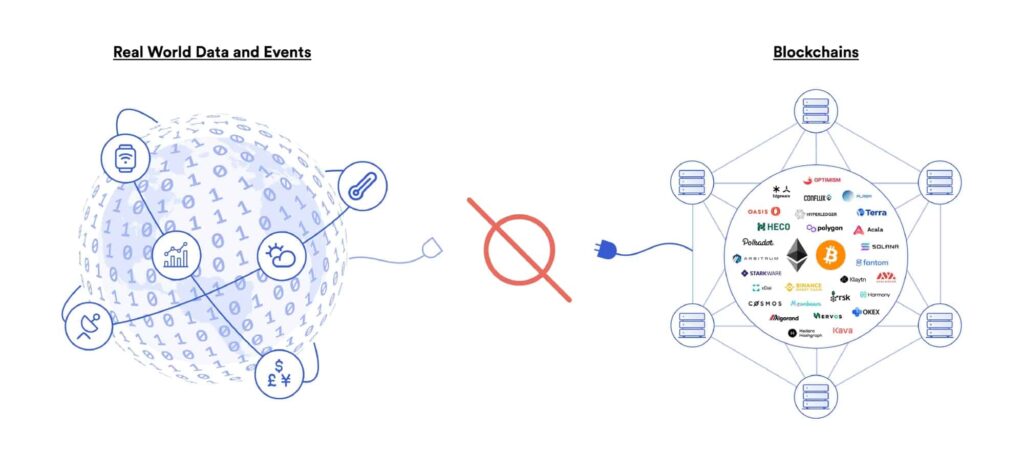
Blockchain oracles are protocols in charge of retrieving, verifying, and displaying data from the real world (off-chain) to the blockchain (on-chain). Oracles are the bridge between blockchain ecosystems and external data. So, oracles have become the lynchpin for blockchains.
Using oracles, blockchain ecosystem can utilize various non-blockchain data. Oracle protocols eliminate significant drawbacks of blockchain technology while bringing many advantages to users. This opens up new possibilities for blockchain.
The majority of blockchain and crypto applications utilize a Decentralized Oracle Network (DON). So, DON can display data from outside networks in real-time to the blockchain in a decentralized and secure manner. The two most popular DON protocols today are Chainlink and Pyth.
Why Blockchain and Crypto Assets Need Oracles?
As explained, blockchain cannot interact with systems and data outside of its ecosystem. Blockchains are intentionally isolated from external systems to make them more resistant to hacking and attacks. However, this severely limits the capability of blockchain ecosystems.
Blockchain oracles are a solution to bridge this gap in capability. Oracles ensure smart contracts applications can access a wide range of accurate and secure off-chain data. Crypto applications usually retrieve external data such as global crypto prices, stock prices, weather data, property markets, and so on.
Blockchain Oracles are also important to create synchronization for off-chain data within crypto. Conversely, oracles also come into play when a crypto application performs a set of instructions that impact external data. DeFi applications require accurate price data to execute swap, lending, and buy-sell transactions.
Blockchain oracles are already an important part of various sectors in the crypto industry. DEX applications like UniSwap or GMX utilize oracles to display accurate and synchronized prices. Furthremore, DeFi lending protocol also utilizes oracles to update prices in real-time to trigger liquidation, determine APR, etc. Without oracles, many crypto apps cannot perform their functions properly.
How Do Blockchain Oracles Work?
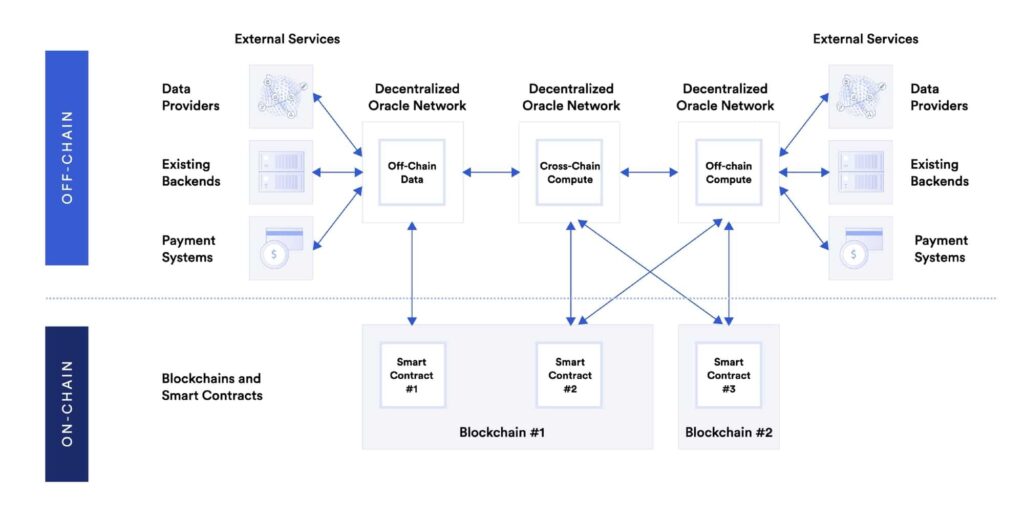
How does a blockchain ensure that the data it pulls is not manipulated, accurate, and secure? How does the blockchain stay connected to external data? These two questions are commonly referred to as The Oracle Problem.
A blockchain oracle needs to fulfill three conditions: accuracy, availability, and incentive mechanism. So, accuracy and availability ensure that off-chain data is accurate and can always be retrieved by smart contracts on the blockchain. The incentive mechanism requirement relates to the accountability of off-chain data providers. So, an oracle needs to have an incentive mechanism to reward or penalize off-chain data providers.
Blockchain oracles fulfill the three requirements by implementing various protocol designs. So, most decentralized oracles architecture incorporates off-chain nodes and on-chain contracts. Nodes take data off-chain from data providers and forward it to users (in this context applications). Meanwhile, the on-chain component of blockchain oracles is the oracles’ smart contracts that compute and verify.
Each oracle assigns different tasks to its smart contracts. These contracts forward data requests from applications to nodes and feed them back to applications. The contract is also usually in charge of data aggregation (merging) and adjusting it for the application.
In displaying data, blockchain oracles are generally divided into two models:
- Push model: This oracle model pushes data from off-chain nodes constantly to applications. The push model is the most common but comes at a significant cost (especially on chains like Ethereum) because the data must be displayed without lag.
- Pull model: Oracles with pull model displays off-chain data on-demand from the application. The application pulls the data by sending a message to the oracle contract that will be forwarded to the data provider. So, the pull model is more efficient pricing-wise.
Two Most Popular Blockchain Oracles in Crypto
1. Chainlink
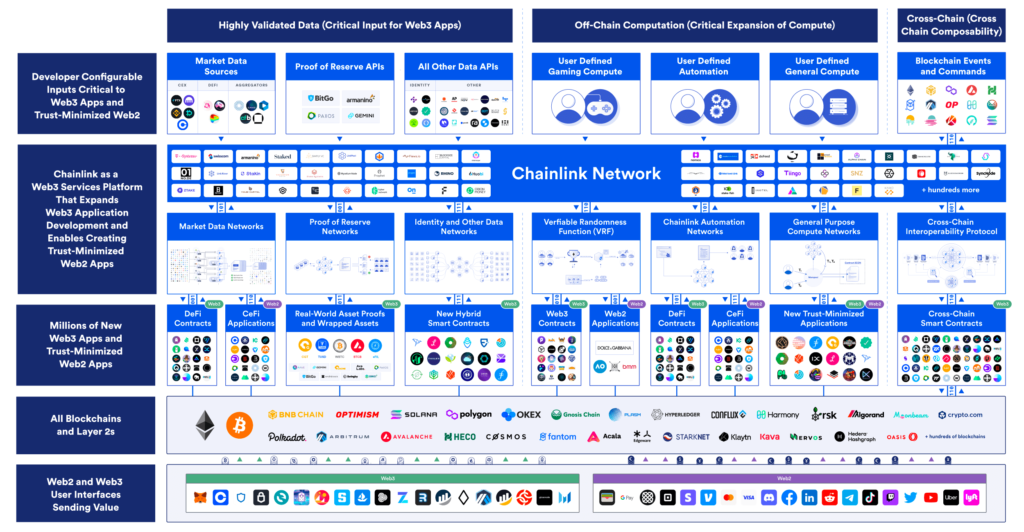
Chainlink is the largest and most popular oracle protocol in the crypto industry. The project has been around since 2014 and was the first protocol to create a Decentralized Oracle Network (DON) for blockchain. Chainlink already has more than 984 oracle networks, is connected to 17 blockchains and 1871 crypto projects, and transmits 10.3 billion data.
With so many oracles, Chainlink’s network architecture is highly decentralized. Chainlink’s oracle model is a combination of push and model. However, the push model remains the primary way Chainlink displays off-chain data.
Chainlink has a proven secure oracle network infrastructure as it has never been hacked or successfully attacked. The network's security makes it the top blockchain oracle for many crypto projects.
To reduce the high cost of the push model, Chainlink releases Off-Chain Reporting (OCR). OCR reduces Chainlink’s node operator costs by 90% by moving complex computations from on-chain to off-chain. Thus, intensive calculations such as data aggregation are performed off-chain by Chainlink’s DONs. The latest version of OCR (2.0) also connects Chainlink’s network of operator nodes, creating the foundation for the CCIP (Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol) feature.
Also read Pintu Academy’s articles on Chainlink: What is Chainlink and What is Chainlink’s CCIP Protocol?
In addition to performing the common functions of an oracle such as sending off-chain data and displaying real-time price feed, Chainlink has several other innovations. Two of Chainlink’s innovative products are VRF (Verifiable Random Function) and smart contracts automation.
Chainlink’s VRF has become an industry standard as a protocol for performing random number generator (RNG) or randomization. Many projects use VRF for randomization mechanisms that require RNG such as NFT minting, loot boxes, rewards, and random elements in blockchain-based games. VRF is used by Axie Infinity, NBA Topshot, and AAVEGotchi.
Meanwhile, automation is a Chainlink product that provides automation services for smart contract instructions that require off-chain data. Smart contract automation allows developers to automatically trigger certain functions. For example, an application will automatically print an NFT after a user has staked a certain number of tokens or trigger the liquidation of a loan whose collateral value is no longer sufficient.
Chainlink is already the industry standard for decentralized oracle network services. Currently, Chainlink is focused on building an economy that revolves around its LINK token and its DON ecosystem. In addition, Chainlink’s CCIP protocol will open up opportunities for traditional financial institutions such as banks to enter the blockchain ecosystem.
2. Pyth Network
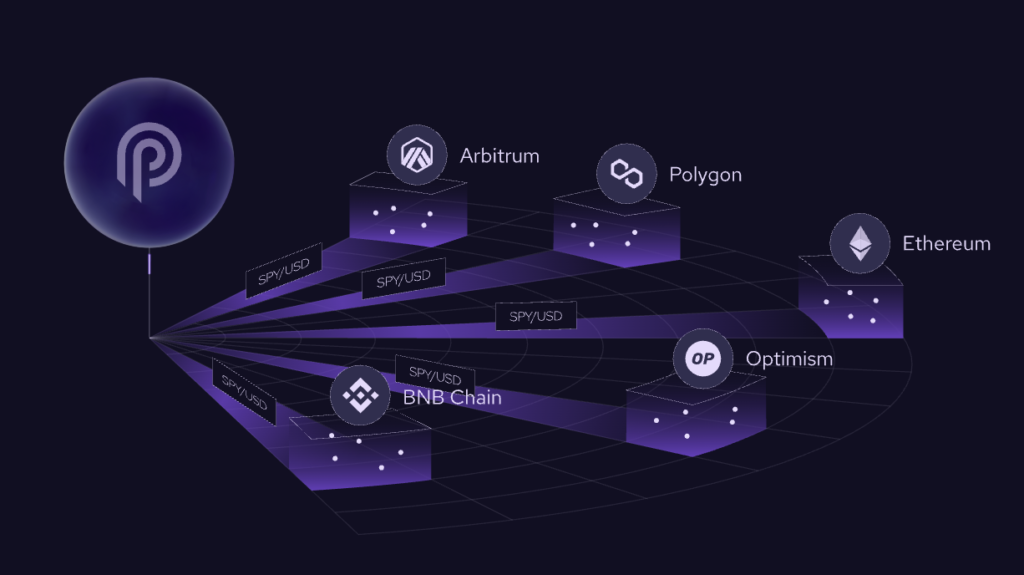
Pyth Network is a decentralized oracle built using the Solana software framework. Pyth was created in 2021 and initially only provided oracle services on Solana. However, now Pyth has its network called Pythnet and provides oracle services to 16 blockchains, is connected to more than 90 data providers, and is used by around 200 applications.
Pyth’s network infrastructure has two important components: publishers (data providers) and oracle programs (smart contracts). Publishers are in charge of sending data to program oracles in Pythnet and Solana that work in tandem. Then, the Pyth oracle program aggregates all incoming data and sends them with a certain confidence interval to the application.
Pyth, in contrast to Chainlink, does not directly send price data in exact numbers. Pyth uses confidence intervals (CI) because it considers them more realistic and in line with liquidity in many applications and blockchains. So, an ETH price at $1,500 with a 97.7% CI will display a price range between $1,485 and $1,515.
Pyth utilizes the Pythnet blockchain network to transmit data to all blockchains except Solana because Pyth has a dedicated oracle network in Solana. Furthermore, the one key differentiating Pyth from Chainlink is that Pyth does not have a network of off-chain data providers. All of Pyth’s data providers are on-chain in Pythnet and Solana. Moreover, because Pythnet is in Solana, which is cheaper and faster than Ethereum, all computations can be done directly on-chain.
Another fundamental difference between Pyth and Chainlink is that Pyth uses a pull model that utilizes Wormhole cross-chain messaging protocol. Pyth’s oracle data retrieval is done based on requests from applications via messages sent to Wormhole. The Pyth oracle program then verifies all incoming messages before sending them back.
The combination of the pull model and Wormhole makes Pyth a fast-performing oracle in real-time price feed. Pyth can provide high update frequency with more efficient transaction costs. Unlike Chainlink with its myriad of products, Pyth focuses on providing accurate and real-time price data.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology has formed the basis for the development of decentralized financial sectors and applications. However, a major drawback of blockchain is its inability to directly interact with systems and data outside of its ecosystem. Blockchain oracles address this issue by retrieving, verifying, and relaying external data to the blockchain, bridging the gap between on-chain and off-chain data. So, oracles enable smart contract-based applications to execute their functions with precise and secure external data.
Chainlink and Pyth Network are two leading oracle protocols that provide decentralized solutions. Chainlink, as an industry pioneer and leader, offers a diverse range of innovative products and has a proven reputation for security and reliability. Pyth, built on the Solana framework, is an alternative solution that offers speed and accuracy for real-time price feed.
How to Buy Cryptocurrencies on the Pintu App
You can start investing in cryptocurrencies by buying them on the Pintu app. Here is how to buy crypto on Pintu:
- Create a Pintu account and follow the process of verifying your identity to start trading.
- On the homepage, click the deposit button and top up the Pintu balance using your preferred payment method.
- Go to the market page and look for your favorite asset.
- Click buy and fill in the amount you want.
- Now you are a crypto investor!
In addition, the Pintu application is compatible with various popular digital wallets such as Metamask to facilitate your transactions. Go and download the Pintu cryptocurrency app on the Play Store and App Store! Pintu is regulated and supervised by Bappebti and Kominfo.
You can also learn crypto through the various Pintu Academy articles which are updated every week! All Pintu Academy articles are for educational purposes, not financial advice.
References
- What Is an Oracle in Blockchain?, Chainlink, accessed on 22 September 2023.
- @KencarvAPI, “Oracles”, Ethereum, accessed on 22 September 2023.
- “What is a blockchain oracle and how does it work?”, Cointelegraph, accessed on 25 September 2023.
- Andrea dal Mas, “Blockchain Oracles: The Bridge Between the Blockchain and the Real World”, Think in Crypto Linkedin, accessed on 25 September 2023.
- Gustavo Lobo, “Oracle Networks: A Deep Dive Into Data Bridging Solutions”, The Tie, accessed on 26 September 2023.
- Bluepine, “Pyth Oracle: A Worthy Opponent Of Chainlink?”, Builder.news, accessed on 26 September 2023.
- “Design Overview – Pyth Network Documentation”, Pyth Network, accessed on 26 September 2023.
